Chemical Energetics
- %%Energetics of a Reaction:%% Chemical reactions involve a transfer of energy between the system (the chemical reaction) and its surroundings.
| Exothermic reaction | Endothermic reaction |
|---|---|
| Heat energy is released into the surroundings | Heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings |
| Bond making reactions | Bond breaking reactions |
| Surrounding temperature increases | Surrounding temperature decreases |
Energy Level Diagrams
- Energy level diagrams show the relative energies of the reactant and product.
- The energy change of a reaction is represented through the difference in height between the reactant and its product.
- Activation energy: the minimum energy required for the reaction to take place
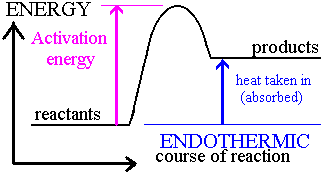
Endothermic energy level diagram:
Energy is gained by the system; higher activation energy required
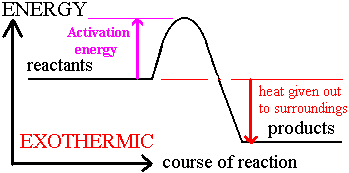
 Exothermic energy level diagram:
Exothermic energy level diagram:Energy is lost by the system; lower activation energy required
Bond Energy
This is the amount of energy required or released when a bond is formed or broken respectively. The unit measure of this energy is kJ/mol.
Formula for energy change:

%%If overall heat energy value is negative, reaction is exothermic%%
%%If overall heat energy value is positive, reaction is endothermic%%
Production of Energy
- %%Fuel%%: substance that can be used as a source of energy.
- Burning fuels to form oxides is an exothermic reaction.
- The heat from burning fuels is used in power plants to create steam from water and turn turbines.
- A combustion process requires the presence of a fuel, oxygen and heat.
%%A good fuel is:%%
- Cheap
- Available in large quantities
- Liquid at room temperature
- Have high efficiency (produce a large amount of energy)
- Does not produce polluting gases
Hydrogen
- Produced by reacting methane gas with steam
- Used in fuel cells and rockets
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Releases a lot of energy | Difficult to transport as it is a gas at room temperature |
| Does not produce pollutants | Forms explosive mixture with air when stored under pressure |
| Renewable and abundant | Is expensive to produce (requires a lot of energy) |
%%Fuel Cell%%
- In this electrochemical cell, fuel loses electrons at one porous electrode while oxygen gains electrons at the alternate porous electrode.
- The product is water: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2 O
Reaction at anode:
2H2 → 4H+ + 4e-
Reaction at cathode:
4H+ + O2 + 4e- → 2H2 O
The flow of the electrons, through the electric circuit, from the cathode to the anode generates a current.
