Chapter Four
Chapter 4.1
The Big Picture: Globalization, the trend of the world economy toward becoming a more interdependent system, is reflected in three developments: the rise of the “global village” and e-commerce, the trend of the world becoming one big market, and the rise of both megafirms and internet-enabled mini-firms worldwide.
Learning Objective(s):
Identify three influential effects of globalization.
Although it is one of the largest exporters in the world, the US imports more than it exports. In 2022, the nation imported over $3 trillion in goods and $600 billion in services.
This trade imbalance highlights the importance of understanding global supply chains and the interconnectedness of economies, as countries rely on one another for goods and services.
The International Institute for Management Development (IMD) defines competitiveness as how well countries “manager their competencies to achieve long-term value creation”. The IMD ranks countries each year based on the following:
Economic Performance- Refers to the overall economic health of a country, which includes indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment levels.
Government Efficiency- Refers to the ability of a government to effectively manage public resources, implement policies, and deliver services to its citizens without unnecessary expenditures or delays.
Business Efficiency- Refers to how well businesses operate within a country, including factors such as productivity, innovation, and the regulatory environment that affects business operations.
Infrastructure- Refers to the fundamental facilities and systems that support the functioning of a country, including transportation networks, utilities, and communication systems that are essential for economic activity and overall quality of life.
There are many reasons the high scoring countries achieve their status, but they didn’t do it by themselves. It has something to do with Globalization, the trend of the world economy toward becoming a more interdependent system.
Global Village- Refers to the concept that the world is becoming increasingly interconnected through communication, technology, and trade, allowing for the sharing of ideas, culture, and resources across borders.
Global Economy- Refers to the increasing tendency of the economies of the world to interact with one another as one market instead of many national markets.
Chapter 4.2
The Big Picture: Studying international management prepares you to work with foreign customers for a foreign firm in the US or a US firm overseas. Successful international managers aren’t ethnocentric or polycentric but geocentric.
Learning Objective(s):
Describe the characteristics of a successful international manager.
A multinational corporation is a business with operations in several countries. For example, McDonald’s is a well known multinational corporation with more than 38,000 sotres in more than 100 countries.

A multinational organization is one that operates across national borders, adapting its strategies to meet the diverse cultural, economic, and regulatory environments of each market.
Ethnocentric Managers tend to prioritize their home country's culture and practices over those of the host countries, which can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts in diverse environments.
Parochialism is a narrow-minded focus on one's own culture or country, often resulting in an inability to appreciate or understand the differences and nuances of other cultures, which can hinder effective communication and collaboration in a multinational setting.
Chapter 4.3
The Big Picture: Multinationals expand to take advantage of availability of supplies, new markets, lower labor costs, access to finance capital, or avoidance of tariffs and import quotas. Five ways they do so are by global outsourcing; importing, exporting, and countertrading; licensing and franchising; joint ventures; and wholly owned subsidiaries.
Learning Objective(s):
Outline the ways in which companies can expand internationally.
Why do companies expand internationally?
Availability of Supplies
New Markets
Lower Labor Costs
Maquiladoras are manufacturing plants located in Mexico that import materials and equipment on a duty-free and tariff-free basis for assembly or manufacturing, which are then exported back to the United States and other countries.
Access to financial capital
Avoidance of Tariffs
How companies expand internationally:
Global Outsourcing: Companies can reduce costs and increase efficiency by delegating certain business processes to external providers in different countries.
Importing, exporting, and countertrading are essential strategies for companies looking to tap into international markets, allowing them to sell goods abroad and source materials from global suppliers.
Licensing and Franchising: These methods enable companies to enter new markets by allowing local businesses to produce and sell their products or services under the company's brand, facilitating rapid expansion while minimizing risk.
Joint Ventures: Involving collaboration between two or more companies, joint ventures allow businesses to share resources, expertise, and risks while pursuing specific projects or entering new markets together.
Wholly Owned Subsidiary: This strategy involves a company owning and controlling 100% of its foreign operations, providing full control over management and operations, but also requiring a significant investment and exposure to risks associated with the local market.

Chapter 4.4
The Big Picture: barriers to free trade include tariffs, import quotas, and embargoes. Organizations promoting international trade are the World Trade Organization, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. There are two major trading blocks, NAFTA (now USMCA) and the EU.
Learning Objective(s):
Discuss barriers to free trade and ways companies try to overcome them.
Free Trade is defined as the unrestricted exchange of goods and services between countries, allowing for greater economic efficiency and consumer choice.
Countries often use trade protectionism- the use of government regulations to limit the import of goods and services- to protect their domestic industries.
Barriers to International Trade:
Tarrifs
Taxes imposed on imported goods to increase their price and make domestic products more competitive.
Import Quotas
Limits set on the quantity of specific goods that can be imported into a country, thereby controlling supply and protecting local industries.
Sanctions and Embargoes
Measures taken to restrict trade with specific countries, often used as a political tool to influence behavior or policies. These can include prohibiting exports to or imports from a particular nation.
The three principal organizations designed to facilitate international trade are the World Trade Organization, World Bank, and, International Monetary Fund.
Trading Bloc - A group of countries that come together to promote trade among themselves by reducing or eliminating tariffs and other trade barriers, thereby fostering economic cooperation and integration.
The Exchange Rate is the price of one currency in terms of another, which can significantly impact international trade by influencing the cost of imports and exports.
Chapter 4.5
The Big Picture: managers trying to understand other cultures need to understand the importance of national culture and cultural dimensions and basic cultural perceptions embodied in language, interpersonal space, communication, time orientation, religion, law, and political stability.
Learning Objective(s):
Explain the value to managers of understanding cultural differences.
Cross-Cultural Awareness is essential for effective management in a globalized economy, as it enables leaders to navigate diverse work environments and build strong relationships with employees from various backgrounds.
A nation’s culture is the shared set of beliefs, values, knowledge, and patterns of behavior common to a group of people.
Low-Context Culture vs. High-Context Culture:
Low-Context Culture: Communication is typically explicit, direct, and relies heavily on spoken or written words. Examples include the United States and Germany, where clarity and precision are valued in interactions.
High-Context Culture: Communication is often implicit and relies on context, non-verbal cues, and the relationship between speakers. Countries like Japan and Saudi Arabia exemplify this, where understanding the nuances of communication is crucial for effective interaction.
Hofstede Model of Four Cultural Dimensions:
Individualism vs. Collectivism: This dimension examines whether people in a culture prioritize individual goals over group goals, or vice versa. Individualistic cultures, such as the United States, emphasize personal achievement, while collectivist cultures, like China, focus on group harmony and cooperation.
Uncertainty Avoidance: This dimension measures how cultures cope with uncertainty and ambiguity. Cultures with high uncertainty avoidance, like Greece and Japan, tend to have strict rules and regulations to manage unpredictability, whereas cultures with low uncertainty avoidance, such as the United States and Sweden, are more open to change and innovation.
Power Distance: This dimension reflects the extent to which less powerful members of a society defer to more powerful ones. High power distance cultures, like Malaysia and the Philippines, accept hierarchical order without much question, while low power distance cultures, such as Denmark and New Zealand, promote egalitarianism and challenge authority.
Masculinity vs. Femininity: This dimension explores the distribution of roles between genders in a culture. Masculine cultures, like Japan and Austria, value competitiveness, achievement, and material success, whereas feminine cultures, such as Sweden and Norway, prioritize care, collaboration, and quality of life.
GLOBE Project is a massive and ongoing cross-cultural investigation of nine cultural dimensions involved in leadership and organizational processes.
The Nine Cultural Dimensions are as follows:
Power Distance
Uncertainty Avoidance
Individualism vs. Collectivism
Masculinity vs. Femininity
Long-Term Orientation vs. Short-Term Normative Orientation
Indulgence vs. Restraint
Assertiveness
Future Orientation
Performance Orientation
Chapter 4.6
Learning Objective(s):
Describe how to develop your diversity, equity, and inclusion competency.
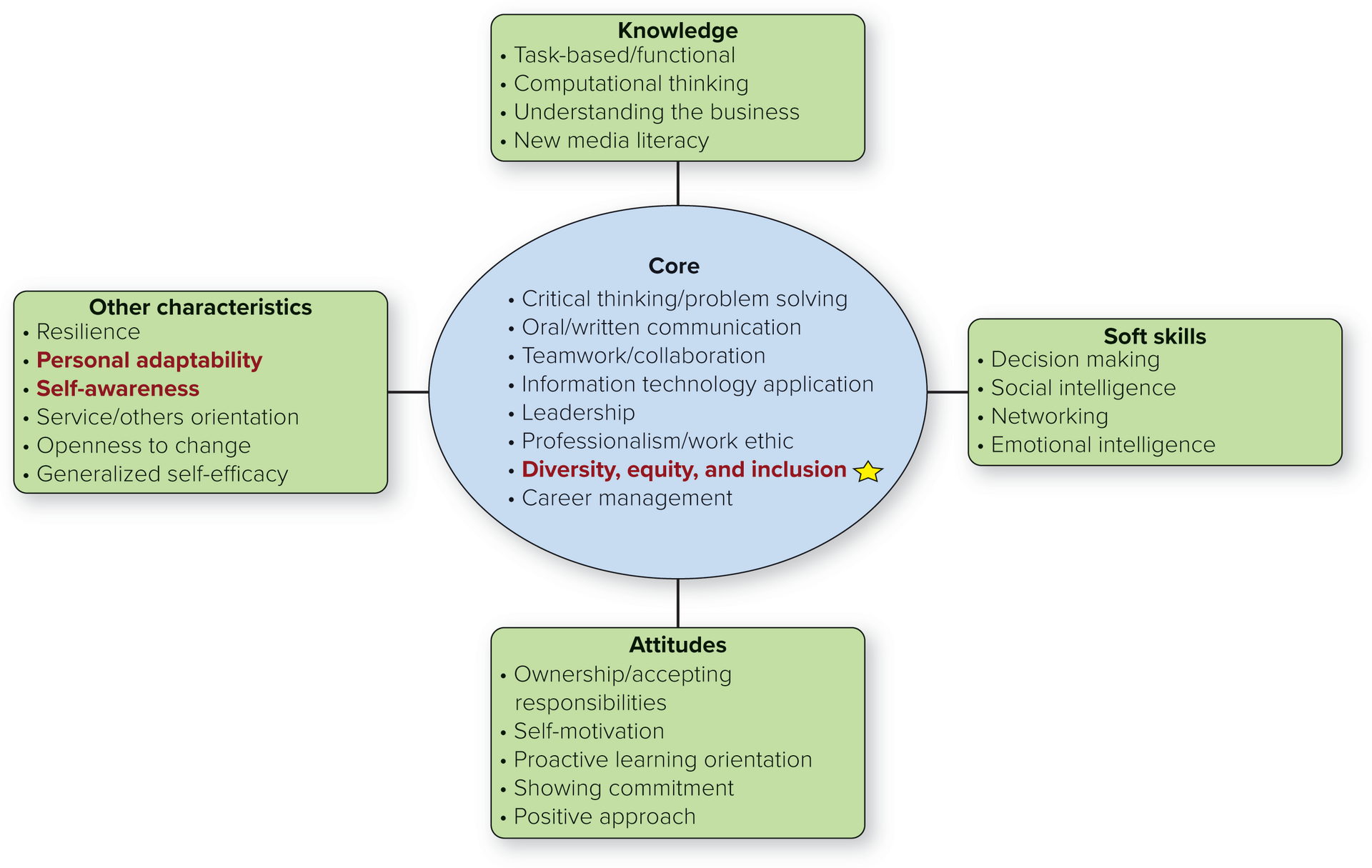
Key Terms
Context
Countertrading
Cross-cultural awareness
culture
embargo
ethnocentric managers
European Union
exchange rate
expatriates
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
geocentric managers
 Knowt
Knowt