Science for midterms (bio)
Heredity
Trait: A feature that can vary in size or form between individuals within a species, such as eye color, hair color, and height.Heredity: The biological process through which patterns of traits are passed from parent to offspring. This involves the transmission of genetic information through DNA.
Cell Structure and Function
Cells: The smallest unit of life, with estimates indicating there may be as many as 37.2 trillion cells in the human body. Cells carry out all functions necessary for life.
Nucleus: The organelle at the center of a cell, acting as its control center. It stores DNA and is critical for regulating cellular activities, including growth and reproduction.
DNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid):
A molecule that carries genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms.
Contains the unique genetic code for each individual, similar to an instruction manual for synthesizing proteins essential for body functions.
Composed of phosphates, sugars, and four nitrogen bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
The structure forms a double helix, with specific base pairing: A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes:
Tightly coiled and compact sections of DNA, with each chromosome containing hundreds to thousands of genes.
Human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46, with one set inherited from each parent.
The 23rd pair determines biological sex: XX for females and XY for males.
Specialized Cells
In multicellular organisms, different cell types emerge due to the selective expression of genes. Each specialized cell type reads unique portions of DNA to produce specific proteins that fulfill distinct functions in the organism. For example, muscle cells express genes necessary for muscle protein production, thus enabling movement.
Gene Mutations
Gene Mutation: A change in the sequence of bases in a gene, which can occur as:
Addition: Insertion of an extra base.
Deletion: Removal of a base.
Substitution: Replacement of one base with another.
Mutations can have various impacts, including positive, negative, or neutral effects on the organism, and some can be passed on to offspring, potentially influencing evolutionary processes.
Mutagens
Mutagen:
Any substance or factor that causes mutations in DNA.
Sources of mutagens include:
Natural Factors: Such as solar radiation and radioactive gases.
Human Activities: Including exposure to chemicals and nuclear radiation.
Examples of Mutagens: Viruses, cigarette smoke, pollutants (e.g., mercury), and various forms of radiation.
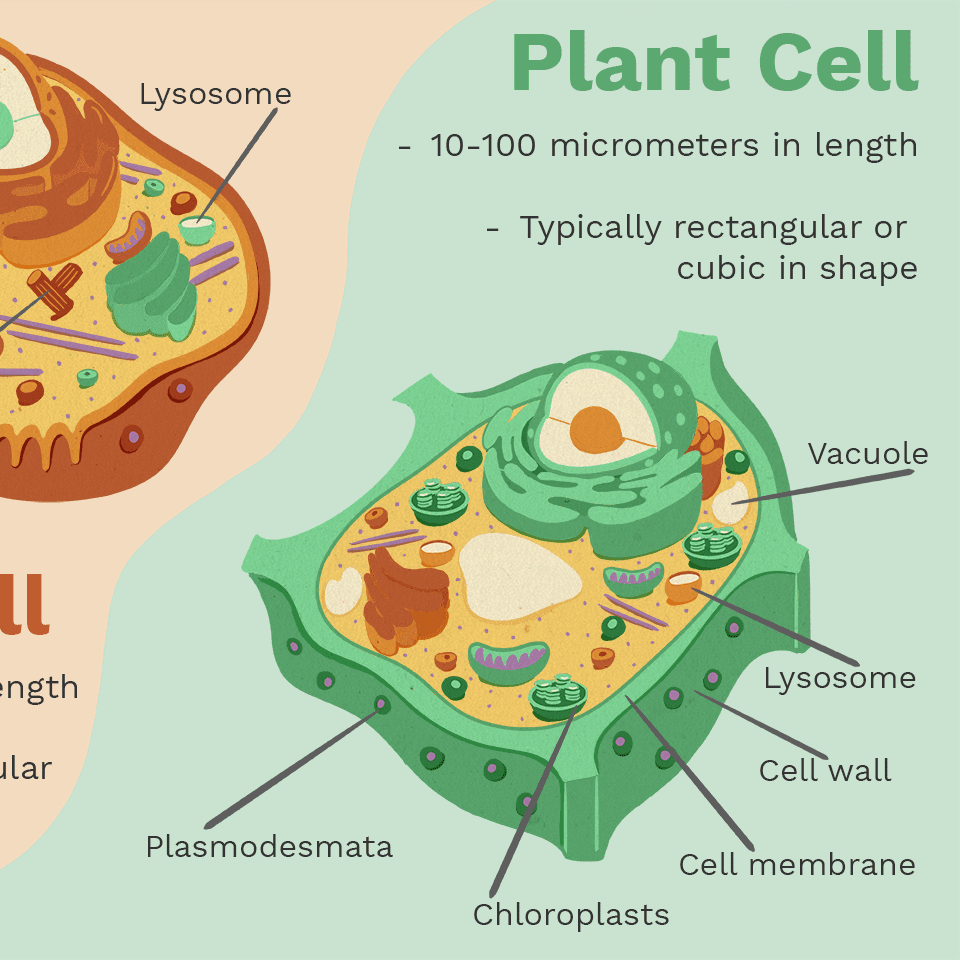
Plant Cell Structure
Plant Cell Diagram:
Cell Wall: A rigid outer layer providing protection and structure to plant cells.
Cell Membrane: A semi-permeable membrane controlling the entry and exit of substances, maintaining homeostasis.
Chloroplasts: Organelles responsible for photosynthesis, containing chlorophyll which captures sunlight for energy conversion.
Vacuole: A large storage cavity in plant cells that holds nutrients, waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure for structural support.
Mitochondria: Energy-producing organelles through respiration, converting glucose and oxygen into ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in the synthesis of proteins and lipids, with rough ER containing ribosomes and smooth ER lacking them.
Ribosomes: Small structures that facilitate protein synthesis.
Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or use within the cell.
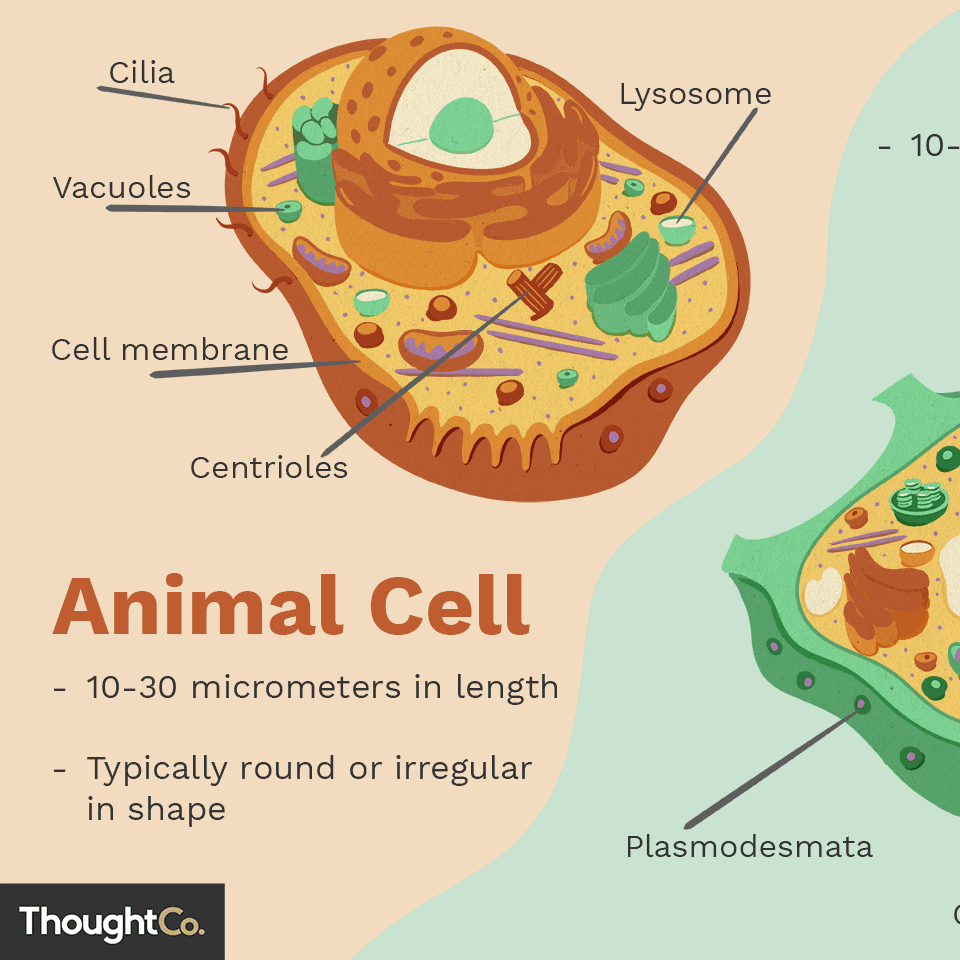
Animal Cell Structure
Animal Cell Diagram:
Cell Membrane: Functions similarly as in plant cells, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
Nucleus: Stores genetic information and coordinates cellular activities.
Cytoplasm: Surrounds organelles and serves as the site for various metabolic processes.
Mitochondria: Also the powerhouse of animal cells, generating energy for the cell's functions.
Ribosomes: Sites of protein synthesis embedded in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Two types exist - rough and smooth, with important roles in protein and lipid synthesis.
Golgi Apparatus: Involved in the processing, packaging, and transport of proteins and lipids.
Lysosomes: Organelles that contain enzymes for digesting waste materials and cellular debris to maintain cellular cleanliness.
Centrioles: Organelles that assist in cell division and the organization of the mitotic spindle during eukaryotic cell division.
Vesicles: Small sacs that transport substances within the cell, often involved in exocytosis and endocytosis processes.
 Knowt
Knowt
