0.0(0)
Other AP Biology unit study guides
AP Biology Ultimate Guide
Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function
Unit 3: Cellular Energetics
Unit 4: Cell Communication and Cell Cycle
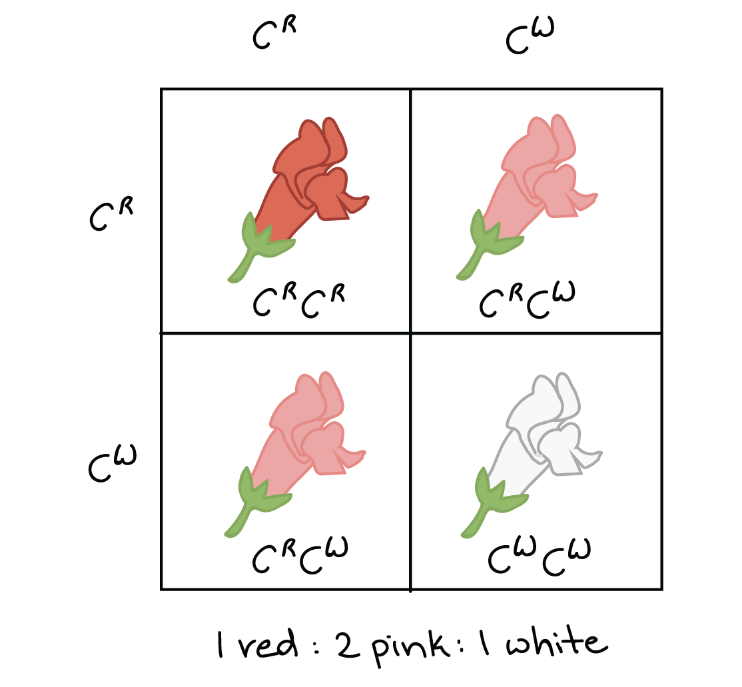
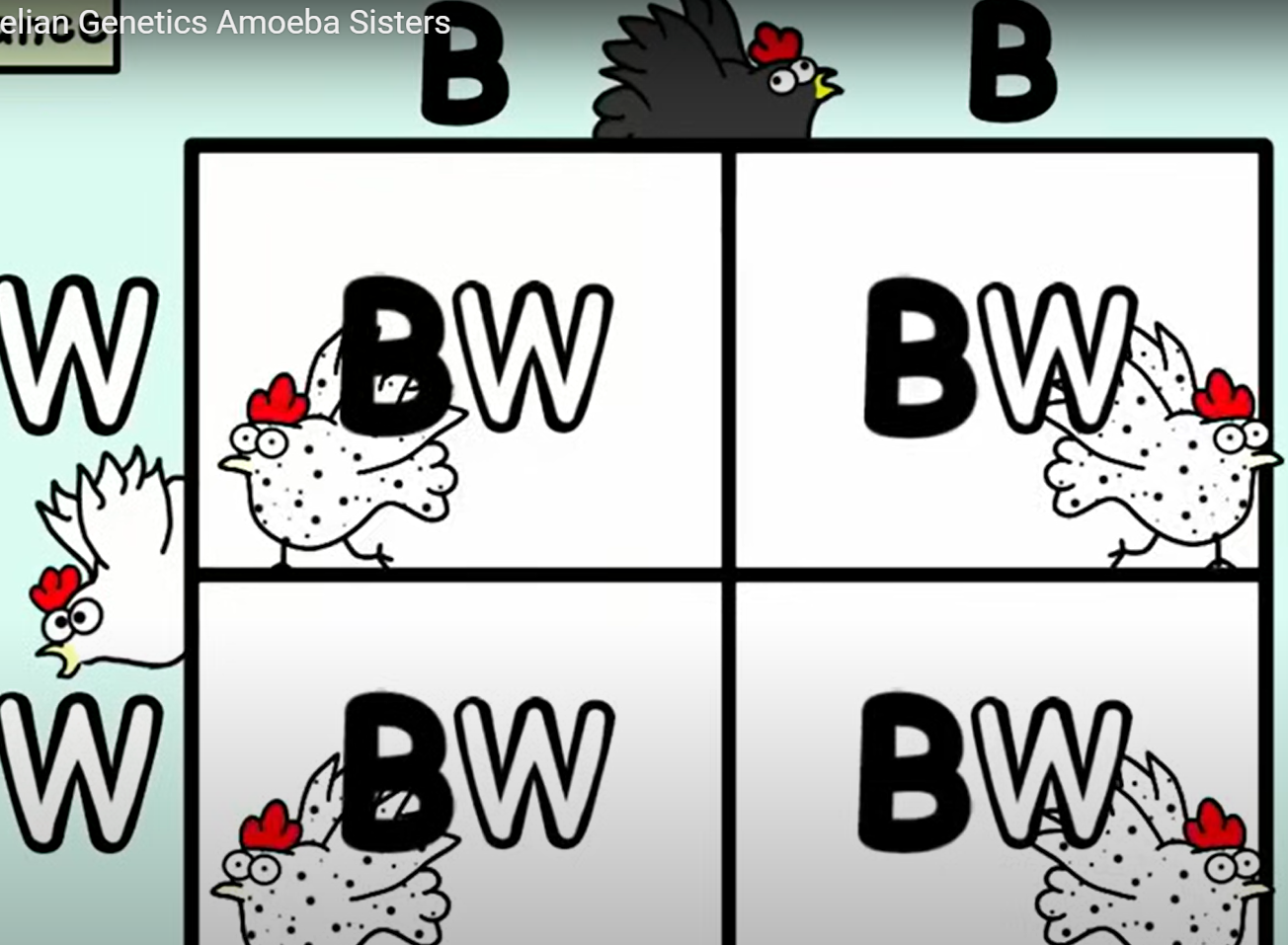
Unit 5: Heredity
Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation
Unit 7: Natural Selection
Unit 8: Ecology
Studying for another AP Exam?
Check out our other AP study guides
 Knowt
Knowt