Chapter 3: What are the Essential Cultural Value Patters
Functions of Cultural Values
Values
Values - Shared ideas about what counts as important/unimportant, fair/unfair, ethical/unethical conduct
Examples of Values
diversity
conformity
power
modesty
achievement
tradition
security
inclusivity
stability
conservation
openness
past
nature
excellence
silence
spirituality
collaboration
honor
humility
family
harmony
cooperation
hedonism
learning
change
self-restraint
children
conformity
ancestry
benevolence
justice
creativity
obedience
community
innovation
What Values Give US
Sense of Self - Infused w/ myriad of values (gender, personal, spiritual, ethnic/macro, professional, relational)
Cultural values - Exist on a personal (socialization and life experiences) and cultural system level
Cultural system - Level values “stable and enduring“— Protecting culture in times of crisis
Crisis - when you value is being challenged
Guide (frame) - Our perceptions, communication, actions, expectations, and motivations
IC Communication Knowledge - Promotes introspection on cultural beliefs and values; helps one find common ground with diverse cultural others
Criteria - used to evaluate our own and the behaviors of others
Levels of Values
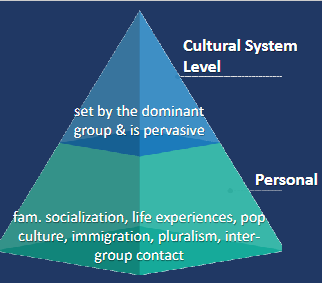
Cultural Level - Set by the dominant group and is pervasive
Personal Level - Family Socialization, life experiences, popular culture, immigration, pluralism, intergroup contract
American Values:
Freedom - Individual liberties and personal choice
Equity - Equal treatment/opportunities for all
Justice - Fair legal system and protection of rights
Diversity - Appreciation for different cultures and perspectives
Hard Work and Innovation - Value of effort and encouragement of creativity
Respect and Patriotism - Dignity for others and pride in the nation
Cultural Value Continuum Dimensions
Cultural Values Patterns
Dimensions and variations
Hofstede
Studies 50 countries in 3 regions from IBM
116,000 managers and Employees surveyed
Categories:
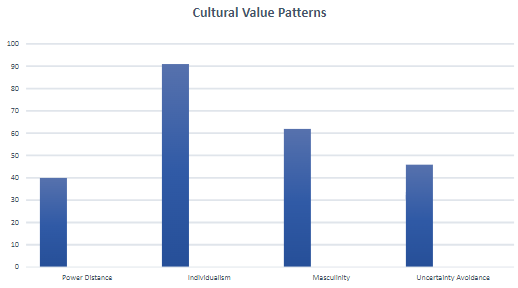
Individualism vs Collectivism
Feminine vs Masculine
Small power distance vs Large Power distance
Weak Uncertainty Avoidance vs Strong Uncertainty Avoidance
Individualism vs Collectivism
Individualism
Individuals identities (I over We) over the groups
US, Great Brittan, Australia, Italy, New Zealand
1/3 of human population
wealthy, urban, and industrialized
Independent, competitive, unique, seek social recognition, look after self & immediate-family, hedonistic, non-conforming, loosely linked ties, freedom, personal decisions
Collectivism
Groups identity (We over I) over individuals
Asia, Africa, Central and South America, Middle East, Pacific Islands
2/3 of human population
Poorer, Rural, and Traditional
Interdependent, Harmony, Face saving, Conformity, obedience, respecting parents wishes, tightly tied to others in community, guilt guides behavior, compliance, collaboration, lifetime support because of reciprocity, accountability
Feminine vs Masculine
Masculine
Social gender roles as distinct and complementary
Japan, Ireland, Italy, Mexico
Women - Tender; modest; concerned about the quality of life; relational-based; nurturing
Men - Assertive; Focused on material success; task-based accomplishments; complementary sex roles; ambitious
Feminine
Social gender roles as fluid and overlapping
Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Costa Rica
Men and Women - modest; tender; caring; relational-based; concerned about the quality of life; work-family balance above work performance; flexible/overlap in sex role norms
Small Power Distance vs Large Power Distance
Inequalities in all societies; PD is the extent to which those with less power in a society expect and accept being treated unequally
Small
Value equal power distributions; Equal rights (few honorifics); equitable rewards/punishments based on performance
Austria, Israel, Norway
ex:
Children contradict parents & speak their
mind; democratic decision-making in
families
◦ Work space as relationship-oriented,
decentralized w/ democratic leadership
Large
Accept unequal power distributions; hierarchal rights (deference/honorifics): Punishments and rewards based on status, age, rank, title
Mexico, Venezuela, Arabic Countries
EX:
Children obey parents, punished for
contradicting; parents/grandparents
assume decision-making role for family
Work spaces as task-oriented, centralized
w/ autocratic leadership
Weak Uncertainty Avoidance vs Strong Uncertainty Avoidance
Extent to which a culture does not mind conflict and uncertain situations and extent to which they avoid them
Weak
Encourage risk-taking (tolerance for innovation and counter behaviors; exploration); conflict approaching modes
U.S., Hong Kong, United Kingdom
Conflict viewed as a natural part of org. productivity
Fam. roles and behavioral expectations actively negotiated
children given lat. to explore own values/morals
Strong
Prefer clear procedures (resistance to deviance/innovation; defined roles; strong rules/laws to counteract uncertainties in social interactions); Conflict-avoiding Behaviors
Greece, Portugal, Japan, El Salvador
Org. seeks to eliminate conflict and job descriptions essential
Fam. roles clearly established and family rules expected to be followed
Father Knows Best Analysis
Hofstede scores US (Cultural system level) in particular ways concerning its “cultural values dimensions/patterns“
Additional Value Orientation Patterns
Kluckhohn & Strodtbeck (1961) - Universal questions that humans continuously or continuously seek to answer. 3 questions
Meaning
Question 1
What do people consider meaningful in their everyday activity?
Doing - focusing on achievement-oriented activities
Mid-class African American - Compact racism through activism and social achievements
Asian American and Latin X American - Work hard, make money to fulfill obligations toward fam
European American - Focus on tangible accomplishments
Being - Living with emotional vitality and being relationally connected with significant others
African and African American - Attach positive meanings to a sense of aliveness, culture infused with a belief in more to life than sorrow and a renewal of joy
Latin X American - Enjoy the moment to the fullest - share celebrations and recreation with friends/family
Being-in-Becoming - Self in development - achieving human or spiritual potential
Indigenous American - Focus on spiritual self-renewal/personal enrichment more than material gains and losses
Destiny
Question 2
What is the relationship between people and nature?
Control (Mastering; Self-Over-Nature) - Middle class European American believe in mastery/control over nature and environment.
Harmony (Flowing; Self-With-Nature) - African, Buddhist, Asian American, Indigenous American, and Latin X cultures believe that what is human, nature, and spirit are all extensions of one another
Subjugation (Yielding; Self-Under-Nature) - Polynesian, Middle Eastern and Indian Cultures are fatalistic/submissive (fate and karma) attitude believing that nature and supernatural as forces beyond human control to be respected.
Internal Locus of Control - I can change the outcome
External Locus of Control - The outcome is out of my hands
Time
Question 3
Is the temporal focus in the culture based on the future, present, or past?
Future-Oriented - Planning for desirable short-to-medium-term development and setting clear objectives to realize them
Middle class European Americans
Present-Oriented - Valuing her and now, especially current interpersonal relationships
Latin X American
Past-Oriented - Honoring ancestral ties and respecting wisdom of elders
Traditional Asian Immigrants and Indigenous Americans
Past-Present - past looms as a large historical canvas to understand present and to strategically plan the future
African American and French (Vietnamese American - Buddhist precepts of karma and rebirth)