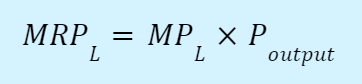4.5(2)
Other AP Microeconomics unit study guides
AP Microeconomics Ultimate Guide
Unit 1: Basic Economic Concepts
Unit 2: Supply and Demand
Unit 3: Production, Cost, and the Perfect Competition Model
Unit 4: Imperfect Competition
Unit 5: Factor Markets
Unit 6: Market Failure and the Role of Government
Studying for another AP Exam?
Check out our other AP study guides
 Knowt
Knowt