Macro Unit 1
1.1 Scarcity
Scarcity - we have unlimited wants but limited resources
Opportunity Cost
Explicit costs - out of pocket expense
ex) money payments or exchange of items of value
Implicit costs - value of resources that could be used elsewhere
ex) resource allocations not item exchange
Positive vs Normative Statements
Positive - based on facts. Avoids value judgements (what is)
Normative - Include value judgements (what ought to be)
5 Economic Assumptions
Society has limited wants and limited resources. (scarcity)
Due to scarcity, choices may be made. Every choice has a cost. (a trade-off)
Everyone’s goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own “self-interest”.
Everyone makes decisions by comparing the marginal cost and marginal benefits of every choice.
Real-life situations can be explained and analyzed through simplified models and graphs.
Marginal Analysis
Marginal = additional
Marginal analysis (aka thinking on the margin) making decisions based on increments
Point: You will continue to do something as long as the marginal benefit is greater than the marginal cost.
Trade offs vs. Opportunity Cost
ALL decisions involve trade-offs
Trade-offs - all the alternatives that we give up when we make a choice
ex: Going to the movies
Opportunity cost - most desirable alternative given up when you make a choice
Economic Terminology
Utility - satisfaction
Marginal - additional
Allocate - distribute
Price vs. Cost
Price - amount buyer (or consumer) pays
Cost - amount seller pays to produce a good
Investment - the money spent by BUSINESSES to improve their production
ex: 1 million dollar new factory
Consumer goods - created for direct consumption
Capital goods - created for indirect consumption
Goods used to make consumer goods
Four Factors of Production
Land - all natural resources that are used to make goods and services
Labor - any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid
Capital
Physical capital - any human made resource that is used to create other goods or services
Human capital - any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
Entrepreneurship - ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services
Profit = revenue - costs
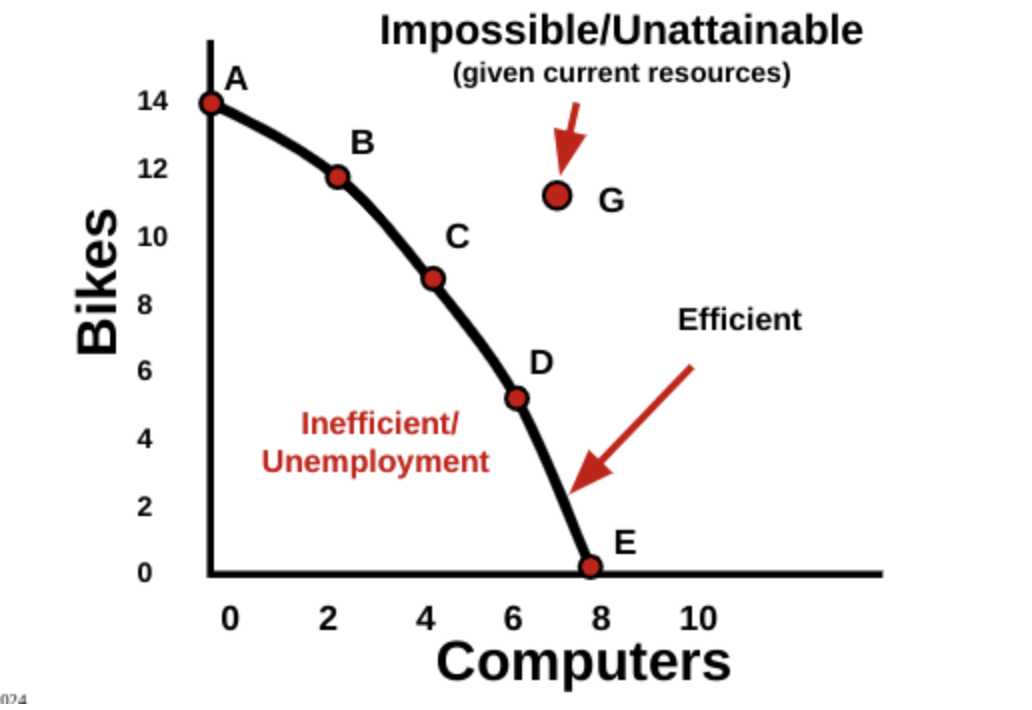
1.2 Opportunity Cost and the PPC
Product possibilities curve (PPC) or frontier, is a model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources
This model demonstrates scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
4 Key Assumptions