UNIT 4 AP HUMAN GEO STUDY GUIDE
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE
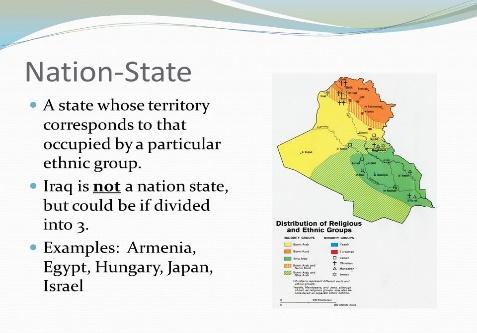
Independent states are the primary building blocks of the world political map.
There are 7 political entities that make up the world’s political map. (This Section is on the Quiz!)


Colonialism, imperialism, nationalism, independence movements and devolution along national lines have influenced political boundaries. (This Section is on the Quiz!)
Colonialism: the policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
Imperialism: a policy or ideology of extending a country's rule over foreign nations, often by military force or by gaining political and economic control of other areas.
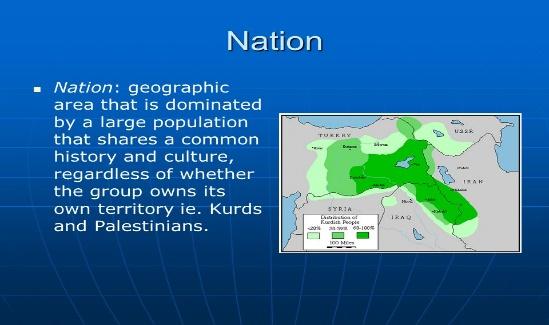
Nationalism: A group of people being loyal and showing love for their country often with a feeling of supremacy
Independence movement: effort by people to create a new sovereign state in a place inside of another state (devolution failed)
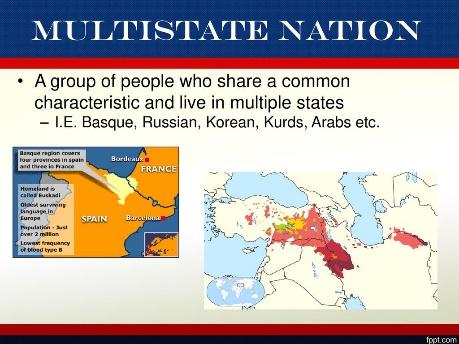
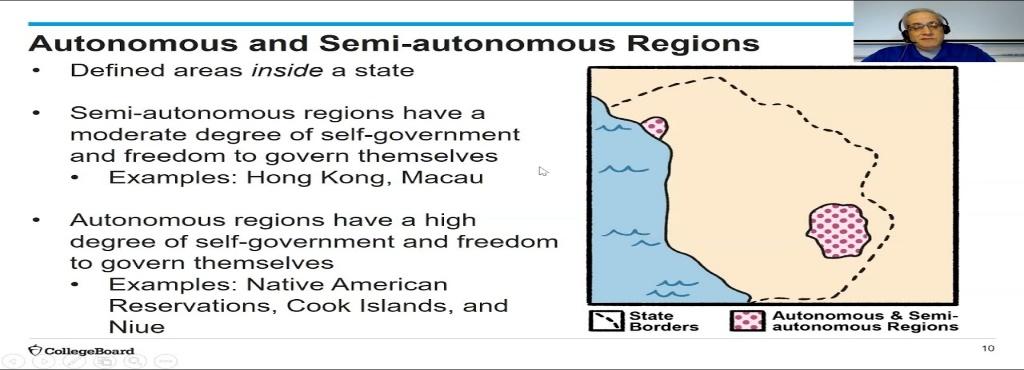
Devolution: Process of transferring some power from the central government to regional government. Transfer of power that occurs when a state breaks up, when regions that were once unified in one central government gain power and sometimes independence.
Neocolonialism: or neo-imperialism is the practice of using capitalism, globalization and cultural imperialism to influence a developing country instead of the previous colonial methods of direct military control or indirect political control.
Territoriality: is the connection of people, their culture, and their economic systems to the land.
Political Boundaries (This Section is on the Quiz!)

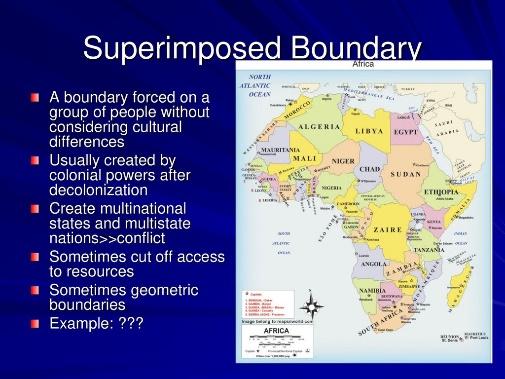
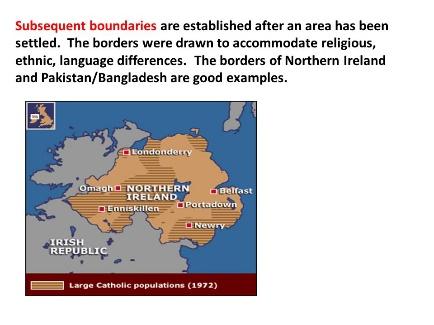

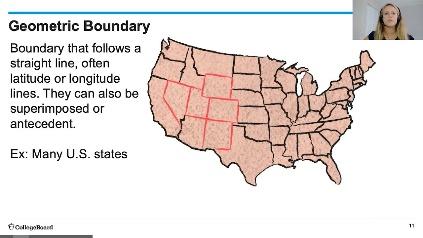
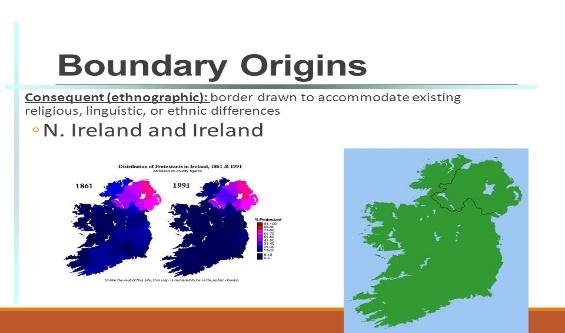
Political boundaries are often based on cultural, economic or national divisions. However, some boundaries are based on DMZ or a policy.
Demilitarized zone: DMZ or DZ is an area in which treaties or agreements between nations, military powers or contending groups forbid military installations, activities or personnel. A DMZ often lies along an established frontier or boundary between two or more military powers or alliances.
The Berlin Conference would fall under the category of policy that affected political boundaries.

Land and Maritime Boundaries (This Section is on the Quiz!)
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) defines the rights and responsibilities of nations in the use of international waters, established territorial seas, and exclusive economic zones.
Law of the Sea: set of UN laws establishing states’ rights and responsibilities concerning the ownership and use of the Earth’s waters and their resources.
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ): A sea zone over which a state has special rights over the exploration and use of marine resources stretching 200 nautical miles from the coast.
Median-line principle: A line that is drawn in the water equidistant from each competing party to settle a question of sea resource access (when there’s an EEZ conflict)
Devolution of States Factors (This Section is on the Quiz!)
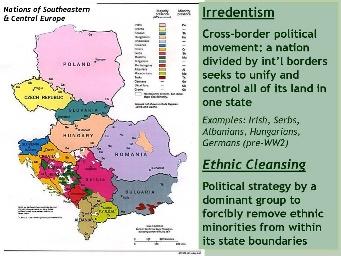


Supranationalism (This Section is on the Quiz!)
Supranationalism: the process of nation states organizing politically and economically into one organization or alliance (The alliance usually consists of 3 or more states.)
Benefits/advantages: Larger market, more trade – free trade. Greater international influence. Economic and political power. Open borders for labor/workers and tourists. Common currency. Common policy. War is less likely
Drawbacks/disadvantages: Loss of identity. Loss of control over individual policy. Give up some sovereign control.
Advances in communication technology have facilitated devolution, supranationalism and democratization.
Global efforts to address transnational and environmental challenges and to create economies of scale, trade agreements, and military alliances help to further supranationalism.
Supranational organizations – including the United Nations (UN), North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), European Union (EU), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Arctic Council, and African Union – can challenge state sovereignty by limiting economic or political actions of member states.
Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces (This Section is on the AP Exam not the Quiz!)

Forms of Governance (This Section is on the AP Exam not the Quiz!)
Unitary states tend to have a more top-down centralized form of government, while federal states have more locally based, dispersed power centers. Unitary states tend to be homogeneous while federal states
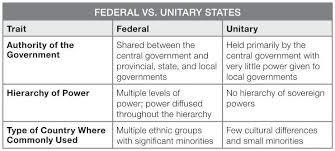
Examples of Unitary States: Europe, UK, Norway, China, Japan, Finland
Examples of Federal States: United States, Russia, Brazil, Canada, India
Confederal states: A system consisting of a league of independent states, each having essentially sovereign powers.