Quest Review
1. Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant environment in the body
Important for maintaining i) Temperature ii) Water levels iii) Glucose concentration iv) pH levels
Maintaining Blood pH( Respiratory system and kidneys)
Acidosis(Low blood pH): depression of the central nervous system (creates disorientedness and comatose)
Alkalosis(High blood pH): hyperexcitability of the nervous system
Creates spontaneous nervous stimulation, spasms, muscular contractions and nervousness
Kidneys regulate blood at proximal and distal tubules
Maintaining body temperature (Integumentary System)
Sweating: body heat stimulates sweat glands to release sweat that later evaporates
Vasodilation: capillaries filled with blood draws closer to skin so heat is lost
Vasoconstriction: Capillaries get constricted for blood to get taken away from the surface of the skin
Piloerection: Hairs “stand up” to trap air that is warmed by body heat
2. Negative Feedback Systems
Any homeostatic control system that works with three components
Receptor: Detects changes in the internal environment
Control center: processes information from the receptor
Effector: creates the initial response
Small changes are prevented from being to large
3. Nervous System
Network of specialized cells that process information and causes reactions
Sends, receives, and processes nerve impulses to the body for organs to function
Nerves connect the brain to the body to carry information throughout the body in the form of electrochemical signals (or impulses)
Reflex arc: a simple nerve circuit that creates an automatic response
Neuron: structual and functional unit of the nervous system
Afferent neurons: carries impulses from sensory receptors to the Central Nervous System
Efferent neurons: carries impulses from the CNS to the skeletal muscles
Interneurons: relays impulses between afferent and efferent neurons
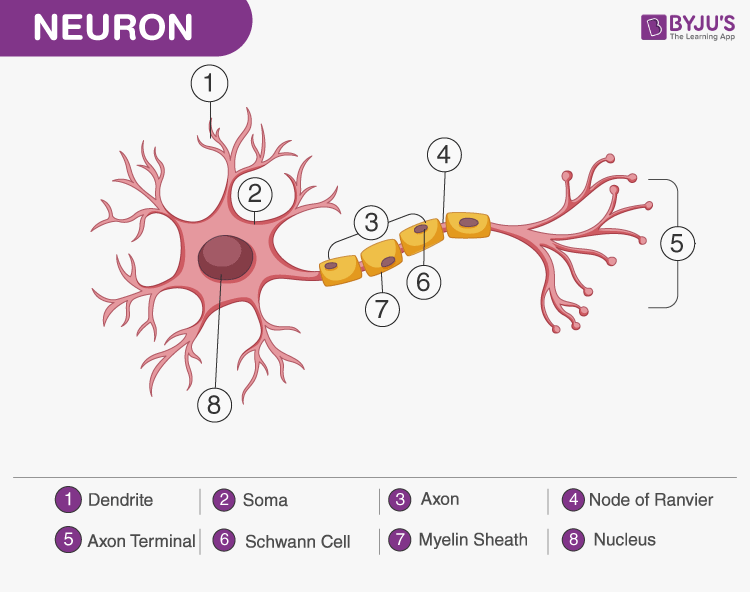
Nerve Signaling: A membrane potential that is a localized electrical gradient
Cations (Extracellular)
K+ the principal intracellular cation
Na+ the principal extracellular cation
Anions (Intracellular)
Proteins, amino acids, sulfate, and phosphate are principal intracellular aions
Cl- principal extracellular anion
Action potential: All or Nothing depolarization
55mV achieves a threshold potential (initial trigger)
Chemical Synapse steps
Action potential depolatizes the plasma membrane at the synaptic terminal
Action potential opens up voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in presynaptic terminal for an influx of Ca2+
Ca2+ concentration causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane
Vesicles release neurostransmitters into presynaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters binds to receptors of ligand-gated ion channels for diffusion of Na+
Neurotransmitters release from receptors to close channels and diffuses out of the synaptic cleft or become degraded by an enzyme
Different Types of Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine: an excitatory neurotransmitter tjay opens up sodium ion channels for depolarization
Also inhibitory om cardiac muscle cells to slow down cardiac muscle concentraion, Released by botulism toxin
Cholinesterase: released from the postsynaptic membrane to hydrolize Acetylcholine
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine: Excitatory and inhibitory that is secreted in the CNS and PNS amd adremal glands
Dopamine: Excitatory (sometimes inhibitory) that affects sleep, mood, attention, and learning
Lack of Dopamine = Parkinson’s Disease Excessive Dopamine = Schizophrenia
Serotonin: Inhibitory, same effects as Dopamine, secreted only in the CNS
Vertebrate Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Contains fluid-filled spaces (cerebospinal fluid)
White Matter: Bundles of myelinated axons
Gray Matter: unmyelinated axons, cell bodies and dendrites
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves that carry information between organs of the body and the CNS
Somatic Nerves: controls skeletal muscles and skin
Sensory nerves: relays information about the environment of the CNS
Motor Nerves: creates a response to external stimuli
Automatic Nerves: controls internal organs, smooth and cardiac muscle
Sympathetic Nervous System: prepares body for stress
Dialates pupils
Inhibits Salivary glands
Accelerates heart
Relaxes Bronchi
Parasympathetic Nervous System: restores normal balance
Constricts pupil
Stimulates salivary glands
Slows heart
Constricts bronchi
Left Hempishpere: controls the right side of the body
Language, math, logic operations, motor control
Right Hempisphere: controls the left side of the body
Pattern recognition, spatial relationships, emotions
Brain structures and roles
Brainstem (lower brain): functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, conduction of impulses to and from higher brain centers
Medulla & Pons: controls automatic nerve functions, relays information to and from higher brain centers
Cerebellum: Coordinates motor activities, relays sensory information, and coordinates motor commands
Thalamus: relays sensory information from the cerebrum, regulates emotion and arousal
Hypothalamus: Regulates autonomic activity, body temperature, hunger, thirst, and the pituitary gland