CHAPTER 2: HEREDITY & CONCEPTION
the influence of heredity on development
heredity
based on biological transmission of traits and characteristics from one generation to another
genetics
branch of biology that studies heredity
genetic (inherited) influences
physical traits
intelligence, emotional, and personality traits
behavioral traits and psychological issues
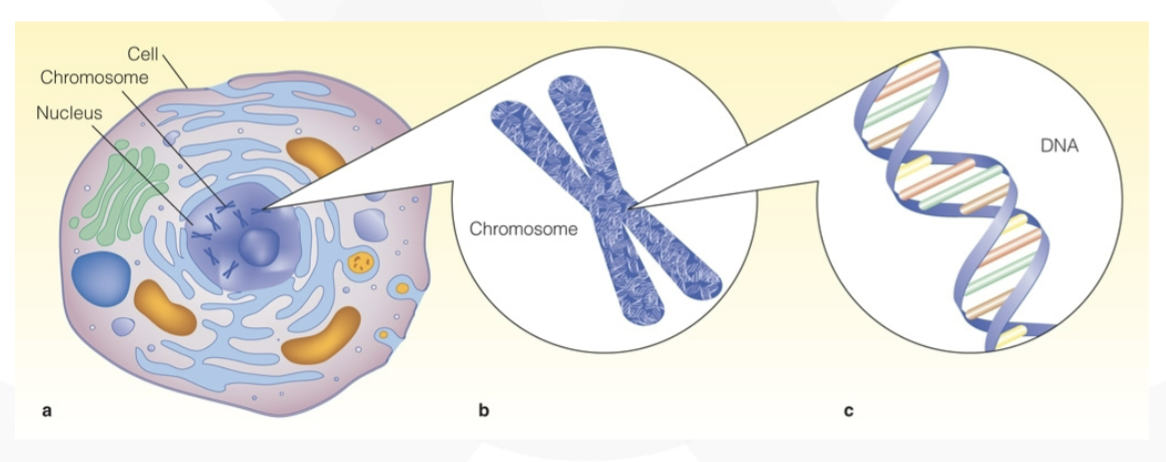
chromosomes & genes
chromosomes
found in cells
23 pairs of rod-shaped structures
genes
segments within chromosomes
regulate development of traits
transmitted by a single gene or may be polygenic (determined by combinations of pairs)
20k to 25k genes in every cell
DNA
large strands make up genes
double spiral (helix)
composed of phosphate and simple sugar
base pairs adenine with thymine (A-T) or cytosine with guanine (C-G)
mitosis & meiosis
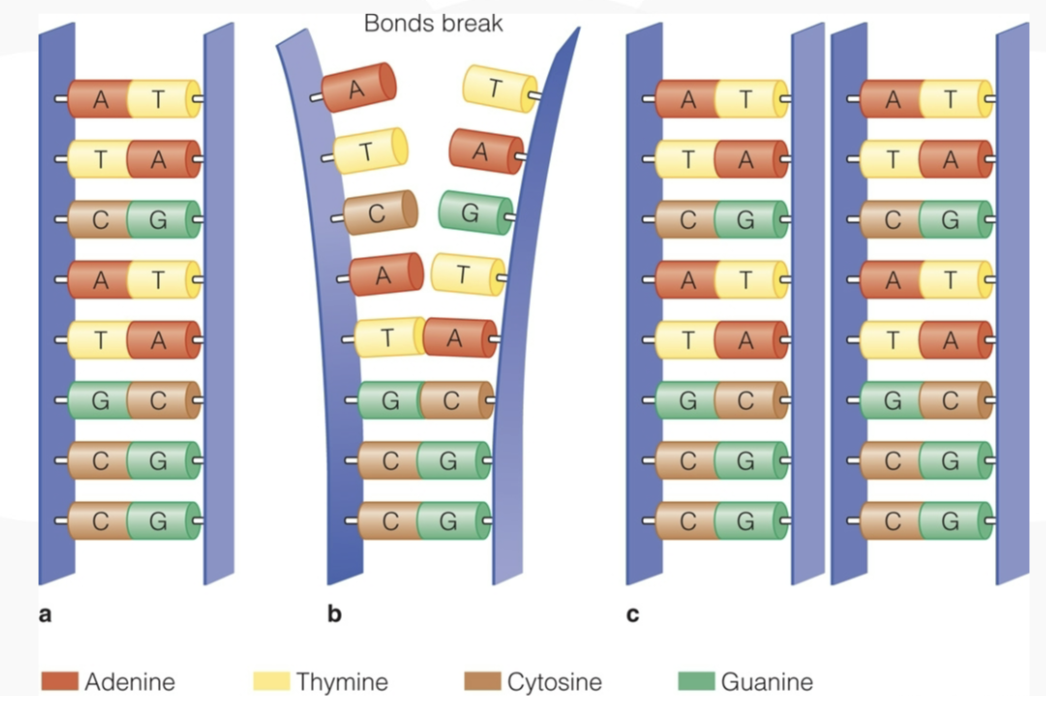
mitosis
cell division by which growth occurs and tissues are replaced
strands of DNA break apart, duplicate, and are rebuilt
result is identical copies of DNA strand
mutations are exceptions
meiosis
cell division by which sperm and ova are produced
23 chromosome pairs divide
result is a new cell with only 23 chromosomes
22 pairs are autosomes
23rd pair are sex chromosomes
determines sex: x from mother and x or y from father
identical & fraternal twins
monozygotic (identical) twins (MZ)
derived from a single zygote that has split in two
dyzygotic (fraternal) twins (DZ)
derived from two zygotes
share 50% of genetic material
probability of twins increases
maternal age- less regular ovulation
use of fertility drugs
dominant & recessive traits
traits are determined by pairs of genes
each member of a pair is an allele
homozygous
both alleles for a trait are the same
heterozygous
alleles for a trait are different
Gregor Mendel
established the laws of heredity
averaging
effects of both alleles are shown
incomplete dominance or codominance
law of dominance
dominant allele paired with recessive allele
dominant allele appears in offspring
combinations of dominant and recessive genes
carriers
chromosomal or genetic abnormalities
occur in autosomes or sex chromosomes
may be caused by a single gene or combinations
multifactorial problems
chromosomal abnormalities
down syndrome
cause: extra chromosome on 21st pair
probability increases with increased age of parent
characteristics of children
facial features
deficits in cognitive, language, and motor development
adjustment problems
sex-linked chromosomal abnormalities
most are infertile
male with extra sex chromosome
XYY: extra Y chromosomes
XXY: Klinefelter syndrome
female with abnormal number of sex chromosomes
X: Turner syndrome
XXX: Triple X syndrome
genetic abnormalities
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Huntington disease
Sickle-cell anemia
Tay-Sachs disease
Cystic fibrosis
sex linked
carried on X sex chromosome
Hemophilia
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Diabetes
Color blindness
some types of night blindness
determining probability of abnormalities
genetic counseling
addresses probability of genetic abnormalities
information about couple’s genetic heritage
prenatal testing
Amniocentesis
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Ultrasound
Blood tests
genetic counseling & prenatal testing
Amniocentesis
usually performed on mother about 14-16 weeks after conception
can detect more than 100 chromosomal and genetic abnormalities in fetus
indicates the sex of the baby
some risk of miscarriage
improved ultrasound and blood tests is reducing use of Amniocentesis
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
can diagnose abnormalities earlier than Amniocentesis
equal or slightly higher risk of miscarriage compared to amniocentesis
Ultrasound
sonogram “picture’ of fetus
used to track fetus’ growth and determine age, sex, and structural abnormalities
Blood tests
can reveal presence of recessive genes in parents
Alpja-Fetoprotein (AFP) assay
reaction range
range of possibilities for the expression of the trait
genotypes
sets of traits inherited from parents
phenotypes
actual sets of traits
product of genetic and environmental influences
canalization
environmental influences on genotype within reaction range
canalization: sequence of development is invariant
infant motor development
less canalization
intelligence
personality
environmental correlation (genetic)
passive correlation
environment that child is placed into
evocative correlation
child’s genotype elicits responses
active correlation
environment child chooses
epigenetic framework
development reflects the continual bidirectional exchanges between genetics and environmental influences
effects of genetics & environmental influences
Kinship studies
genetic closeness of relatives
Twin studies
monozygotic twins share 100% of genes
dizygotic twins share 50% of genes (same as other siblings)
reared together vs. reared apart
adoption studies
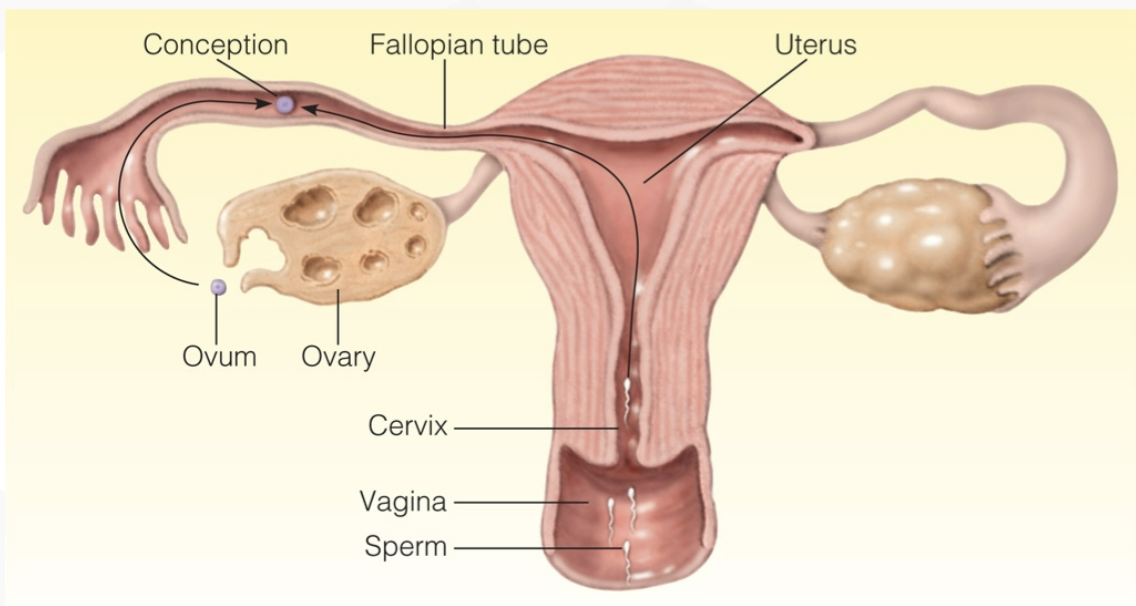
conception
ovarian follicle ruptures releasing the egg
hundreds of millions of sperm are ajaculated
only a few thousand survive through the cervix and uterus
a few hundred bombard the ovum in the fallopian tube
sperm and ovum unite
ova
begin to mature at puberty
monthly release of mature eggs into fallopian tube
egg is propelled by cilia and perhaps by contractions in the wall of the fallopian tube
if not fertilized, egg is discharged along with endometrium
sperm cells
each contains 46 chromosomes, including one X and one Y
self propelled and smaller than ova
sperm with Y chromosome swim faster than sperm with X chromosome
more boys are conceived than girls
from 200 to 400 million in ejaculate
only 1 in 1000 arrive in vicinity of ovum
attracted by chemical odor secreted by ova
sperm must penetrate gelatinous layer around ova
sperm cells secrete an enzyme that briefly thins the layer
when one sperm penetrates, the layer thickens, locking other sperm out
chromosomes from sperm cell combines with egg chromosomes to form 23 new pairs with unique genetic instructions
infertility
fertility problems among men
symptoms
low sperm count
deformed sperm
low sperm mobility
diseases
injury of testes
autoimmune responses
causes
genetic factors
environmental poisons
diabetes
STI
overheating testes
pressure to testes
aging
drugs
major fertility problems among women
symptoms
irregular or absence of ovulation
fertility drugs are used to cause women to ovulate
declining hormone levels due to aging
endometriosis
obstructions or malfunctions of reproductive tract
causes
hormone irregularities
stress
malnutrition
infections that produce obstructions, as from scarring
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
solutions to infertility
artificial insemination
sperm injected into mother’s uterus
in vitro fertilization
ova and sperm are fertilized, then implanted in mother’s uterus
donor IVF
ovum harvested from donor woman; fertilized in vitro and implanted in recipient’s uterus
embryonic transplant
surrogate mothers
“substitute” who carries a baby to term for another woman
ethical and legal risks because the surrogate mother may not want to give up the baby
adoption
greater diversity of adopted children and adoptive parents
consideration of adopted children needs
relinquishing mothers also experience effects