AP BIO Unit 6 Review - Gene Expression and Regulation
<<Transcription<<
Vocab
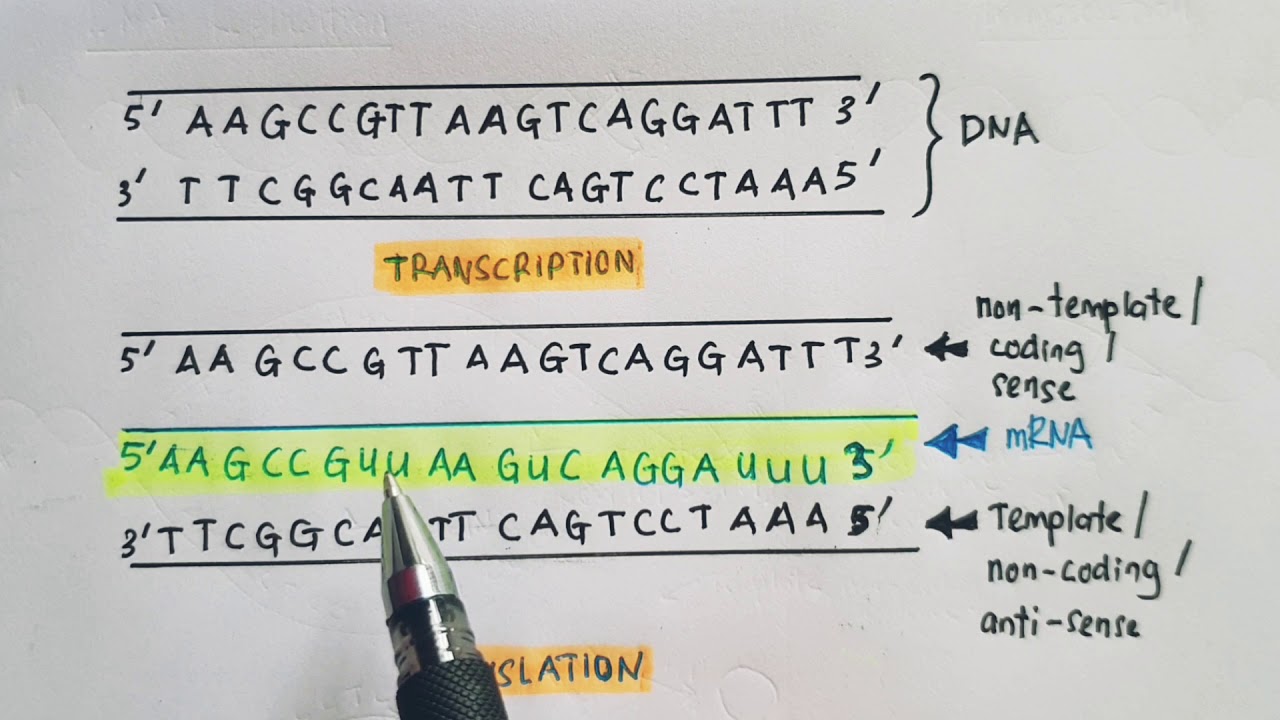
%%Transcription%%: The synthesis of RNA using a DNA template
Complementary/
%%Coding Strand%%: The DNA strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (RNA)
%%Template Strand (non-coding/antisense)%%: The strand that is used during transcription to produce RNA
- the RNA synthesized using the template strand will have the same base pairs as the coding strand (except for T and U)
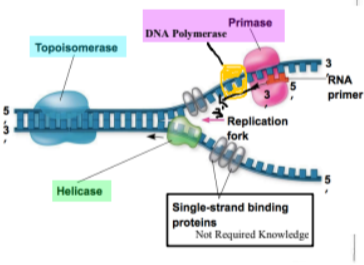
%%origin of replication%%: Site where the replication of a DNA molecule begins, consisting of a specific sequence of nucleotides
%%replication fork%%: A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where the parental strands are being unwound and new strands are being synthesized
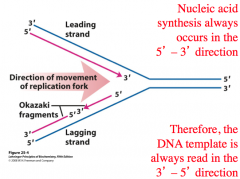
Nucleic acid synthesis occurs in the __ direction
- 3’ → 5’
DNA is read from __
5’ → 3’
{{Enzymes:{{
==Helicase==
- unwinds strands (zipper)
==polymerase==
- synthesizes new strands of DNA (builder)
- limitations
- requires RNA primers
- discontinuous on the lagging strand
==Ligase==
- joins fragments (glue)
==Topoisomerase==
- prevents overwinding
- relives stress from unoiling
==Primase==
- creates primers where DNA synthesis is initiated
==single strand binding proteins==
- stops the single strands from joining and reforming
Other Vocab
^^Leading Strand:^^ The new complementary DNA strand is synthesized continuously along the template strand toward the replication fork in the mandatory 5′ → 3′ direction
^^Okazaki Fragments^^: A short segment of DNA synthesized away from the replication fork on a template strand during DNA replication. Many such segments are joined together to make up the lagging strand of newly synthesized DNA
^^Lagging Strand^^: A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates using Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5′ → 3′ direction away from the replication fork
<<Translation<<
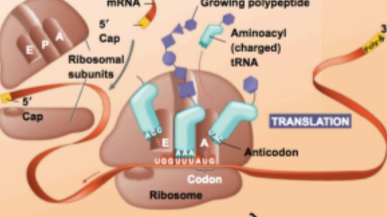
mRNA is translated as codons into amino acids
- @@codon@@ - A sequence of three consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid
Translation starts in the ribosome
- when rRNA interacts with mRNA
- AUG start codon
Stops at a stop codon
UAG, UAA, UGA
signal the end of the polypeptide chain during translation
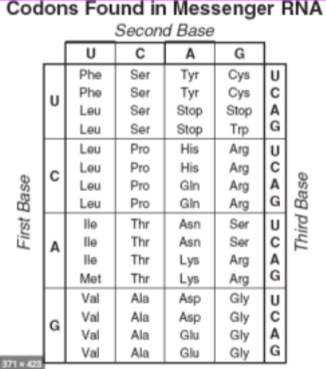
Many amino acids are encoded by more than one codon
@@wobble@@ - the redundancy in the genetic code such that the same amino acid may be encoded by multiple codons
{{Pro vs Eu{{
In prokaryotic cells, transcription and translation happen simultaneously in the cytoplasm
in eukaryotic cells, transcription happens in the nucleus, and mRNA must be exported
intron and exon spicing occurs in eukaryotic cells
- alternative splicing → different variation
in eukaryotic cells, a poly-A tail and gtp cap are added
- prevents degradation from hydrolytic enzymes
- facilitate the export of mRNA from the nucleus
- help attach to ribosomes
}}Regulation and Operons}}
Operons - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F7wRwHV_J5Q
{{Lac operons{{
when lactose is present, the repressor becomes inactive
- genes are expressed to break down lactose
{{Trp Operon{{
When trp is not present, the repressor stats inactive
- genes are expressed to synthesize trp
^^Histone Acetylation^^ - Loosens chromatin structure promoting the initiation of transcription
^^Methylation^^ - can condense chromatin and lead to reduced transcription
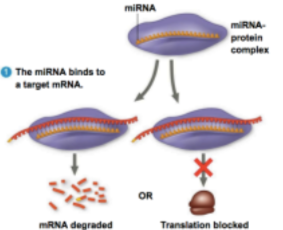
%%RNA Interference%% - Inhibition of gene expression by RNA
%%MicroRNA%% - small, single-stranded RNA molecules that bind to complementary mRNA sequences
- degrade mRNA
- block its translation
%%Small Interfering RNA%% - a double-stranded RNA molecule that is non-coding operating in the RNA interference pathway
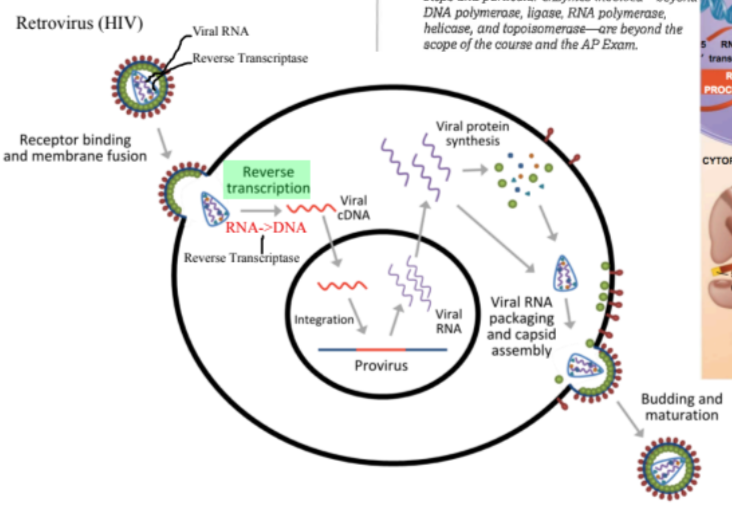
[[Reverse Transcriptase[[
<<Reverse transcriptase<<
- A reverse transcriptase is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription
the normal sequence of information
- DNA → RNA → Protein
Sequence in retrovirus
RNA → DNA → RNA → Protein