Unit 3 Food: Note 1 Soil Formation
Soil Development: the starting bedrock material and weathering/erosion processes determine the mixture of components in dirt
Dirt compositions:
Iron - Clay, iron oxide
Feldspar - Clay, K Na Ca ions
Quartz - Quartz
Muscovite Mica - Clay, K ions
Calcite - Ca, CO ions
Color is used as a guide to let us know what the organic content and chemical compositions of the soil is
the darker the brown, the more organic matter there is
Munsell Soil Color Chart
Soil Formation: soil is formed from the weathering of bedrock mixed with the deposition of other eroded rock plus organic materials
Soil Types: sand, silt or clay, these are designated by their size and texture. Categorized by the Soil Texture Triangle
Sand: medium sized grains drains excessively
Silt: very fine sized grains, drains well
Clay: large grains, drains poorly
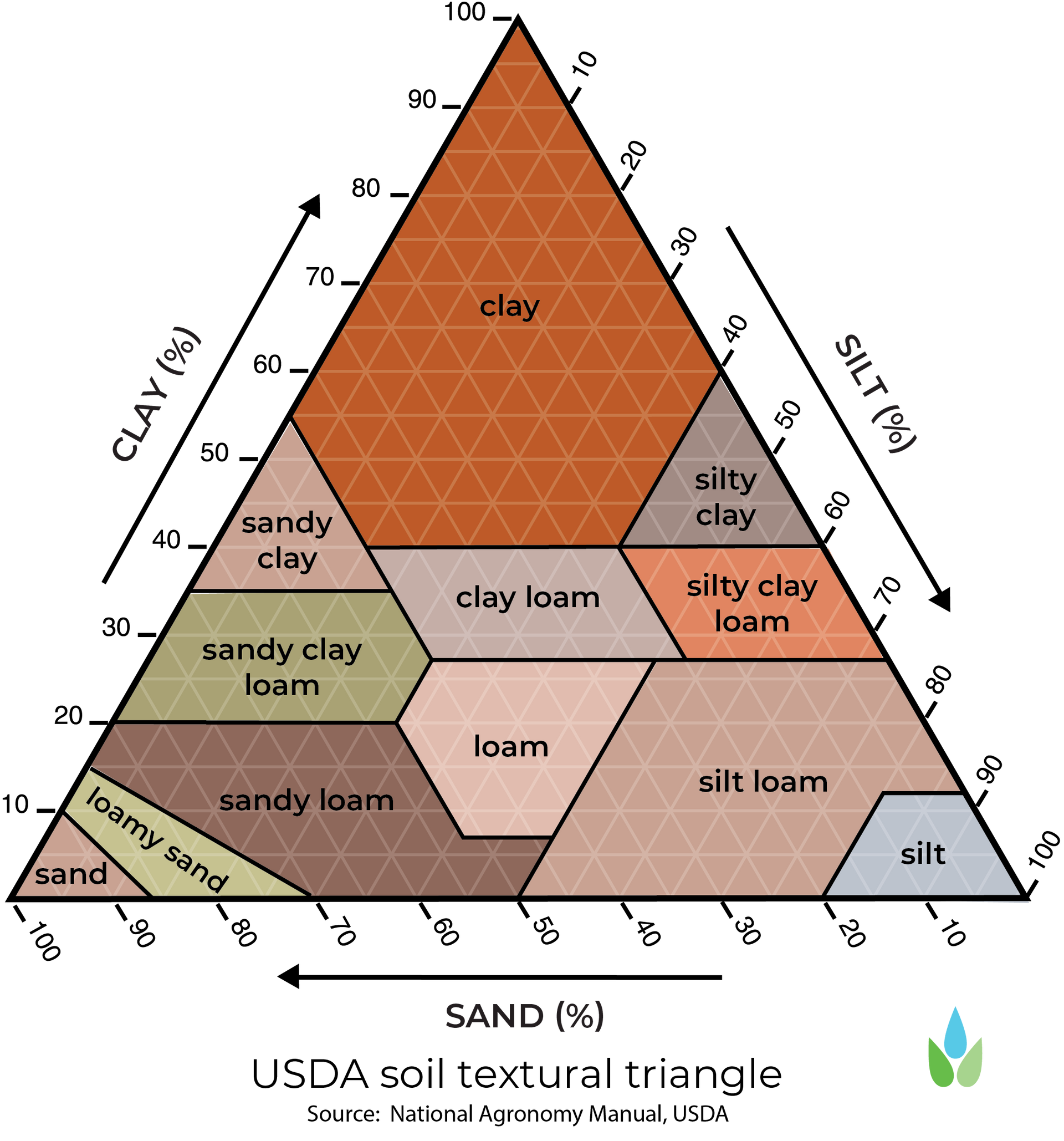
The USDA Soil Classification guide, uses the soil textures to index what type of water drainage they produce
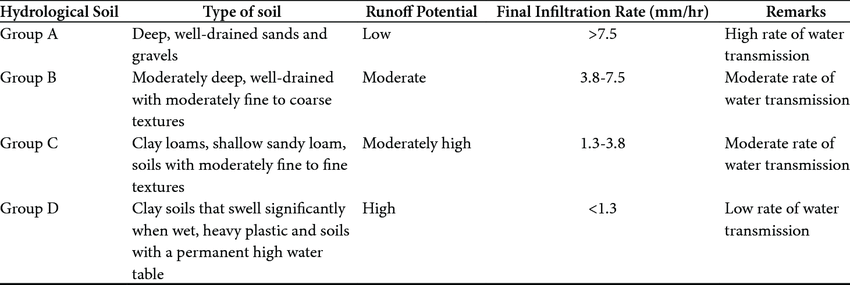
Arability:
Sand - hard to grow
Silt Loam - well to grow
Sandy Clay, and Clay Loam - hard to grow, need fertilizer or added organic materials
Clay Minerals
Some clay minerals have space for water in their crystalline structure
Expansive Structure: clay takes in water and expands, once the water dries the clay shrinks
Soil Horizons
Horizons: soil develops in layers, which are called horizons. This is a results of weathering and erosion
O Horizon - organic
A Horizon - top soil, high concentration of organic matter (leaching)
B Horizon - subsoil (accumulation)
C Horizon - weathered rock (broken bedrock)
R Horizon - rock
Horizons are created in the order of R, C, A, B, the O.
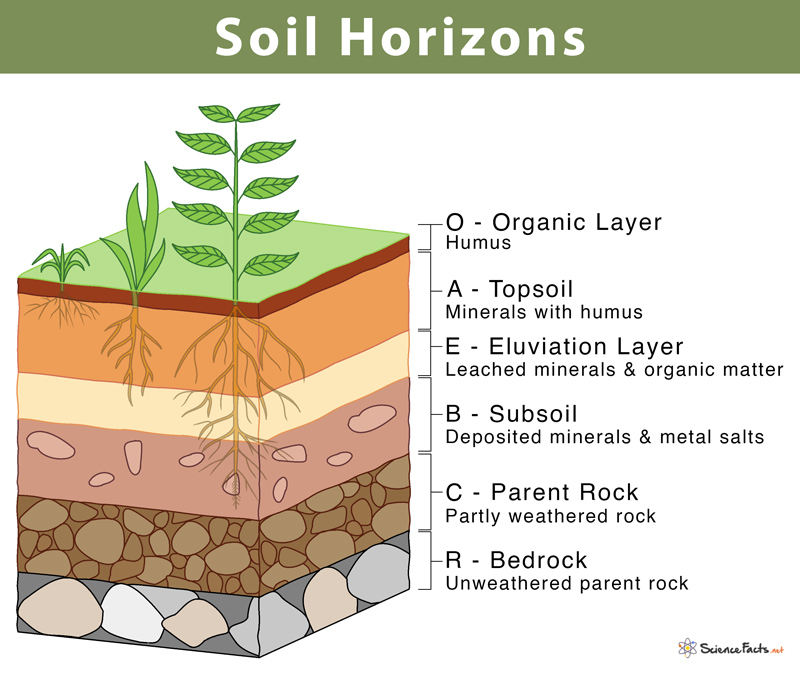
Color changes and texture changes from the compositional change
Factors that affect soil formation:
Climate
Parent material
Time
Plants and animals
Topography
Humans