American Pageant Chapter 18 APUSH Review
Free Soil Movement
- Following the Mexican American War issue of slavery in the territories becomes the key cause of sectional tension
- Free Soil Party formed in 1848: "free soil, free labor, and free men"
- Wanted no slavery in new land to the west
- Keep West an opportunity for whites only
- Not against slavery in the south
- Many southerners saw any attempt to restrict the expansion of slavery as a violation of their constitutional rights
1848 Presidential Candidates
- Whigs took no position or slavery in the election
- Cass supports popular sovereignty:
- People in the territory should decide whether or not to allow slavery
- Free Soil Party opposed extension of slavery in the territories (Wilmot proviso position)
[[GOLD is discovered in California: Near Sutter’s Mill[[
California Gold Rush, 1849
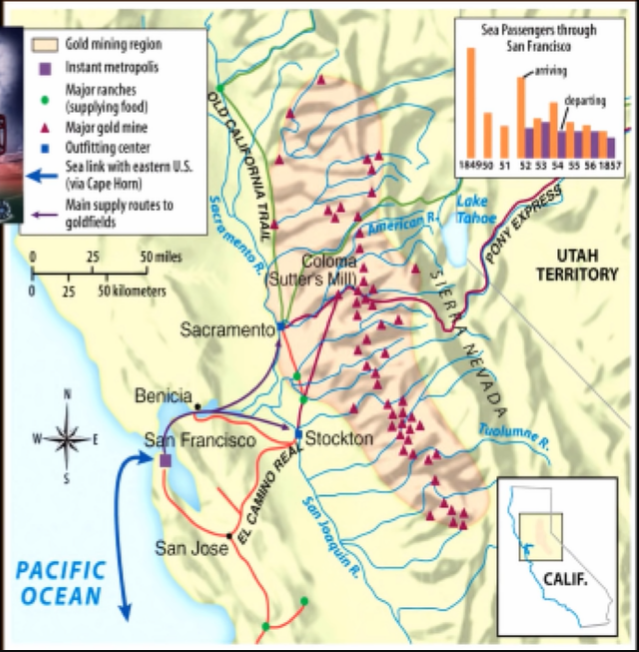
- Sectional tension between the north and south.
- California creates a constitution banning slavery and ask Congress for admission as a free state
Crisis over Mexican Cession
- Until California tried to become a free state, equal balance of power in the Senate
- 15 free states
- 15 slave states
- Southerners increasing defensive over the institution of slavery
- Tallmadge Amendment (1819)
- Wilmot Proviso (1846)
- Underground Railroad
Threats of Secession and then Compromise
- Radical southerners "Fire- eaters" talk openly of secession
- Could there be another compromise?
- Missouri Compromise (1820)
- Nullification crisis (1828-1833) Force Bill and Compromise Tariff of 1833
- Henry Clay and Stephen Douglas favor compromise
Compromise of 1850
- CA admitted as free State
- Mexican Cession land Utah and New Mexico setup as territories Slavery determined by Popular sovereignty
- Ban slave trade in Washington D.C.
- New Fugitive Slave Law for the South
- Settles border dispute between NM and TX in NM favor
President Fillmore called the Compromise of 1850 the “final settlement” of sectional division
Fugitive Slave Act of 1850
- Huge increase in sectional tension in the 1850s as a result of the Fugitive Slave Act
- Fugitive Slave Act turned the north into a hunting ground for fugitive slaves
- Northerners who assisted runaways could be arrested
- Slaves could not testify in court, denied a jury trial
Northern Resistance
- Moderate northerners are suddenly sympathetic to the abolitionist movement
- Growth in the abolitionist movement
- Underground Railroad: helped escaped slaves reach the north or to Canada
- Personal Liberty laws:
- Did not allow use of local jails for housing fugitive slave
- Vigilance Committees: goal to protect fugitive slaves from the slave catchers
- Anthony Burns: 1853 escaped from slavery
[[The 1850's saw the nation becoming more and more polarized.[[
{{Whigs divided over slavery issue{{
National Expansion Challenged
- Debate over slavery slowed any attempts at national expansion (Manifest Destiny)
- Free Soil supporters had suspicion of any expansion attempts under President Pierce
- Ostend Manifesto: plan for the U.s. to buy Cuba from Spain
- Free Soilers denounced this plan
- Northerners increasingly fear that the south was attempting to create a slave empire or "slaveocracy”
Gadsen Purchase
- Although most attempts at expansion fail under President Pierce, the U.S. does agree to purchase a strip of land for $10 million dollars from Mexico in 1853
Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854
- Stephen Douglas wants too secure a RR route and encourage western settlement
- To win southern approval: Set up two territories 1) Kansas 2) Nebraska
- Slavery would be decided by popular sovereignty
- Repeal's the Missouri Compromise of 1820 Slavery can go north of 36 30
- Huge opposition in the north - Republican party formed
- Gave south an opportunity to expand slavery