nervous system ⚙️
🧠 What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is like your body’s communication system. It helps your brain talk to the rest of your body — so you can move, feel, think, and react.
🛤 Two Main Parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Made up of the brain and spinal cord
It's the control center of your body
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
It carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body
🕹 What Does It Do?
Sends messages: Like "move your hand" or "you’re touching something cold"
Receives messages: Like when you feel pain or hear a sound
Controls actions: Like breathing, heart beating, or even blinking
🧠 Quick Example:
If you step on a LEGO:
Your foot sends a message to your brain: “Ouch!”
Your brain quickly sends a message back: “Move your foot!”
All of that happens in less than a second — thanks to your nervous system!
3 Main functions 🛠
1. Sensory Input 👀👂🖐
The nervous system collects information from your senses (like eyes, ears, skin, etc.).
🧠 Example: You see a ball coming at you.
2. Integration 🧠💭
Your brain processes the information and decides what to do.
🧠 Example: Your brain thinks, “I should catch the ball!”
3. Motor Output 🏃♂🖐
The nervous system sends instructions to your muscles to take action.
🧠 Example: Your hand moves to catch the ball.
In short:
👉 Sense → Think → Act
🧠 Nervous System Process (Step-by-Step)
Stimulus 🔔
A change in the environment.
Example: You touch a hot stove.
Receptor 🖐
Special cells that detect the stimulus.
Example: Temperature or pain receptors in your skin.
Sensory Neuron ⚡
Carries the message from the receptor to the brain or spinal cord.
Coordinator (CNS) 🧠
The brain or spinal cord processes the information and decides what to do.
Motor Neuron 🚀
Carries the decision (message) from the CNS to the effector.
Effector 💪
A muscle or gland that carries out the action.
Example: Your arm muscles.
Response 🏃♂
What your body does.
Example: You pull your hand away from the stove.
🧩 Summary Flow:
Stimulus → Receptor → Sensory Neuron → CNS → Motor Neuron → Effector → Response
Neuron ⚛
🧠 What is a Neuron?
A neuron is a special kind of cell in your brain and nervous system that sends and receives messages. It's like a tiny messenger.
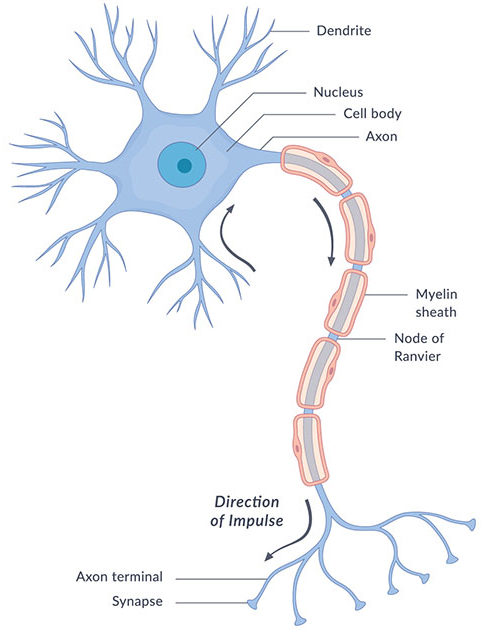
🔌 Parts of a Neuron
Think of a neuron like a tree:
Dendrites (branches): Receive messages from other neurons.
Cell Body (trunk): Processes the message.
Axon (long root): Sends the message to the next neuron.
Axon Terminals (end of the root): Pass the message on.
Synapse (gap between neurons): The site where the message is transmitted to another neuron or target cell. This process involves neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that bridge the gap and facilitate communication.
myelin sheath/ Schwann cells (insulating layer): Wraps around the axon to speed up the transmission of electrical signals, ensuring efficient communication between neurons. makes the signal go faster.
nucleus (cell body component): Contains the genetic material of the neuron and regulates cellular activities, playing a crucial role in maintaining the health and function of the neuron.
📩 How it Works
The neuron gets a signal from another neuron through its dendrites.
The signal is processed in the cell body.
If it’s strong enough, the signal travels down the axon.
The message jumps across a small gap (called a synapse) to the next neuron using chemicals called neurotransmitters.
🕹 Example
When you touch something hot:
Sensors in your skin send a message through neurons.
It travels up to your brain.
Your brain sends a message back telling your hand to move away — all through neurons!
🧩 Summary Flow:
Stimulus → Receptor → Sensory Neuron → CNS → Motor Neuron → Effector → Response
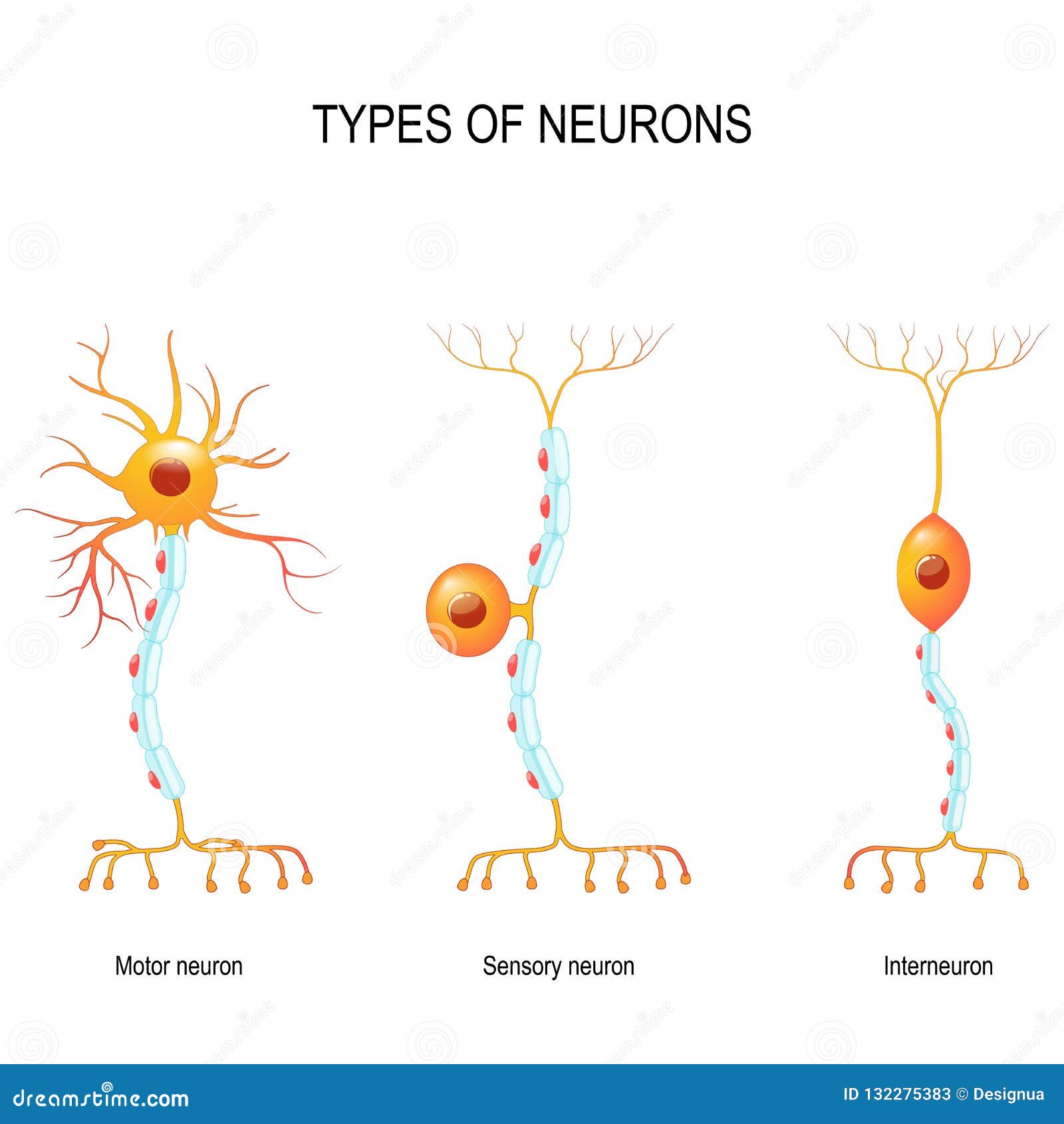
🧠 1. Sensory Neuron (Afferent Neuron)
Job: Carries messages from receptors to the brain/spinal cord.
🖐 Example: You touch something hot, and sensory neurons send that message to your brain.
🔄 2. Interneuron (Relay Neuron)
Job: Found in the brain or spinal cord, they connect sensory and motor neurons.
🧠 Example: The interneuron processes the message: "This is hot — move your hand!"
💪 3. Motor Neuron (Efferent Neuron)
Job: Carries messages from the brain/spinal cord to muscles or glands (effectors).
🏃 Example: Tells your muscles to pull your hand away.
🧩 Flow Summary:
Sensory Neuron → Interneuron → Motor Neuron
Or simply:
Sense → Decide → React