Nucleic Acids
Introduction
Biology 189: Fundamentals for Life Sciences
Topic: Nucleic Acids and Inheritance
Learning Objectives
Understand definitions and functions of nucleic acids:
Define nucleic acids and their roles in living organisms.
Understand nucleotide structure (the monomers of nucleic acids).
Identify five nitrogenous bases and differentiate purines from pyrimidines.
Comprehend base pairing between nitrogenous bases.
Recognize how nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester linkages.
Describe the antiparallel nature of DNA and RNA.
Define genes and genomes, and compare similarities and differences between DNA and RNA.
What are Nucleic Acids?
Definition: Polymers of monomers called nucleotides.
Types: RNA and DNA.
Functions:
Store genetic information (DNA).
Directly involved in protein synthesis (RNA).
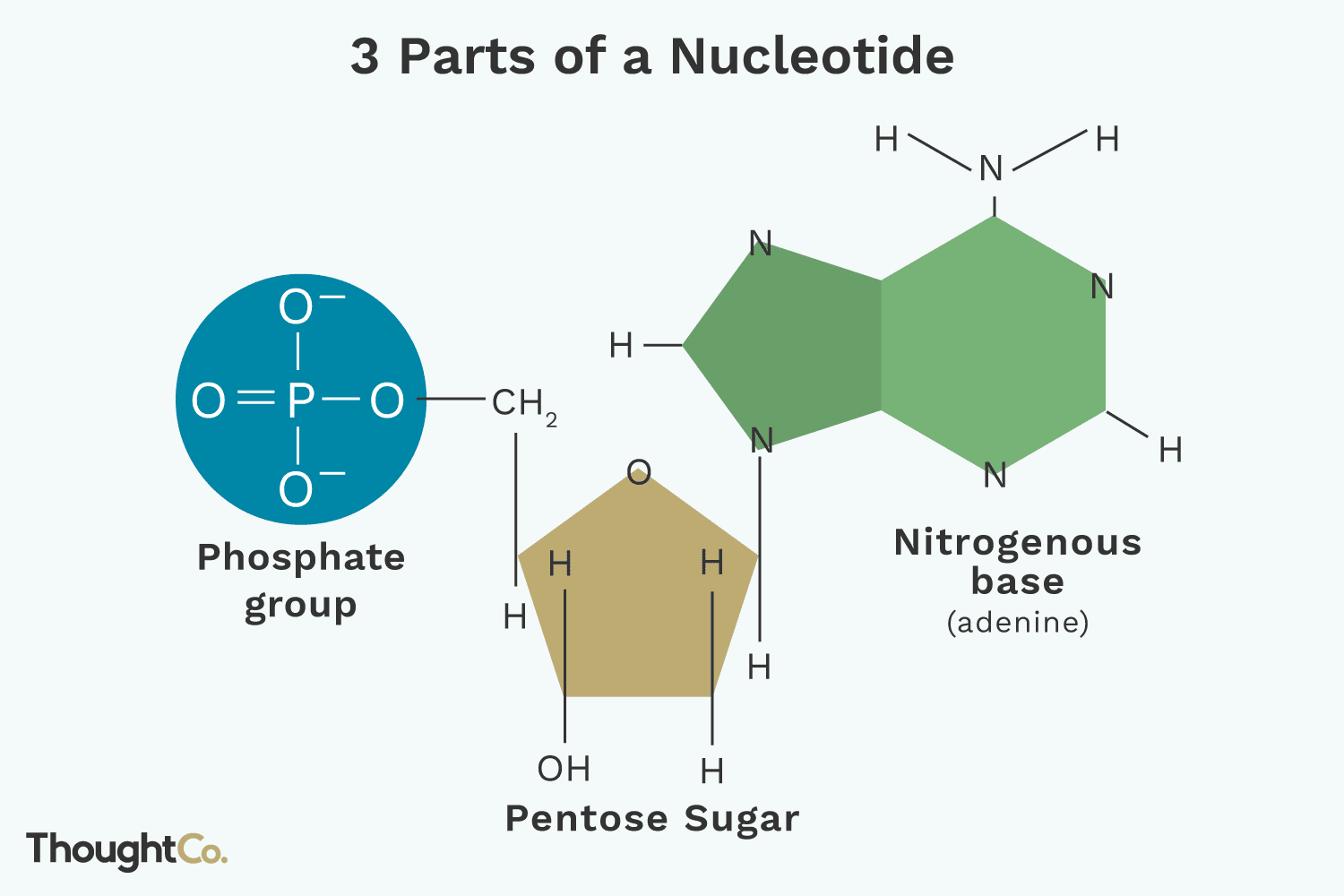
Structure of Nucleotides
Composed of three components:
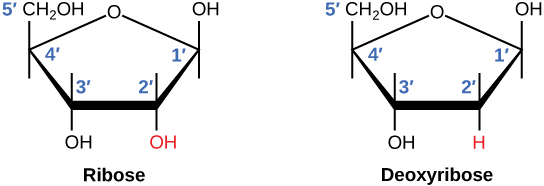
Sugar: Pentose sugar (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA).
Nitrogenous base: Contains various bases outlined below.
Phosphate group.
Sugars of DNA and RNA
RNA: Polymer of nucleotides with ribose sugars.
DNA: Polymer of nucleotides with deoxyribose sugars.
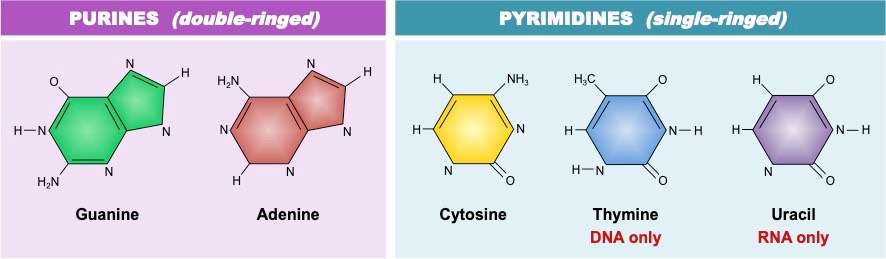
Nitrogenous Bases of Nucleic Acids
Nitrogenous bases are found in nucleic acids
Pyrimidines (single ring):
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T, in DNA), Uracil (U, in RNA).
Purines (double ring):
Adenine (A), Guanine (G).
Joining Nucleotides Together
Nucleotides are not linked by dehydration synthesis; instead, a condensation reaction occurs. (don’t need to worry about it on test)
Phosphodiester Linkage:
Covalent bond linking two nucleotides.
Nucleotides linked by condensation reactions
Forms a sugar-phosphate backbone in nucleic acid polymers.
Structure of DNA
Double Helix: Two DNA strands spiral around each other.
Nitrogenous bases pair and strands are antiparallel (opposite directions)
Base Pairing Rules
Nitrogenous bases pair via hydrogen bonds:
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Chargaff's Rule:
A = # of T; # of C = # of G
DNA Width Maintenance
Correct width maintained by:
Purine + Pyrimidine pairing (consistent width).
Purine + Purine or Pyrimidine + Pyrimidine results in inconsistent widths.
Antiparallel DNA Chains
Strand orientation:
Strand 1: 5’ to 3’ direction.
Strand 2: 3’ to 5’ direction.
DNA and Genetic Information Storage
Genome: DNA sequence that encodes info to make protein (book
Genes: all genes (genetic context) of organism or cell (library)
What is RNA?
RNA has:
Same sugar-phosphate backbone as DNA.
Four nitrogenous bases: Guanine (G), Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), and Uracil (U).
Typically single-stranded and involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Shorter polymers
Variable 3D structure
Structure of RNA
RNA has a variable shape influenced by its primary structure (sequence of nucleotide bases).
3D structure due to hydrogen bonds between bases at distant locations within the strand.
Comparing DNA and RNA
Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
Structure | Double Helix | Usually single-stranded |
Nitrogen Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
Sugar Type | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
Flow of Genetic Information
Process:
DNA undergoes transcription to form mRNA in the nucleus.
mRNA is then translated into proteins in the cytoplasm.
Vocabulary
Nucleotide: Monomer of nucleic acids.
Nitrogenous Base: Component of nucleotides (A, T, C, G, U).
Phosphodiester Linkage: Covalent bond in nucleic acids.
Gene: Sequence of DNA coding for proteins.
Genome: Complete set of DNA.
Antiparallel: Orientation of DNA strands.
Base Pairing: Specific pairing of nitrogenous bases.