Unit 3: Early Europe and Colonial Americas
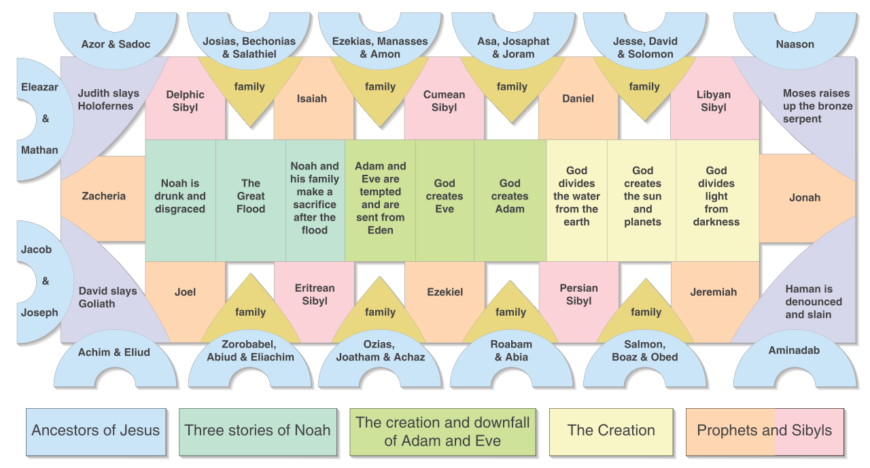
48. Catacomb of Priscilla
Form:
- excavated tufa and fresco made it look like marble
-figures flat and with less detail (roman painting style)
-passageways underneath city of Rome, 100 miles long
-pendentives with picture
Content:
-shelves for bodies; wealthier people: sarcophagus
-scenes of New and old Testament
-curriculum
-Good Shepherd Fresco
-orants figure: arms stretched out
-greek chapel
Function:
-tombs of poor and wealthy for 1000s of people
-poor people has body one on top of the other
Context:
- wealthy woman donated land for her family and other Christians to be buried
-3 stories deep
-Greek and Latin
themes: prefirguration divine intervention


-Depicts a woman’s stages of life, motherhood and marriage

-The good shepard
-Influence of roman painting
-Shows jesus and the sheep

-The last supper is depicted
-symbolism of the breaking of the bread, wine: jesus blood bread: his body
-foreshortening of the dishes
-Influence of sophisticated roman paintings
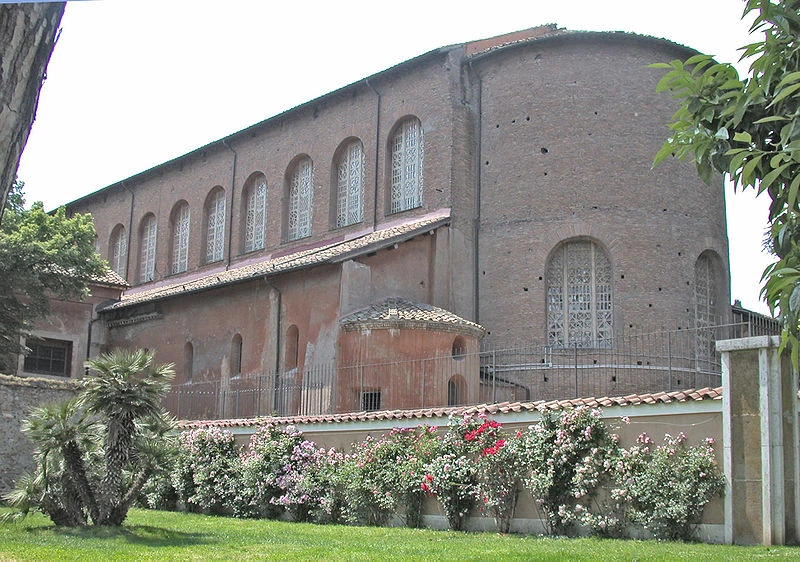
49. Basilica of Santa Sabina, Rome
Form:
-brick, stone, wooden roof
-2 levels: upper (windows), lower (arches/columns)
-spolia (reuse of architectural pieces from other buildings)
Content:
-apse: half dome in back that is decorated
-narthex: lobby
-nave: center aisle separates common folk from the sanctuary, depicts earliest known of the crucifix
-depiction of crucifix on doors
-3 aisled basilica
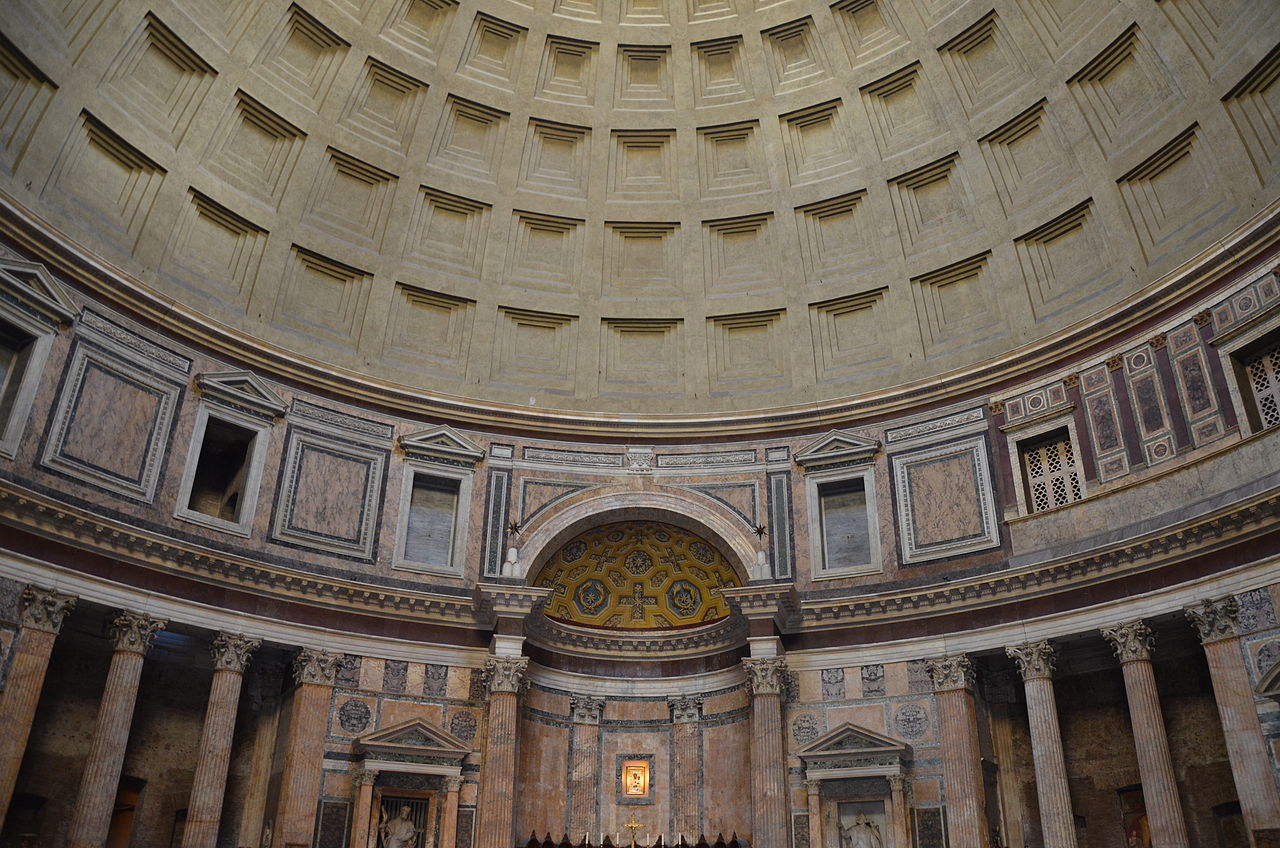
-columns from temple of Juno in Rome (spolia)
-pantheon, oculus
-arcade: whole bunch of arches in a row
spandrel: space between arches
-windows for light weight, light comes in to hit mosaics
porch: giant wooden doors entrance
sanctuary
Saint Sabina is buried in the tomb on the floor, every cathedral has a relic, finger of a saint, wooden sliver of the original crucifix or a tomb
Function:
-basilica- diverse building, civic purpose
-used aisle for law courts
-early Christian church, held large amounts of people
-emphasis on spiritual not physical
Context:
- Rome, Italy 422-432 CE
-Christianity legalized in 313ce. roman christens needed a large place to worship
-Late Antique Europe


50. Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling with the Angel, from Genesis, Vienna Genesis
Form;
-tempera, gold, and silver on purple vellum (animal skin)
-illuminated manuscript (pictures with words)
-continuous narrative
Content:
- stories from Genesis: Jacob was leading his people across a river and he wanted an angel to bless him but the angel did not want to so he wrestled the angel and the angel eventually blessed him
-Jacob wrestles an angel at night
-Rebecca quenches thirst of camels and camel driver
-letters black now bc silver oxidized
-Greek writings> Byzantine
-Rebecca is heavily clothed instead of nude
-registers classical stuff christian art, perspective is skewed, bodies have form
Function:
-tell stories
Context:
-Early Byzantine Empire 6th century CE


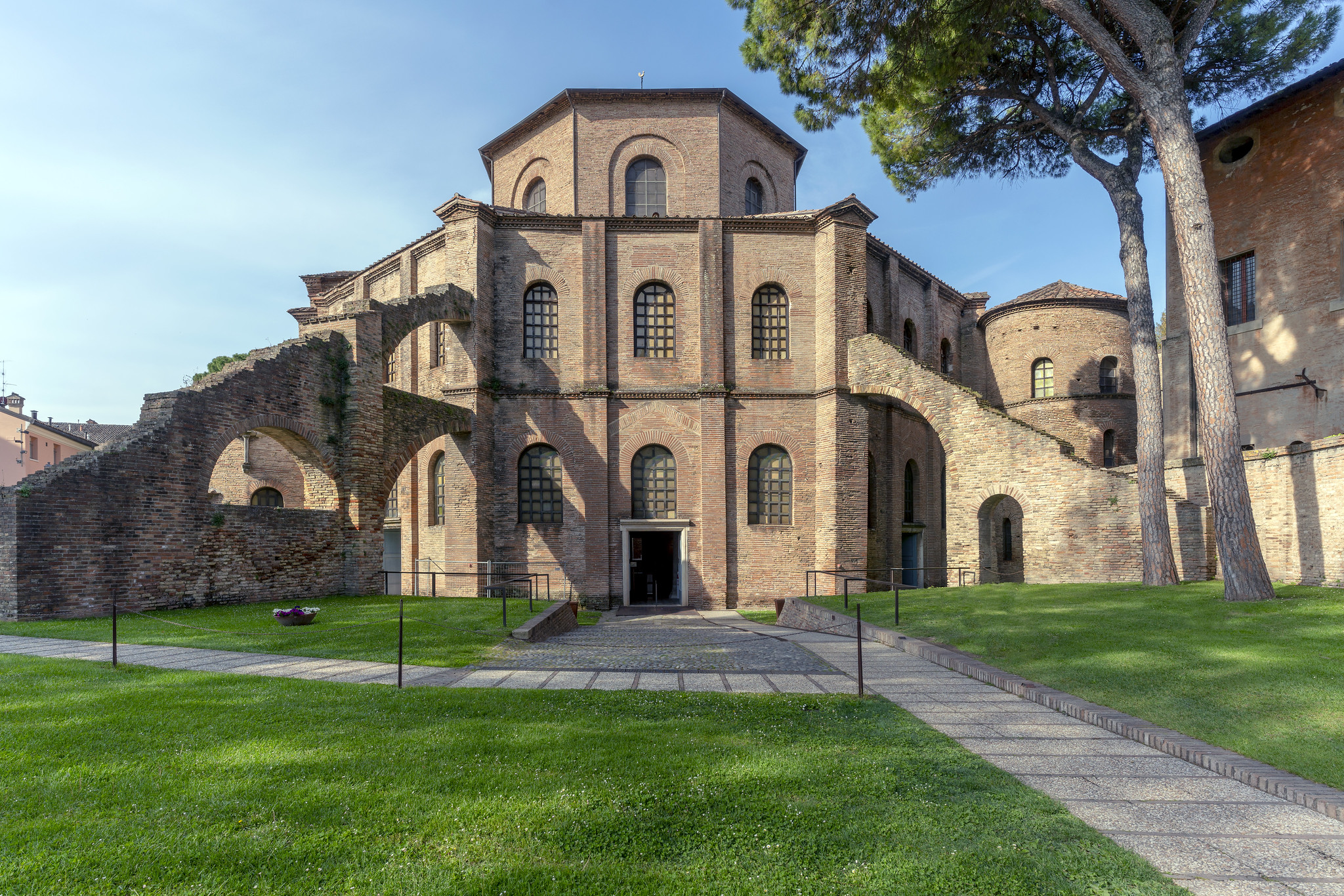
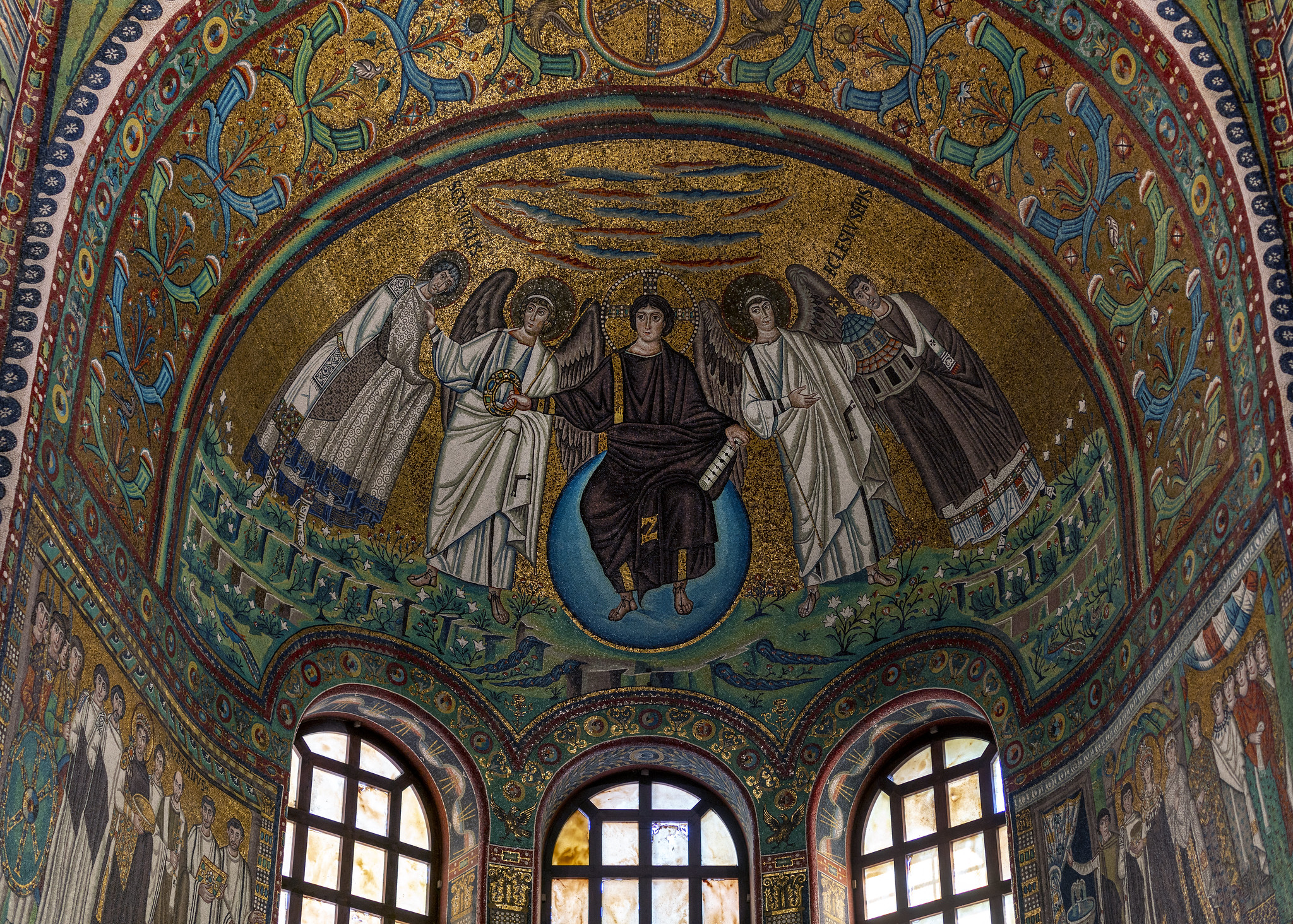
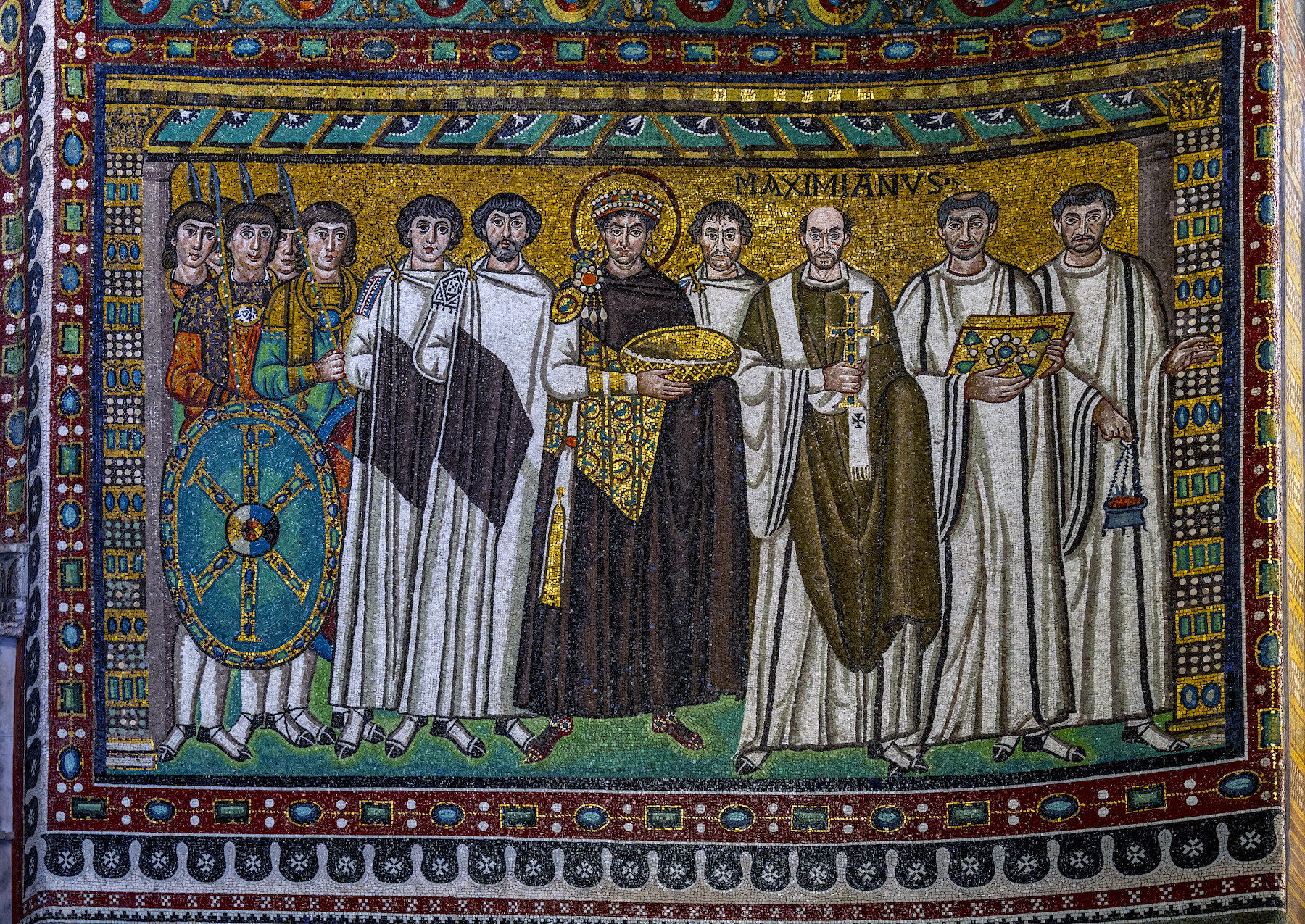
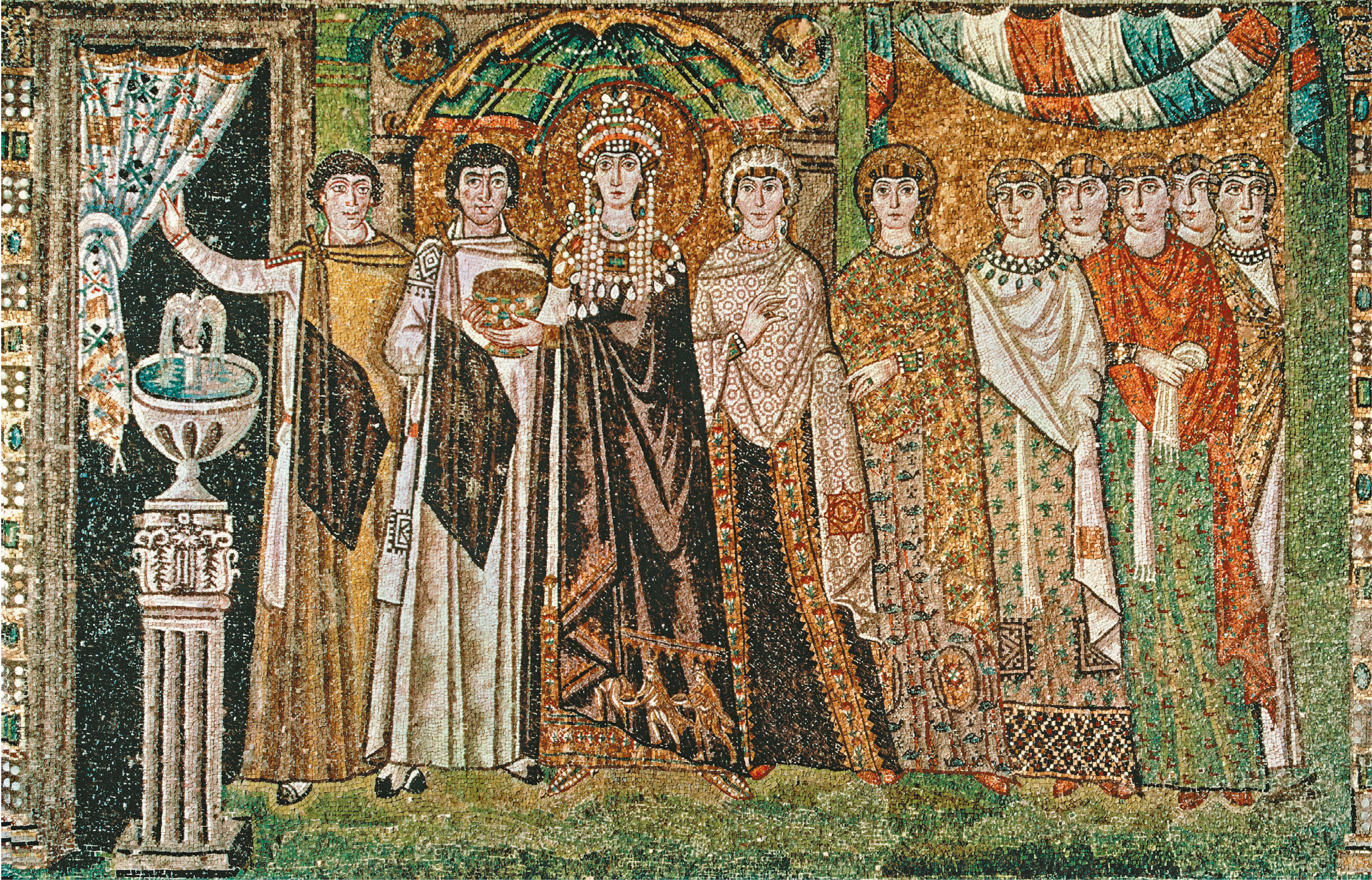
51. San Vitale
Form:
-brick,marble, stone, veneer, mosaic
-all glass covered in gold leaf
-octagonal plan: centrally planned church
-groin vaulting
-not longitudinal
Content:
-central domed octagon surrounded by radiating wall niches (exedrae)- attention directed at the center
-big windows
-covered by vaults
-mosaic: clergy on right, military on left, Justinian in the middle
Function:
-holds icons
-basilica
-reestablish Orthodox Christianity
Context:
- Ravenna, Italy- Early Byzantine 526-547 CE
-Julianus Argentarius financed this building




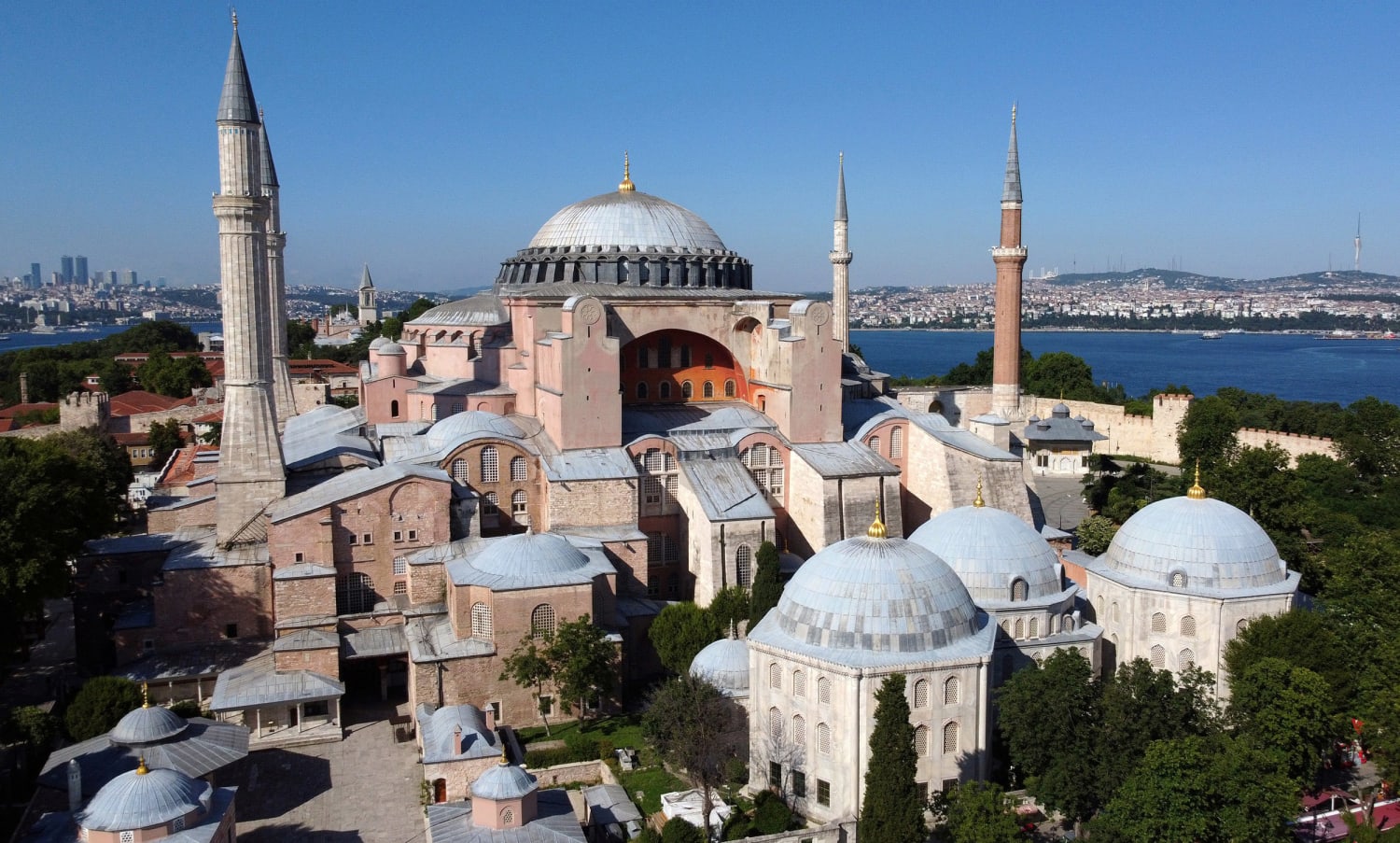
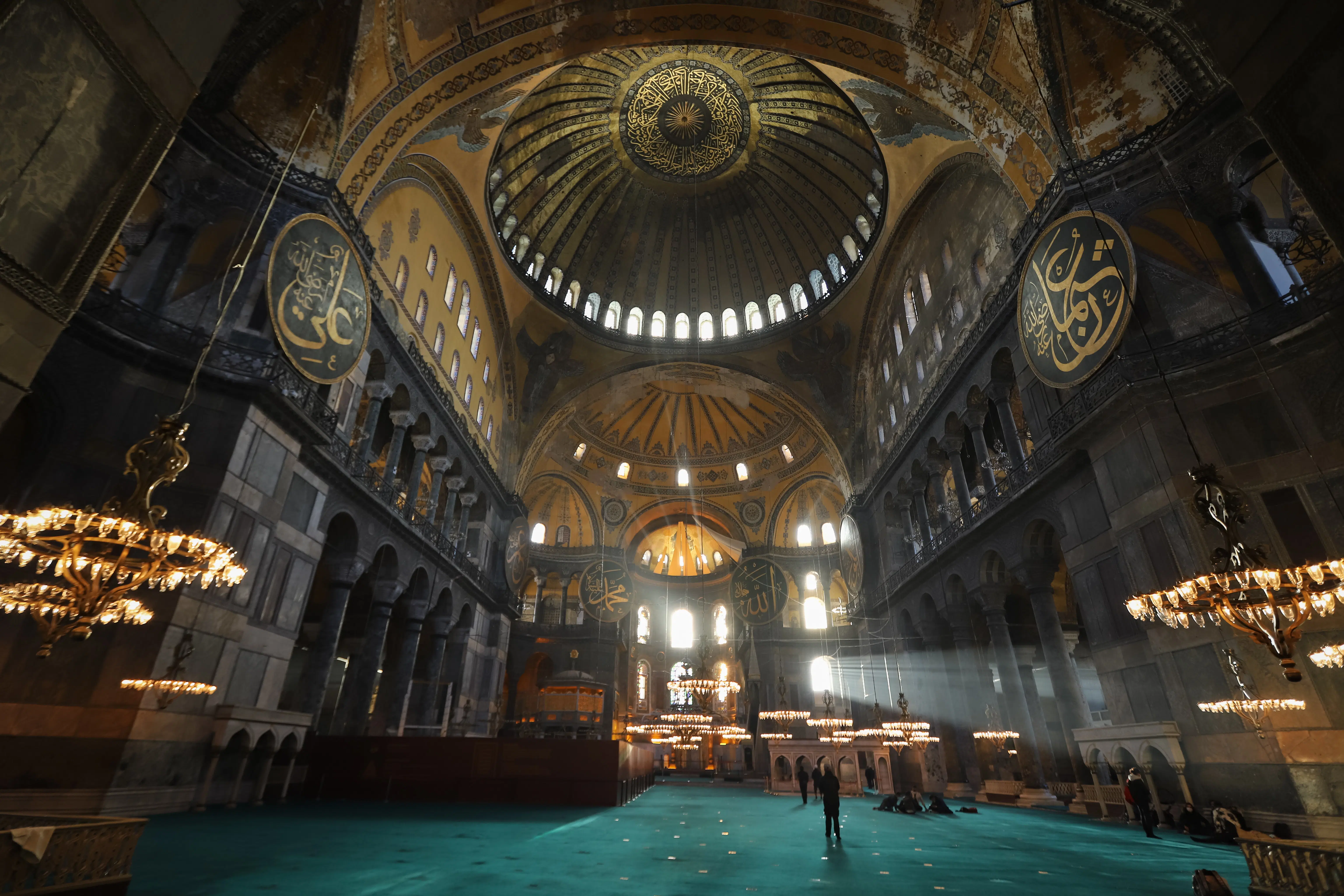
52. Hagia Sophia
Form:
-brick, ceramic elements
-mosaic veneer
-ionic columns
-centralized dome supported by pendentives
-buttress supports
-pendentives: triangular curving vault section
-squinches- quarter domes
Content:
- Byzantine architecture
-attention to detail
-mystical building
-altar at the end of nave (center aisle)
-minarets
-longitudinal and central
Function:
-originally a basilica (church)
-converted to mosque- now has minarets
Context:
-Justinian's reign
-changed to mosque by Ottomans 1452


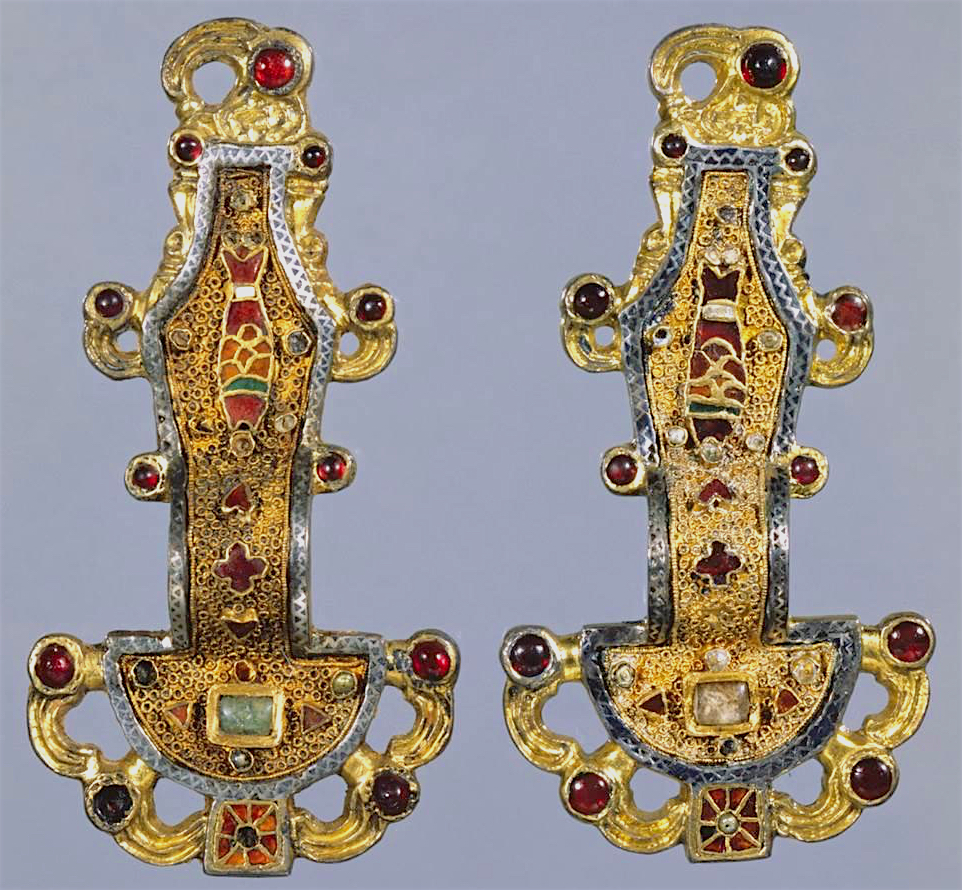
53. Merovingian looped fibulae
Form:
-interlacing (zoomorphic)
-bowed
-filigree 2-4"
-silver gilt (thin layer of gold)
Content:
-animals (fish represents Christ and eagle represents St. John)
Function:
-clip for holding fabric
-clasp that hold fabric to the shoulder
Context:
-mid 6th century CE
-Frankish kingdom
-found in tomb of rich woman

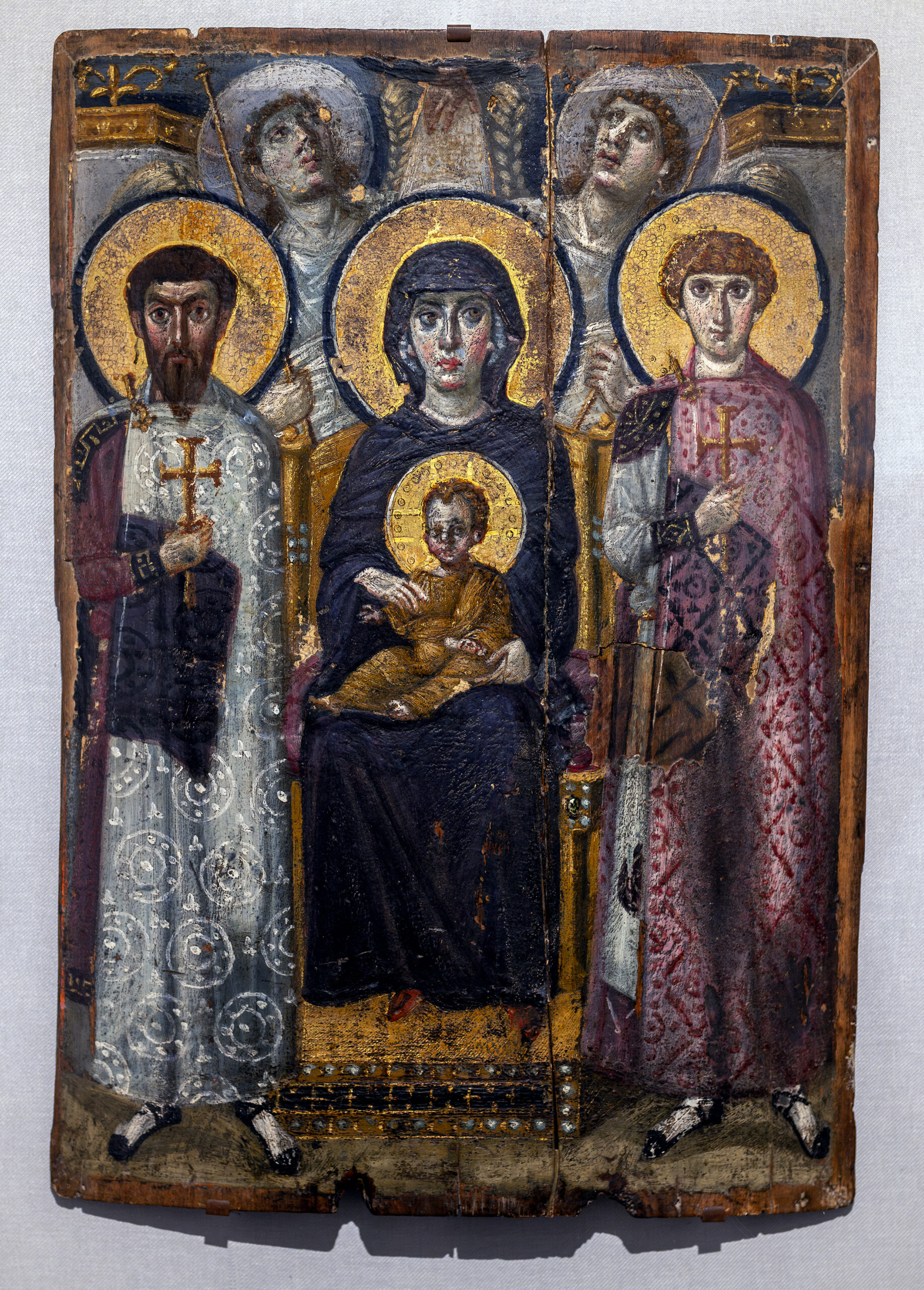
54. Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George
Form:
-encaustic (wax base paint) on wood
-spacial recession but compressed space
Content:
-angels looking towards heaven
-Mary looking over viewers while the warrior saints look directly at viewer
-light falling on Virgin
-depicts Mary and Jesus in a different realm than others
Function:
-portray Mary and Christ protected by saints and the hand of God
Context:the
-6th-7th century
-Early Byzantine
-Egypt,-c. 700-800 illustrates the integration of Christian iconography with traditional Egyptian art forms. -The mosaic style is characterized by vibrant colors and intricate patterns, reflecting the cultural exchange between Byzantine and Egyptian artistic traditions.

55. Lindsfarne Gospels
Form:
-illuminated manuscript
-tedious lines, a lot of detailed lines complex
-Books are very huge
Content:
-cross carpet page: cross forms out of chaos, creates illusion of 3D in which viewer can lose themselves in contemplation
-portrait page (luke): holds quill/looks prepared to write, gold halo (divinity), ox above his head, robe with purple and streaks of red
-incipit page (Luke): it "begins", animal life, spiral forms, swirling vortexes
-weighs over 75 pounds contains old and new testament
-flatter more linear stylized maybe a deliberate artistic choice different than other copies made at that time.
-Anglo Saxon Germanic style very geometric
-icons depicted
Function:
-earliest known translation of the Bible
Context:
-created by monks lindsfarne was founded by Irish missionaries
-writing style is Mediterranean because they had exchanges with Rome, island remote but ideas travel throughout Europe
- c. 700 (Northumbria), 340 x 250 mm-sfarne is an island in England with monasteries, invading by vikings because they wanted the treasures
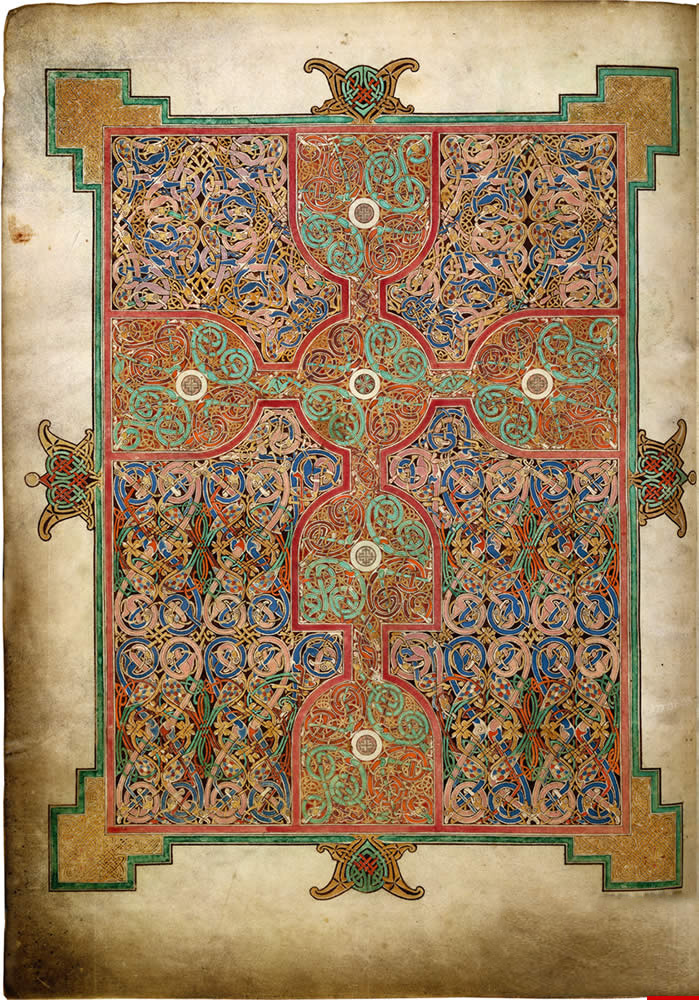


-Saint Mathew depicted in the manuscript. Saints can be identified with an angel next to him
-Has a halo, complex ambitious pose referencing naturalism that comes from ancient Greek and roman tradition

56. Great Mosque
Form:
- hypostyle mosque
-spolia (using roman and Christian pieces from old church it used to be
-vossoir: wet stone that holds arches up
-grid vaulting
-culturally diverse
Content:
-horseshoe arches with vaults above
-mihrab- niche is Qibla wall (mostly decorated in geometry and text)
-wooden cieling
-mosaics everywhere- byzantine artists from Constantinople
-Qibla Wall- direction of where Muslims have to pray to pray towards Mecca
-Kufic calligraphy
-856 columns
Function:
-1st: Roman temple (Janus)
-2nd: Chirstian church
-3rd- mosque
-now: cathedral
Context:
-Cordoba, Spain- Umayyad 785-786 CE

57. Pyxis of al-Mughira
Form:
-ivory
-carvings of text and pictures
-text used as a decoration
Content:
-roaring lions
-4 8-lobed medallions showing pleasure activities
-human and animal figures
-geometrical and vegetal motifs
Function:
-luxury cosmetic holder: text on top/decorated richly
-coming of age present from caliph to his younger son possibly as a coming of age gift
Context:
-968 CE Umayyad, Muslim Spain

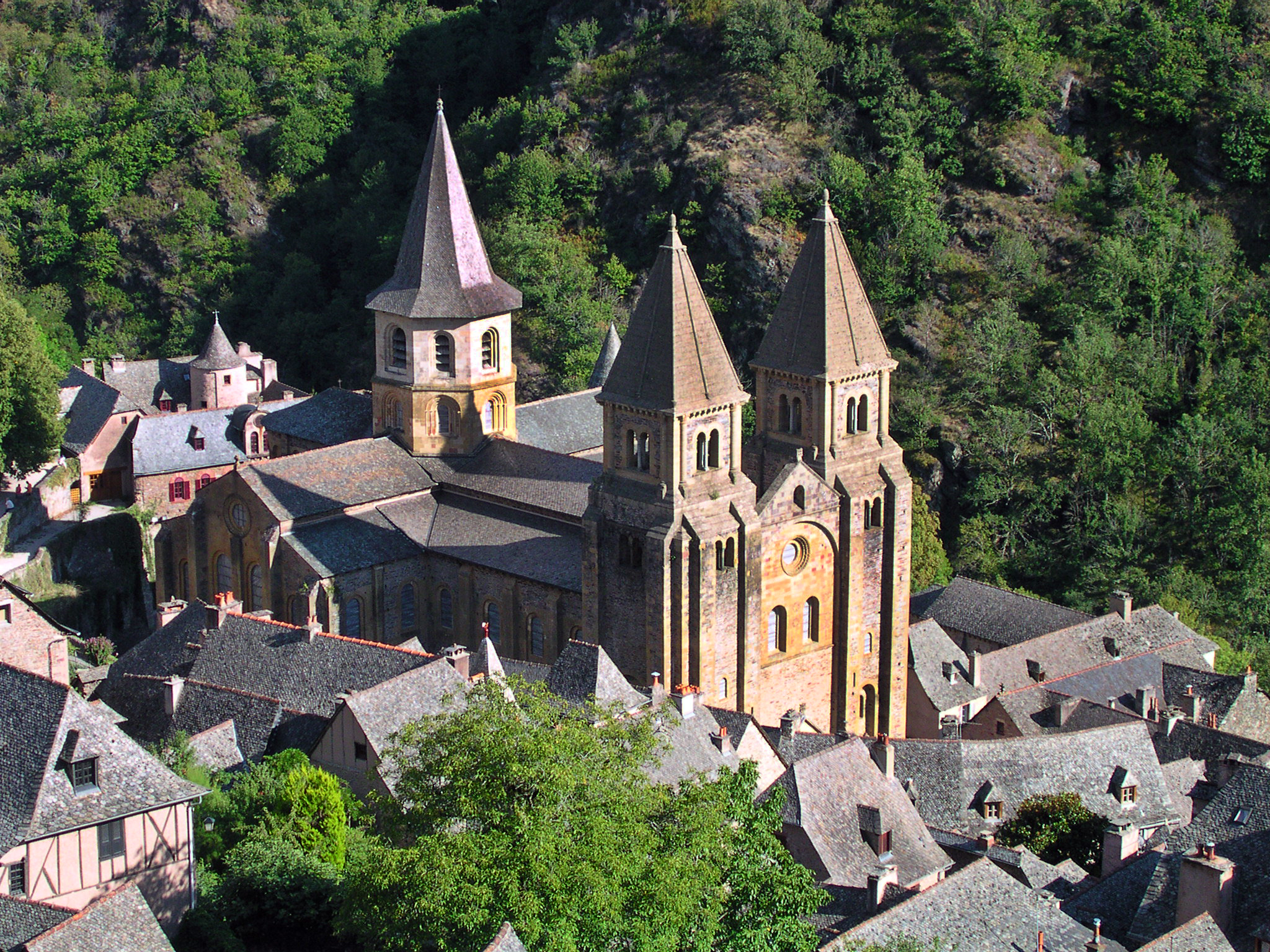
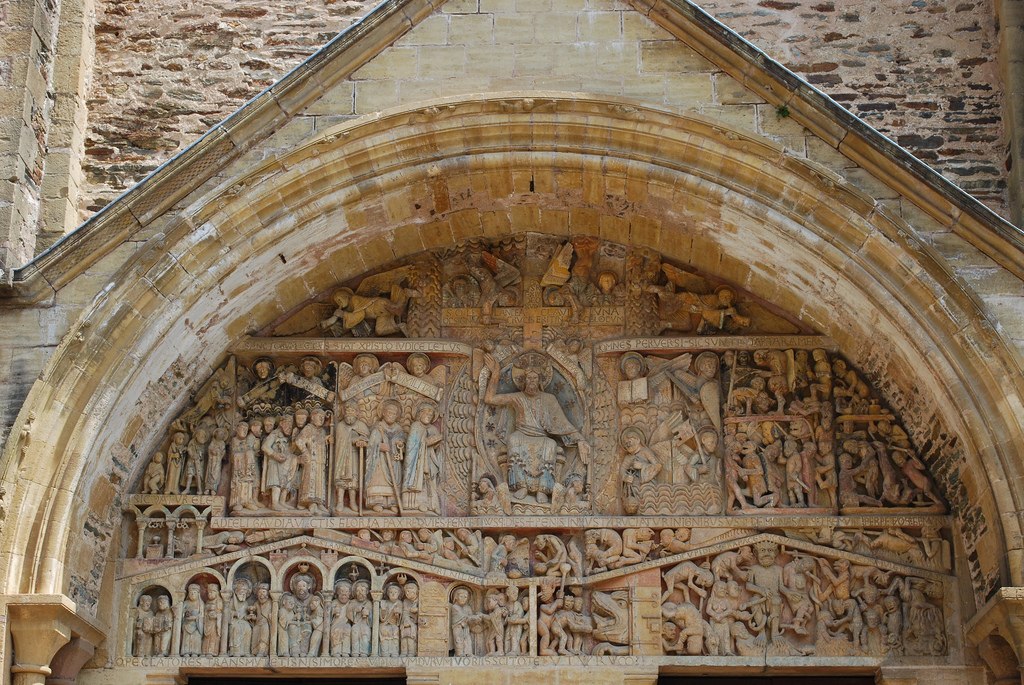
58. Church of Sainte-Foy
Form:
- romanesque style
-symbolic Latin cross plan
-vaulting, groin vaults
-spolia
-archivolts: bands that go around tympanum
Content:
- reliquary of Saint Foy
-tympanum of Last Judgement (Christ as the judge of the damned and saved)
-gallery on top (distributes the weight)
-barrel vaulting
-tympanum
-radiating chapels, nave arcade
-transepts arms of the cross
-3 aisles
-dark building
Function:
- pilgrim church, people come to see
-built so that it could handle a lot of people
-reliquaries
- part of monastery where monks lived
Context:
- Conques, France
1050-1130 CE (12th century)



59. Bayeux Tapestry
Form:
-embroidery on linen
-Romanesque (English or Norman)
-2/3 of a football field in length
-continuous narrative
Content:
-a great epic
-2 main scenes
-story of William's conquest of England in the battle of Hastings
-Haley's Comet
Function:
-show Norman conquest
Context:
-Cantebury, NW France
-commissioned by Bishop Odo
-1066-80 CE (11th century)

60. Chartres Cathedral
Form:
-3 phases of Gothic (Early in facade, High French in back, Late in the North Spire)
-painted arches, rib vaults- Gothic elements
-colors vivid
-knowledge, nature, light
-limestone, stained glass
-rose window
Content:
-stained glass- triforium
-narrow passageway
-jamb figures
-relic: Mary's dress
Function:
-Church with great beauty that honors Mary and gives her the respect she deserves
-built after they found Mary's Tunic unharmed in the fire
Context:
-Chartres, France
1145-55 CE
reconstructed in 1194 because of a fire
Roman> Gothic

61. Bible Moralisees
Form:
-dedication page
-Gothic
-gold leaf, tempera, ink on vellum
-illuminated manuscript
Content:
-King Louis IX
-Blanche of Castile
-passages from Old and New Testament
Function:
-made for French royals' home (King Louis IV)
-create a moral through visionary readings
Context:
-Paris, France 1225-45 CE (center of learning and bookmaking)

62. Rottgen Pieta
Form:
-painted wood
-Medieval/Gothic and realistic
Content:
-Mary holding her dead son after Cruxifiction
-Mary is pained and anguished
Functions:
-versperbils (German devotional)
-feel the pain she feels
-intended to be used in contemplation and prayer
-devotional image
-shows them closer to the humanity side
Context:
-Bonn, Germany 1300
-German Gothic

63. Arena (Scrovegni)
Form:
-fresco
-brick and architechture
-painted plaster
-grisaille (gray tones)
-quatrefoils
-tracing
-plain outside, transformative inside
Content:
-Last judgment scene
-lancet windows
-Scrovegni at the bottom offering up chapel to Jesus (artist portrait included)
-The Lamentation (Jesus has been crucified and now he is being mourned)
-Mary with others grieving
-Life of Mary>Passion of Jesus
Function:
- private family chapel (connected to a house)
Context:
-Padua, Italy
-on the grounds of an old arena
-artist: Giotto di Bondone
1303 CE
-Italian Gothic
-Proto-Renaissance

64. Gold Haggadah
Form:
-illuminated manuscript
-pigments and gold leaf on vellum (animal)
Content:
-Left: plagues of Egypt
-Middle: scenes of liberation (Israelites leave)
-Right: Passover
Function:
-book used by a wealthy Jewish family to tell the story of Passover around the sedar table each year
Context:
-Late Medieval Spain 1320 CE
-similar to Christian Gothic manuscripts

65. Alahambra
Form:
-whitewashed adobe stucco, wood, tile, paint, and gilding
-complex arches
-elevated on top of a hill (power)
-arabesques (organic/natural designs- flowers/vines) on arches
Content:
-court of lions: courtyard with gardens and water- luxurious
-4 quadrants
-channels of water run throughout
Function:
-complex of palaces
-some markets
-garden provokes sense of paradise/heaven
-palace of Nasrid
Context:
-Granada, Spain- Nasrid Dynasty 1354-1391 CE

66. Annunciation Triptych
Form:
-triptych
-altar piece (portable)
-renaissance
-Flemish (oil paint, glowing, vivid color)
-hyper reality/hyper clarity
-closed during the week, open during mass
Content:
-scene of the Anunciation
-Holy Spirit and Jesus coming through window
-couple asking for divine intervention
-Joseph on right making mouse traps
-Mary laying down on pew
-image of Chris coming from the window going to Mary's womb
Function:
-private devotional place
Context:
-workshop of Robert Campin (master of flemalle)
1427-32 CE (15th century)
-Flemish Renaissance

67. Pazzi Chapel
Form:
-masonry
-articulate, everything white on the inside
-dome cieling
-simple geometry
-pietra serena- soft gray tone
-inlaid marble, terracotta tiles
-strigil pattern
-Franciscan
Content:
-entablature
-arch forms
-family crests
Function:
-show Pazzi family wealth
-served as chapter house (meeting room for the Franciscan monks)
Context:
-Filipo Brunelleshi (architect)
-Florence, Italy 1429-61 CE (15th century)- Early Renaissance

68. The Arnolfini Portrait
Form:
-oil on wood
-Renaissance
Content:
-betrothal (engagement)
-dog represents wealth and fidelity
-barefeet- something sacred taking place
-Patron saint of domesticity (St. Margaret
-Vaneyck signature and reflection in mirror
-witnesses of the marriage shown in the mirror
Function:
-shows status, wealth, power
Context:
-artist: Van Eyck
-1434 CE (15th century)
-Flanders

69. David Donatello
Form:
-bronze
-exaggerated contrapposto
-beautiful, ideal, classical, cultured, independent, wealth, power (like Florence)
Content:
-shepherd's hat with flowers of Florence (small can conquer giants)
-biblical figure of Florentine Republic
-religious AND political connotation
-return to the nude powerful figure in contrapposto
-Goliath's head under his foot
Function:
-made for private viewing
-made for Medici
Courtyard
Context:
-Florence 1440-60 CE (15th century)
-early renaissance
-artist: Donatello

70. Palazzo Rucellai
Form:
-3 levels (like classical)
-round arches
Content:
-3 levels: each different column style
-built around the courtyard
-levels around divided by entablatures with frieze
-Medici and Rucellai symbol in frieze
-humanism: domestic architecture
Function:
-show allegiance to Medici
-civic pride
-beautiful city
-residences and businesses
-show their good taste
Context:
-architect: Leon Battista Alberti
-1450 CE Florence, Italy
-Giovanni Rucellai commissioned it
-Early Italian Renaissance

71. Madonna and Child with Two Angels
Form:
-tempera on wood
-3D figures
-sense of space
-elegant lines/curves
-humanism
Content:
-all humanized (mischievous look)
-Mary's halo slowing going away (divinity fading)
-Mary youthful/beautiful
-landscape through window (Flemish background)
-pearls (symbol of immaculate conception
Function:
-relate more to viewers by making humanistic images
-connect us to Mary and Jesus
Context:
-artist: Fra Filippo Lippi (monk of Carmelite order) teacher of Botticelli
-1465 CE
Early Renaissance Italy

72. Birth of Venus
Form:
-tempera on cancas
-curvy body (flexibility)
-neoplatonic love (classical and Christian)
-sense of pattern and beauty
Content:
-Venus standing on seashell
-born by the sea fullgrown
-couple intertwines; pushing Venus to land
-someone on shore ready to receive Venus with cloth
-floating figures
-Earthly and celestial love
Function:
-probably wedding gift
Context:
-artist: Sandro Botticelli
1484-86 CE
-Medici commission
-Venus is goddess of love
-Early Renaisasnce

73. Last Supper
Form:
-linear perspective, spatial illusionism, frieze-like
-triangle in center (Christ @ the point)
-monumental forms
-oil and tempera
Content:
-Jesus and his apostles having a final meal before Jesus is arrested
-the betrayal (Judas)
-the Eucharist (body and blood of Jesus) given to his people
-uses models to paint the people so he can make it more realistic
Function:
-dining hall/refectory for monks eating in silence
Context:
-artist: Leonardo DaVinci
-High Renaissance- Milan 1494-98

74. Adam and Eve
Form:
-engraving on metal
-contrapposto
-tiny details (high renaissance)
Content:
-animals representing temperaments and humors being let into the world
-artist signature on sign
-Tree of Knowledge and Life
-fall of humanity
Function:
-shows his knowledge of the classical act
Context:
-artist: Albrecht Durer (german)
-Latin
-1504 CE
-High Renaissance (north)
-16th-17th century

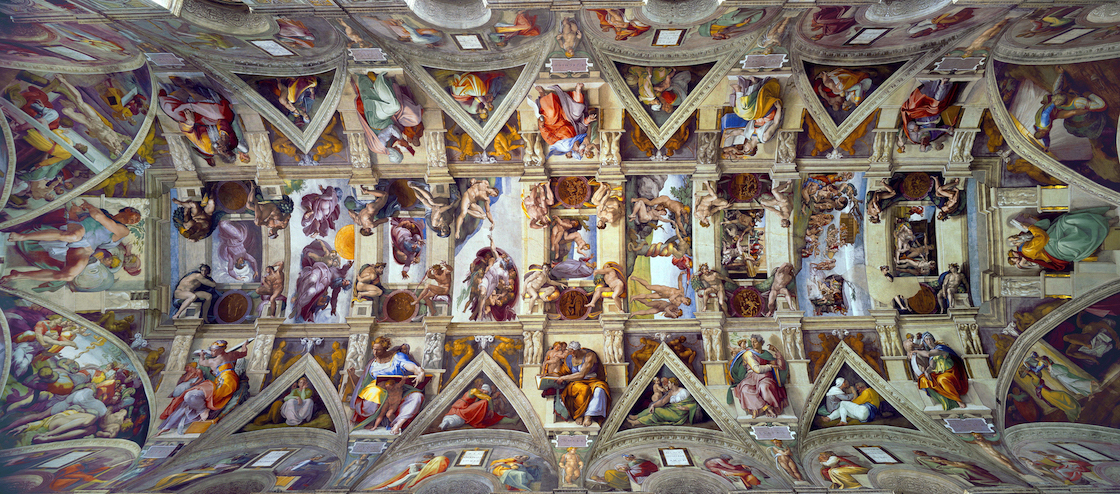
75. Sistine Chapel ceiling and altar wall frescoes
Form:
-frescoes
-sculptural element to his paintins
-neoplatonic (classical and Judeo-classical)
-hellenistic figures
Content:
cieling:
-scenes from the OT (9)
-Noah's Ark
-men working on ark hoping for salvation
-duster seeking sanctuary
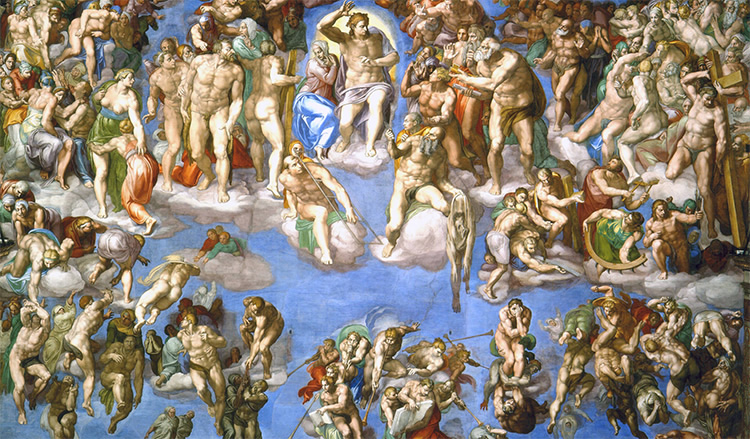
altar wall:
-counter reformation
-last judgement, life and death
-saved and damned people
-sibyls: monumental (hellenistic figures)
-portraits of certain artists on lower walls
Function:
-election of new pope and masses happen in this building
-art is made for this building (Sistine Chapel)
Context:
-artist: Michaelangelo
-High Renaissance 1508-12 (ceiling), 1536-41 (altar wall)
Vatican City, Italy
-under Pope Julius II


76. school of Athens
Form:
-fresco
-spatial illusionism
-fluid/interlocking
-same style as Sistine figures
-roundels
-barrel vaults
-coffers
Content:
-branches of knowledge under faith
-philosophy and science
-Plate: idealism (points up)
-Aristole: realism (points down)
-Raphael self portrait
-Michaelangel on block of marble
-poetry, imagination
-disputah: faith and reason
-heavenly court of prophets and saints
-Jesus in full body halo
-Stanza della Segnatura: room of signatures
-acorns: symbol of family
Function:
-expresses knowledge and faith
Context:
-artist: Raphael
High Renaissance 1509-11 Vatican Palace under Pope Julius II
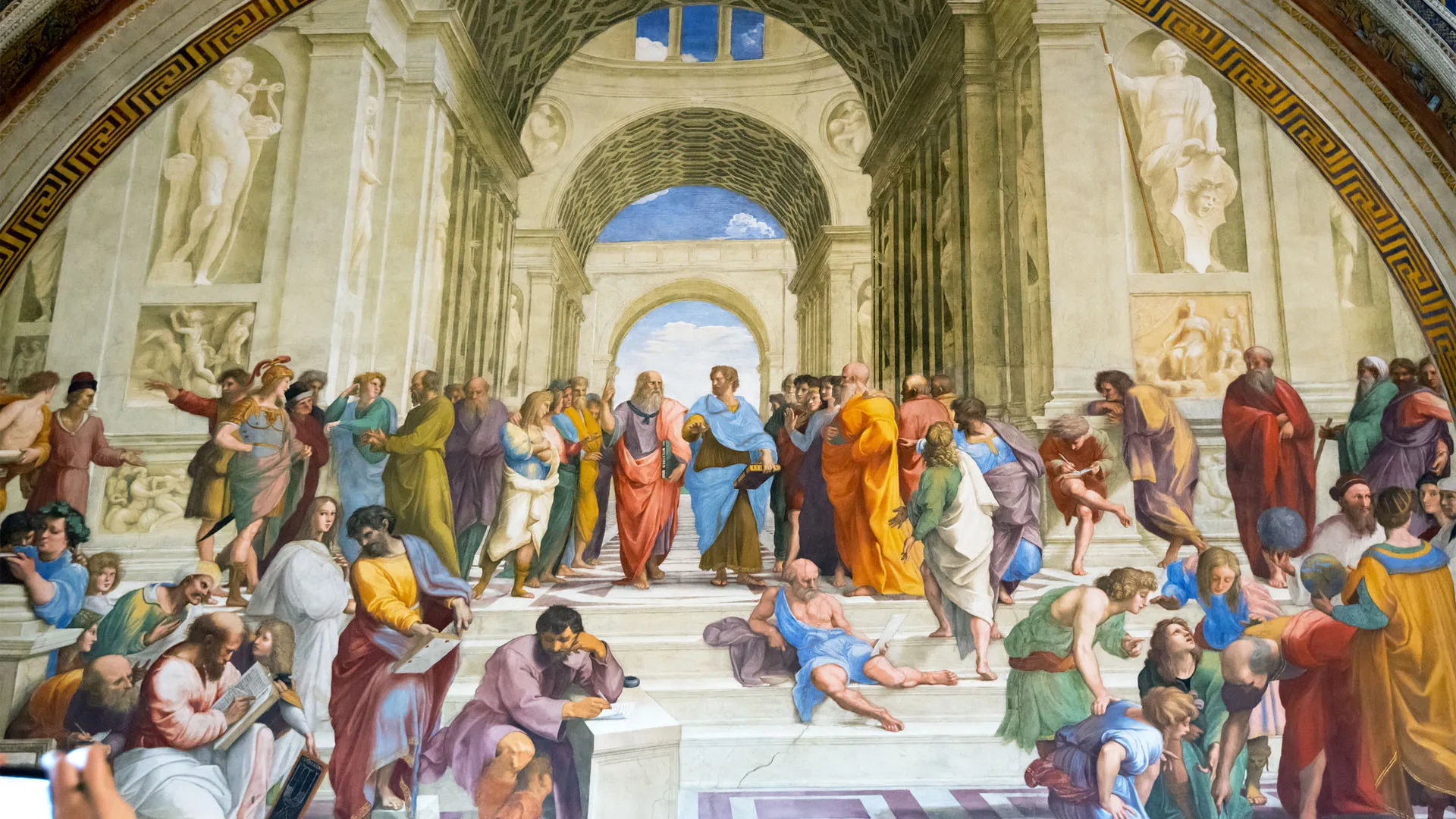

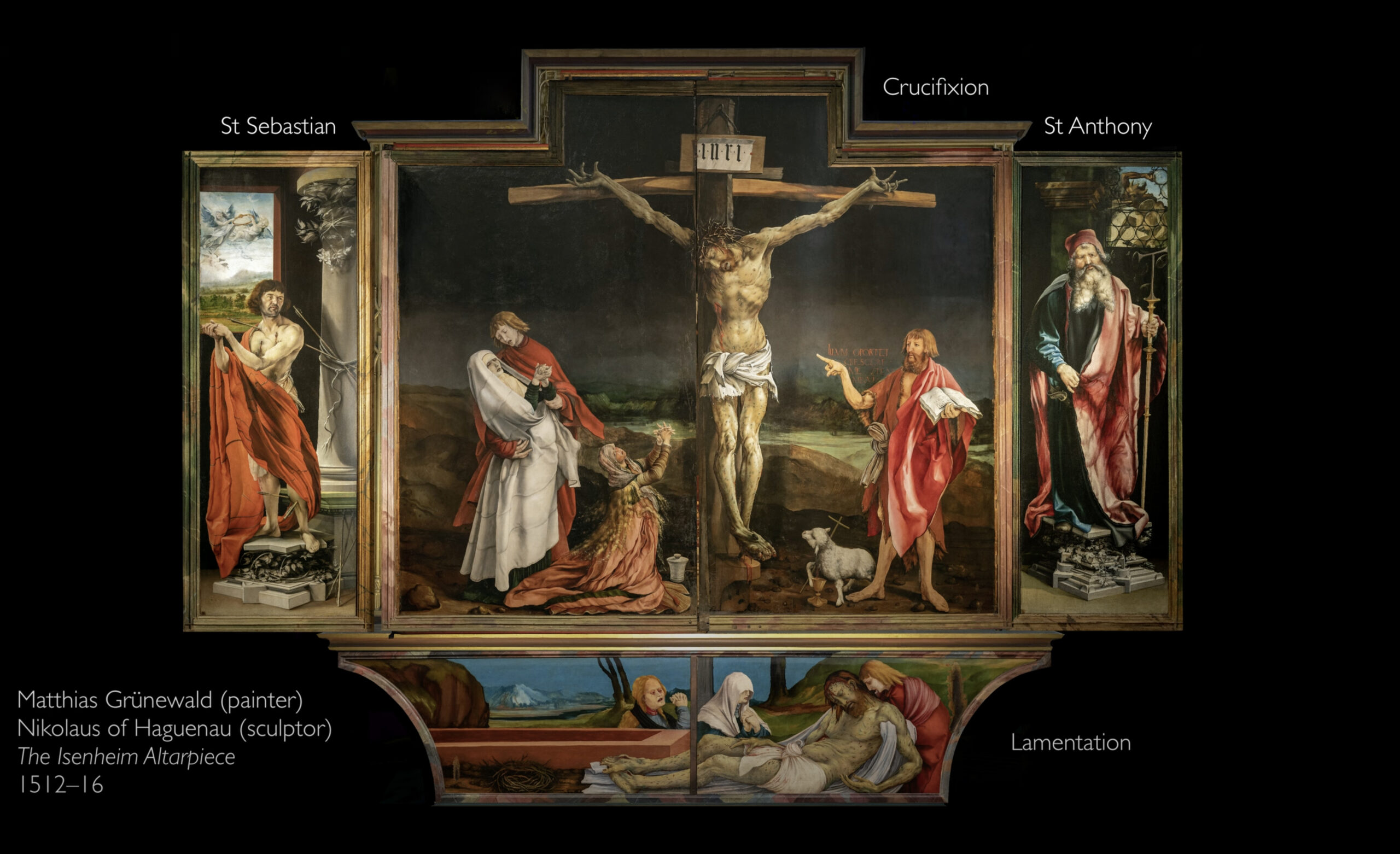
77. Isenheim Altarpiece
Form: oil on wood, diptych (two panels/wings)
Content:
-predella: base of the altarpiece
-1st panel: shows Jesus suffering on the cross symbolizing the suffering of the patients
-2nd panel: shows Jesus resurrection
-3rd panel: statue of St. Anthony who was patron saint of the hospital
Function:
- made for a hospital to relate their suffering to Jesus' suffering to make them feel better
Context:
- no longer in situ
- Boarder of France and Germany
-Made by Matthias Grunewalkd in 1512-1516 CE
78. Entombment of Christ
Form:
-manneristic: shows great knowledge of Renaissance but distorts it
-figures stylized and elongated
-primary colors and white
-roundalls above of Evangelists
-space is nonsensical
-1D (no depth)
Content:
-no symbols of holiness (no cross, etc.)
-Mary proportionately larger
-everyone mournful
-lower Jesus from the cross
-chaotic figures/constant movement
-self portrait
-non balance (lots of different directions)
Function:
-altar piece
-doesn't look Renaissance
Context:
-artist: Jacob de Pontorina
-Florence, Italy 1525-1528
-family chapel

79. Allegory of Law and Grace
Form:
-woodcut, letterpress
-Protestant
-German text
Content:
-written in people's voice
-left: being chased by death (shows 10 commandments)
-right-washes over with Holy Spirit (can only be saved by God's grace
Function:
-propaganda during Reformation
-debates between Catholics and Luthers on how to get to heaven
Context:
-artist: Lucas Cranach the Elder (High Renaissance North 1530 CE)
-German; worked with Martin Luther

80. Venus of Urbino
Form:
-oil on canvas
-rich colors (red)
-nude reclining
-celebrating the female body
-paints a thin layer of paint to create flow and softness, layers upon layers of oil paint
Content:
-woman reclining while maids get her clothing
-dog=wealth
-seduction looks equal to erotic
Function:
-wedding gift
Context:
-artist: Titian
-Ventian Renaissance 1538 CE

81. Frontispiece of the Codex Mendoza
Form:
-codex
-city laid out in 4 sections
-text
-ink and color on paper
Content:
-Part 1: the creation of the City of Tenochtitlan (eagle on cactus describes how the city was founded)
-Part 2: conquests achieved by Aztec alliances
-Part 3: daily life
-Templo Mayor
-canals dividing cities
Function:
-made for the Spanish viceroy
-historical account of the Aztecs
Context:
-Aztecs 1541-42 CE

82. Church of Il Gesu
Form:
-building: marble, brick
-ceiling: fresco and stucco
-Latin cross plan, simple
-single aisle
-Post Reformation
Content:
-faith through the senses
-Last Judgement (ceiling) spatial illusionism, end of the Baroque period
-IHS: interpretation of Jesus' name
Function:
-Mother church for the Jesuits of the world
Context:
-architect: Giacomo da Vignola
-facade: Giacomo della Porta
-ceiling: Giovanni Battista Gaulli
-Jesuits are great defenders of the pope
-ceiling made 100 years later (1676)
-Rome, Italy

83. Hunters in the Snow
Form:
-endless, winter landscape
-panoramic view
-apart of series of 4 seasons
-oil on wood
Content:
-hunters coming back after an unsuccessful hunt (only one rabbit)
-people iceskating and curling (shows daily life)
-broken sign above inn
-vastness and beauty of world
Function:
-part of calendar series
0show how they had to get their food
0for dining room of wealth merchant in Antwerp
Context:
-artist: Peter Bruegel the Elder
1565 High Renaissance North
-Antwerp

84. Mosque of Selim II
Form:
-brick and stone
-similar to Hagia Sophia
-dome, squinches, piers, apses
-richly decorated dome from the inside
-centralized, octagonal mosque
Content:
-slender, tall minarets
-centralized with 8 piers
-courtyard and prayer hall
-madrassa (college for Islamic instruction)
-souk: shops in the mosque
-Qibla wall faces outwards showing openness
Function:
-mosque made to replace Hagia Sophia
Context:
-Edirne, Tukey: Ottoman
-made by architect, Sinan, in 1568-1575 CE
-part of a complex

85. Calling of St. Matthew
Form:
-metaphysical painting
-Baroque (Counter Reformation, through your sense)
-diagonal light (tenebrism)
-realism/illusionism
-unusal setting for Jesus
Content:
-meant to be contemplated
-Jesus extended hand (same hand as in Sistine Chapel)
-Matthew sitting with fellow tax collectors
Function:
-body and soul are between a spiritual reality and physical reality
-Jesus shown in modern environment
-part of 3 part series
-use of light
-in chapel
Context:
-artist: Caravaggio; Rome, Italy
-1559-1600
-Contarelli Chapel

86. Henri IV Recieves Portrait of Marie de 'Medici
Form:
-oil on canvas
-floating figures
-part of a cycle
-shows an event in her life
-Catholic Baroque
Content:
-Henry IV present the picture of Marie that confirmed his religious identity; married a Catholic queen
-marries her so he can have a son and recreate him in a Catholic way
-Jupiter and Juno gives blessing to them
Function:
-"early harmony"
-part of a tribute to her life
-show that their marriage was official bc portrait
-shows political power, sophistication, and stability
Context:
-Peter Paul Rubens (Flemish painter)
-from Marie de' Medici cycle displayed in the Louvre
-1621-25 CE Flemish Baroque

87. Self Portrait with Saskia
Form:
-Dutch Baroque
-difference in emphasis on the figures
-exists in 3 different states
-rich tonal quality
-abrupt spatial construction
-etching (exposing metal)
-genre: private movement between husband and wife
-small scale
Content:
-Rembrandt and wife in historical clothing
-wife, Saskia died at the age of 30 (only piece he did of her)
-Rembrandt drawing his drawing
-exploring who he is
Function:
-self portrait/marriage portrait
-role playing
Context:
-Rembrandt 1636
-he is mostly a portrait maker
-Dutch, Amsterdam
-Dutch Baroque

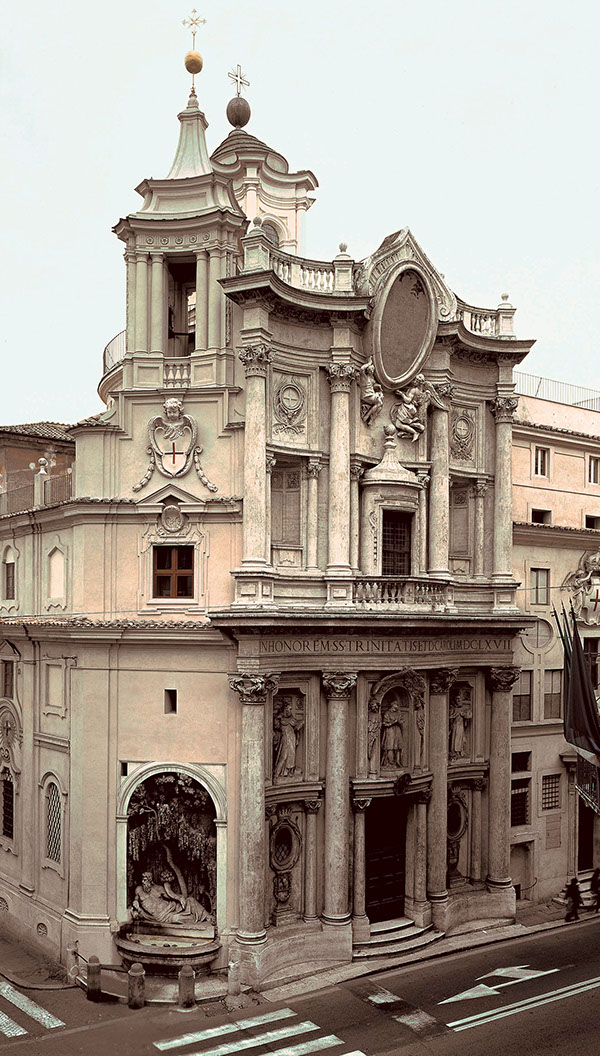
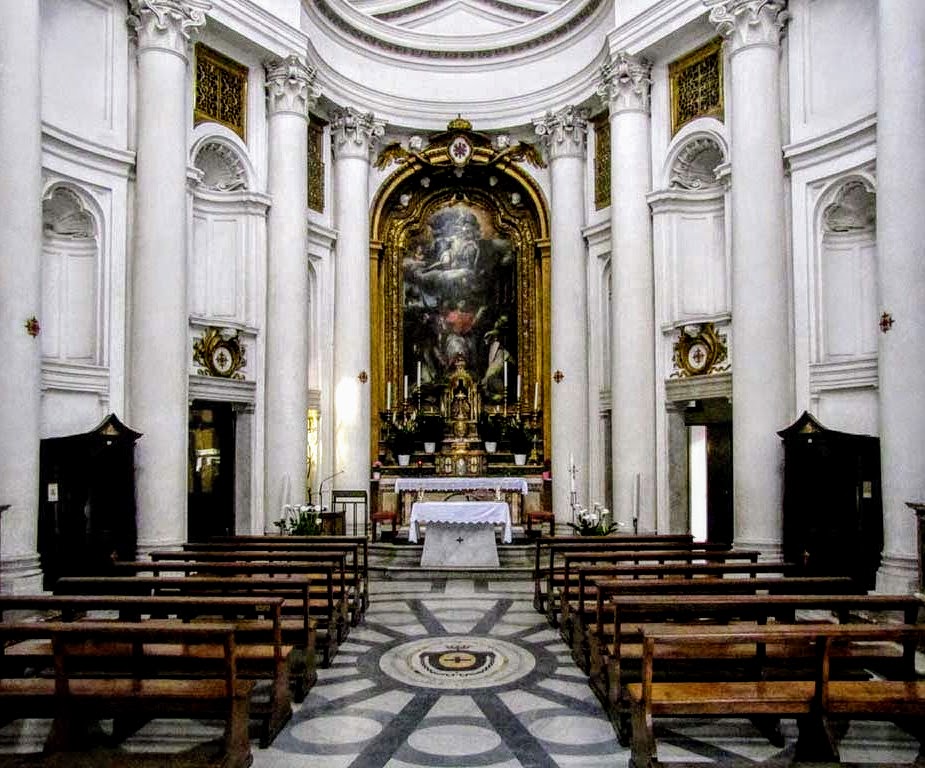
88. San Carlo alle Quatro Fontane
Form:
-pure white inside with complex geometry
-stone, stucco
-rich orientation
-balance convex vs. concave
-flowing walls
-oculus
Content:
-Trinitarian order in centers of ceiling (triangle=HS)
-big columns
-4 fountains
Function:
-dedication to Saint Carlos
-represent the trinity
-a reminder of the Renaissance
-Monastic Church (Trinitarian Order)
Context:
-Rome, Italy
-architect: Borromeo
1638-46 CE (17th century)
-Italian Baroque


89. Ectasy of Saint Teresa
Form:
-marble, stucco, gilt bronze
-rich color
-many shapes and directions
-spiritual vs. physical
-Baroque
-shallow carving
-Counter-Reformation
Content:
-St. Teresa has a vision (physical and spiritual experience)
-fresco on the ceiling
-Holy Spirit as a dove, light coming from HS
-columns serving as a frame as you enter the chapel
-real daylight explosion
-depicted very sensual
Function:
-Bernini's comeback after his scandal with mistress
-inspire and involve the viewer by bringing sculptures to life
-after St. Teresa canonized
-shows the union of the world
Context:
-Rome; 1647-52
-artist: Bernini (very religious)
-sculpter, architect, painter
-Italian Baroque

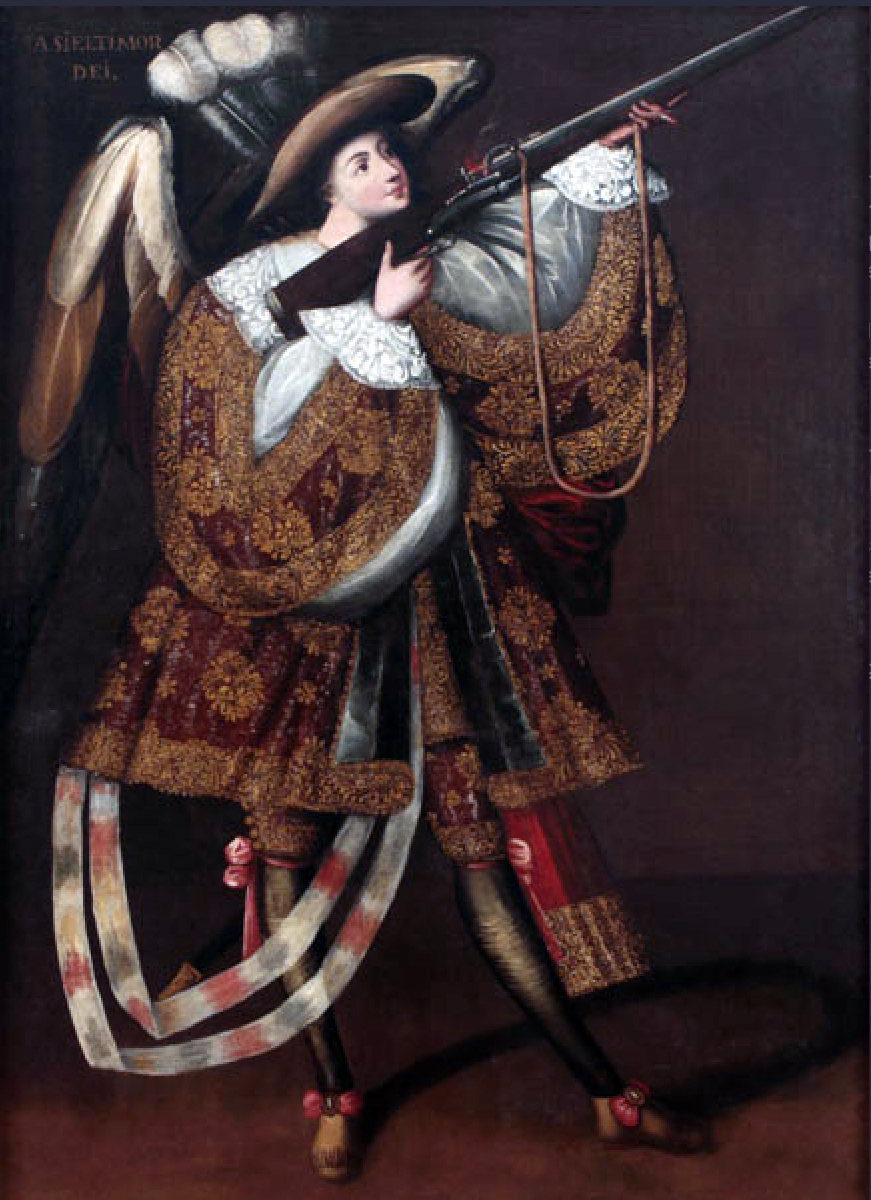
90. Angel with Aequebus
Form:
-Spanish Colonial Baroque
-idealistic
-Latin inscription
-oil paint
-part of a large history
Content:
-guns from 80 years war
-feathered crown
-nobility
-elegant clothing
-Catholic missionary
-Asiel fears God
-Church=army
-angel=soldiers
-aristocratic clothing
-Angel with gun
-native fashion, spanish
Function:
-militarist approach to faith
-propaganda for war
Context:
-17th century Peru
-artist: Asiel Timor Dei

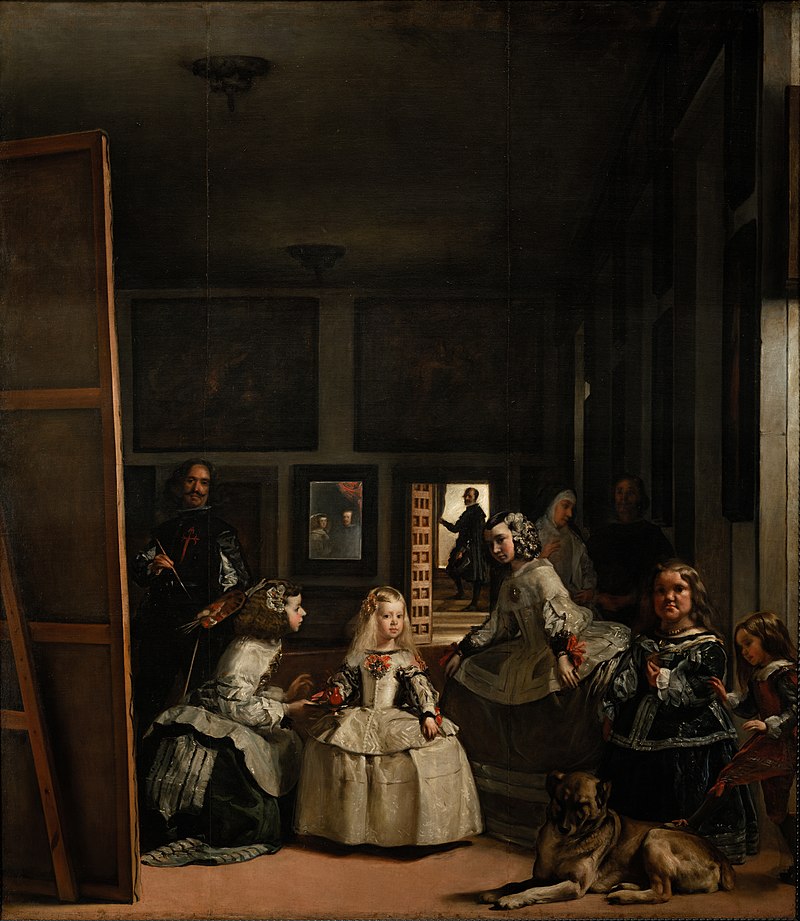
91. Las Meninas
Form:
-use of mirrors (Baroque)
-movement in strokes not as detailed as you think
-large painting
-gaze
Content:
-maids of honor and only daughter( blonde child) of the king and two dwarfs
-dog=wealth
-self-portrait of Velazquez
-painting in a painting
(Velasquez painted this painting
-people looking at the viewer
Function:
-View of palace life
-show wealth/status
-made for Philip IV (the viewer)
-genre painting
Context:
-1656 CE; Prado, Madrid
-artist: Diego Velazquez
-Spanish Baroque

92. Woman Holding a Balance
Form:
-Catholic elements
-Scientific lighting
-genre scene
-small scale, oil on canvas
-use of light
-vanishing point
-color palette
Content:
-women part of the upper class (fine clothing)
-fur coat
-balance has nothing in it
-weighing valuables
The Last Judgement scene above
Function:
-material wealth
-painting for merchants
-religious meaning but not painted just for the Church
-time and change
Context:
-artist: Johannes Vermeer
-1664 Dutch Baroque

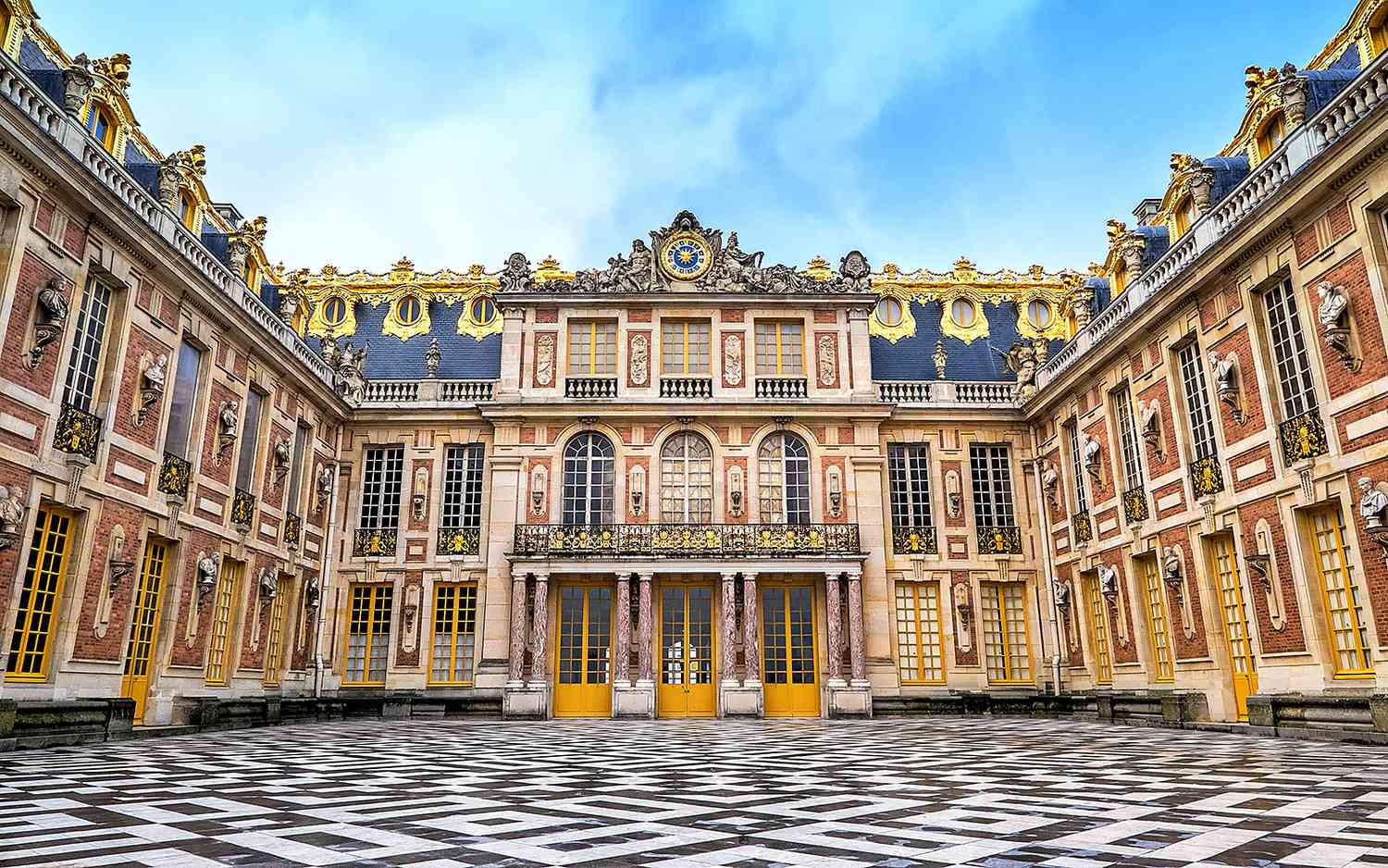
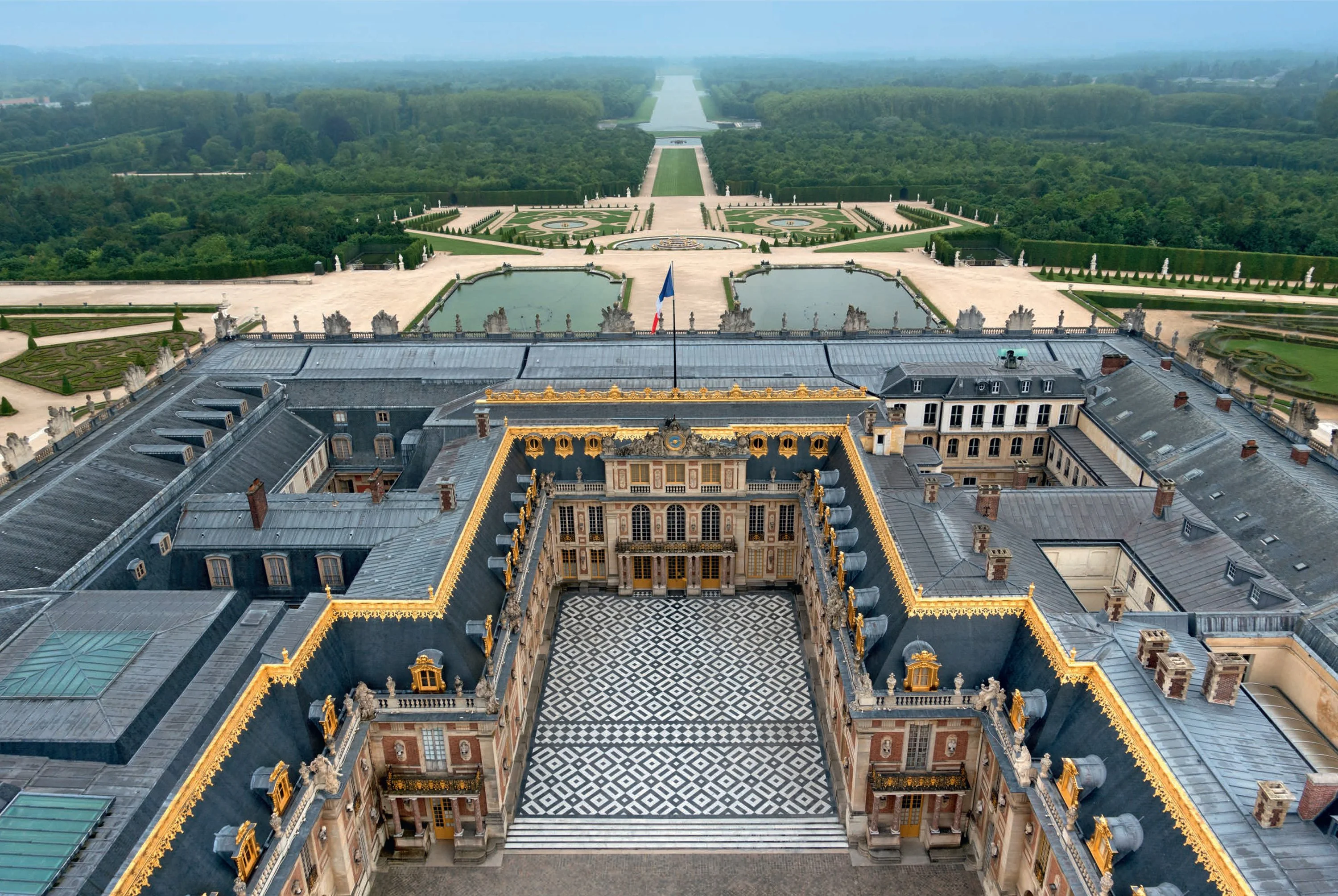
93. The Palace of Versailles
Form:
-east-west axis
-rigorous geometry
-classical architecture (symmetry, repetitive, and based on Greek temples)
-gold
-painted ceilings
-outside is not as "ornate"
-symmetrical
-Greek/Roman influence
-mirrors (hall of mirrors)
Content:
-Hall of mirrors (social gatherings)
-700 rooms
-gardens
-sculptures, paintings, and fountains attributed to him
Function:
-King Louis XIV decided to build a new palace
-example of nobility
-living for the King, his close friends, family, servants, and soldiers, (members of the court)
-emphasize Louis' importance (everything revolves around him
Context:
-Versailles, France
-Louis Le Vaw and Jules Hardouin-Mansart= architects
-began in 1669 CE, French Baroque


94. Screen with Seige of Belgrade and hunting scene
Form:
-Japanese folding screen (Biombo)
-Spanish Colonial Baroque
-tapestry
-temporal/resin on wood
-shell inlay (Aztec)
Content:
-historical event from Europe
-one side: battle scene
-other side: Landscape
-Great Turkish War
-combines multiple cultures
Function:
-expresses the economic power of the Spanish in Colonial Mexico
-made Spanish viceroy
-room divider (biombo- Japanese folding screen)
-relationship between Japan and Latin America
Context:
-Circle of Gonzalez Family, 1697-1701 CE
-Spanish Colonial

95. The Virgin of Guadalupe
Form:
-based upon the original
-oil on canvas on wood inlaid with pearls
Content:
-artist signature
-traditional view
-story of Juan Diego (Aztec man)
-roses with her image
-radiating light off Mary
-indigenous coming to Roman Catholic Church
-dark-skinned people portraits
FunctionL
-tribute to Mary and show her as divine
Context:
-1698 CE, Spanish Colonial
-Mexico City, Basiclia of Guadalupe
-artist: Miguel Gonzalez

96. Fruit and Insects
Form:
-still life
-Baroque
-oil on wood
-colors, detailed
Content:
-insects, fruit
-wheat and grapes= Jesus?
-bringing different compositions together
Function:
-harvest in autumn
-microscopic organisms: used microscope to study these organisms
Context:
-artist: Rachel Ruysch (Dutch arist; last famous still painter)
-Florence, Italy 1711 CE (18th century)

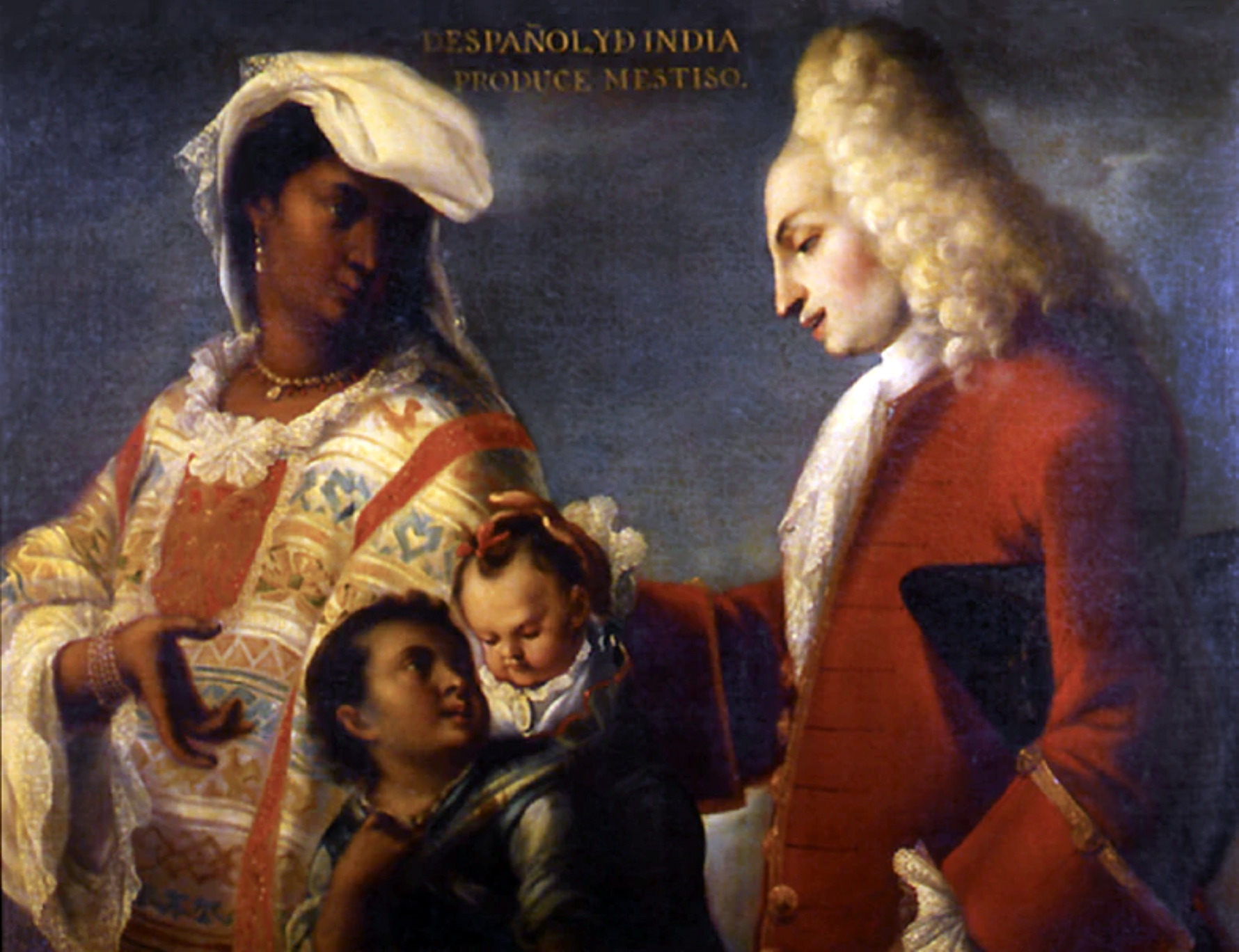
97. Spaniard and Indian Produce a Mestizo
Form:
-casta painting (displays mother, father, and child) possibly modeled after the Holy Family
-text is the title of the piece
-enlightenment
Content:
-woman wearing traditional Indian clothing and white father with their mixed race son (Father wearing French-style European clothing displaying social status as very high)
-servant carrying the son
-family appears content
-racial purity=whiteness
Function:
-displays social status (tied up in one's racial makeup)- helped maintain European power and control
Context:
-artist: Juan Rodriguez Juarez
-1715 CE (height of slave trade)

98. The Tete a Tete from Marriage a la Mock
Form:
-looks like French Rococo (uses to make fun of the French
Content:
-critques upper-class for getting married because of bloodlines and family
-shows the couple is married but not faithful to eachother
-man being sniffed by dog because smell of another woman's perfume
-woman has been out all night trying to become popular
-part of a series (arranged marriages end badly, marriage should be about love)
-sign that sex occurred before husband came back home (flipped over chair)
-merchant gives up on couple because they won't take finances seriously
Function:
-satire from British to French
-art being made for the growing middle class
Context:
-artist: William Hogarth (social critic) that usually makes prints
-1743 CE

 Knowt
Knowt