Endocrine Systems
Endocrine - ductless glands
Types of glands :
Endocrine glands- secrete their hormones directly into the bloodstream
Secreting cell ones to the target cell
Exocrine glands - send chemical substances ( tears, sweat, milk, saliva) via ducts to the outside of the body
Endocrine Disorders
Hypo secretion and hyper secretion of hormones result in several well described disorders
Endocrine System
A chemical communication system that controls many body functions
glands that produce the hormones to regulate the body’s activities
Controller in your body
Works w/ nervous system to regulate
Sends messages using chemicals
Several glands located throughout your body
Homeostasis
when the endocrine system helps maintain a constant internal environment in the body
negative feedback loop - reverses direction of change
Positive feedback loop - amplifies change
Prostaglandins
Usually produced in tissue and only go a short distance
Often called tissue hormones or paracrine glands Types
Made at sites of tissue damage or infection
causes pain or fever
Healing process
Thromboxane - creates blood clot to try to heal
Pituitary Gland
connected to the anterior and posterior pituitary lobe
Anterior lobe is controlled by the hypothalamus hormones
hypothalamic releasing and hypothalamic inhibitory hormones
GnRh (gonadotropin releasing hormone) = FSH/LH (follicle stimulating hormone and Luteinizing hormone) target organ is gonads (male - testes / female - ovaries)
CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) = ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) target organ is adrenal cortex
TRH (Thy-rotropin releasing hormone) = TSH (thyroid- stimulating hormone) target organ is Thyroid
PHR + (Prolactin inhibiting hormone) / Dopsmine - = PRL (Prolactin) . Target organ is mammary gland (milk making hormone)
GHRH + (growth releasing hormone) / Somatostatin - = GH (growth hormone) target organ liver and all body
Posterior lobe is controlled by the hypothalamus nerve signals
hypothalamus makes and releases hormones of the posterior pituitary
posterior lobe stores tow hormones - ADH and oxytocin
Releases hormones when neurally stimulated by hypothalamus
ADH - antidiuretic hormone
also known as vasopressin
target organ - kidneys
Retains urine and reduces output
Regulates blood pressure
Anti diabetic hormone
Oxytocin
Contractions
Produces milk
Emotional bonding hormone
A love hormone
Protected by the sphenoid bone And in between the sella turcica
Hypothalamus significantly influences the pituitary gland
Hypothalamic- Pituitary - Thyroid Axis
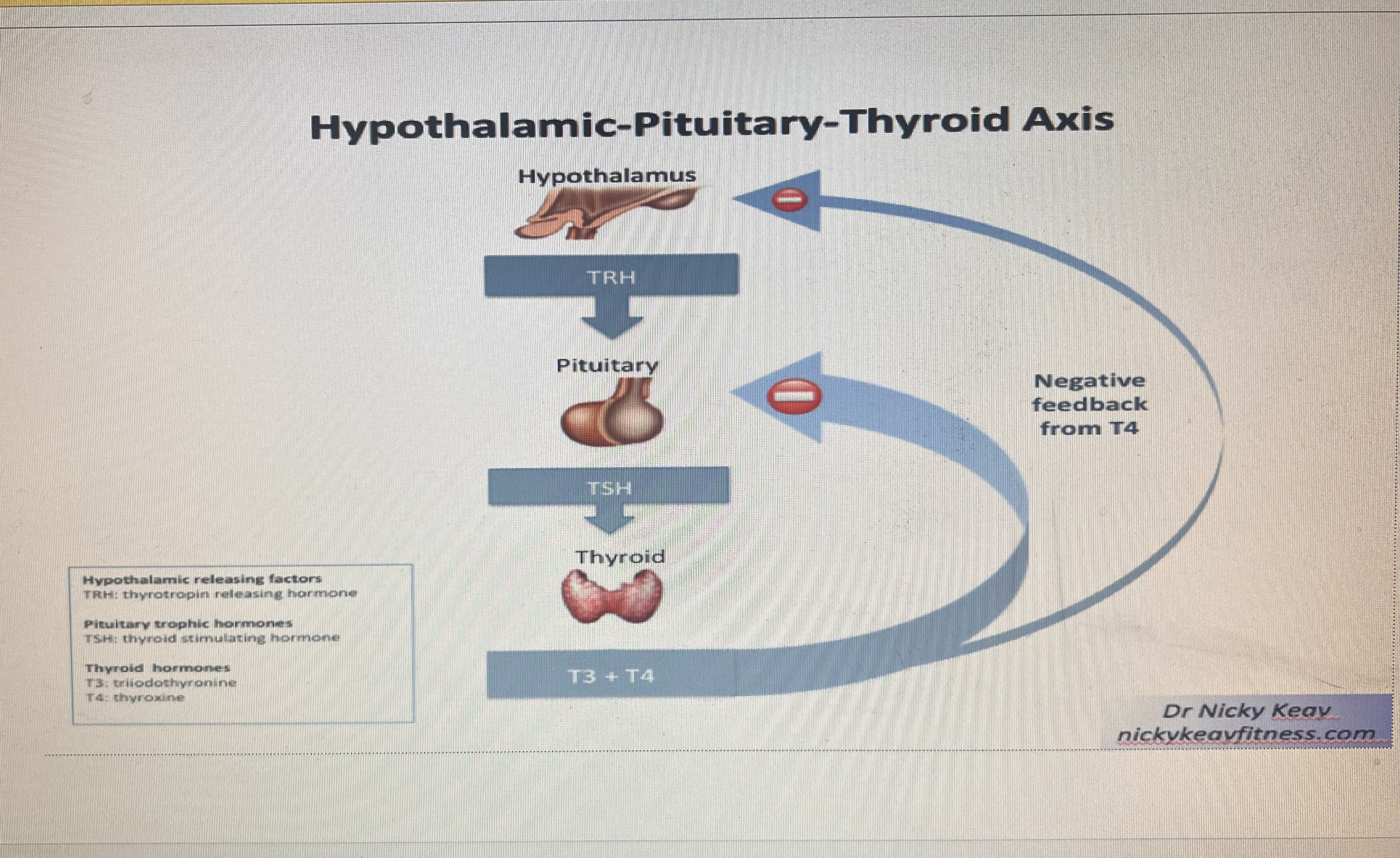
Thyroid Hormones
thyroid is located in throat
Functions
helps in regulating metabolic rate
Controls the heart rate
Helps lower body temp
Helps digest
Affects immune system
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroxine (T4) 90%
Triiodothyronine (T3) 10%
Calcitonin
protects the bones, needs to be level amount if too low bones will be too week if too high bones will become to big
Parathyroid glands - releases PTH (parathyroid hormone) promotes osteoclasts (bone eating activity)
Calcitonin - deposits calcitonin on bones and increases bone strength
Adrenal glands
above the kidneys
Two layers of adrenal glands : cortex and medulla
Adrenal Cortex (outer layer of the adrenal glands)
Zona glomerulosa = mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
Zona Fasciculta = glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone)
Zona reticularis = androgen (hydroepiandrosterone)
innermost layer of the adrenal cortex
Secretes androgen which play a early role in development of reproductive organs
in women they may stimulate sexual drive
Adrenal Medulla (inner part of adrenal glands above)
Adrenal medulla = catecholamines (epinephrine (ER) , norepinephrine (NR))
epinephrine is also known as adrenaline
Responds quickly to stress because of nerve impulse
Produce body’s fight or flight response
Increased BP
Increased blood supply
Increased heart rate
Increased glucose
Aldosterone
controls blood pressure and blood volume
Loves sodium and hates potassium
Retains sodium and water which raises the blood volume and blood pressure
Stress response -
Stress trigger - stress activates the brain
The brain signals the pituitary gland which releases ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
ACTH travels to adrenal gland making them release cortisol and adrenaline
cortisol breaks down muscle protein
Forms gyclcogen (glycogenesis)
too much cortisol will increase blood glucose
It is antiflammatory
Anti immunity
The hormones will trigger some affects
increased blood pressure
Sweating
Increased breathing rate
Accelerated heart rate
Tunnel vision
Digestion slows down
Alpha cells : secrete glucagon (raises blood sugar)
Beta cells : secrete insulin (lowers blood sugar)
eating - blood sugar increases
Exercise - blood sugar decreases
type 1 diabetes
young (less than 35)
Rapid symptoms
Not obese
Body doesn’t produce insulin
Managed by insulin injections, diet, and exercise control
Type 2 diabetes
older
No symptoms early on
Obese
Insulin can be normal or abnormal, but body cells are resistant to insulin
Managed by oral medications, insulin injections, diet, and exercise
Thymus Gland
triangular organ found in lungs
Function
produces thymus in
Responsible for maturation of t-lymphocytes in childhood
Protects the body throughout life from pathogens (germs)
ADH and Oxytocin are produced by cell bodies located in the hypothalamus but are released in pituitary gland making
Pineal Gland
pine nut sized
“The third eye”
Secreting melatonin
reacts to dim light and causes sleep
Increased at nighttime and decreases during the day