Light: Reflection and Refraction
Light and Vision: Light is a form of energy that makes things visible. We see objects because they reflect light into our eyes.
Reflection of Light: When light bounces off a surface, it's called reflection. Mirrors are highly reflective surfaces.
Laws of Reflection:
The angle of incidence (incoming light) equals the angle of reflection (outgoing light).
The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface) all lie in the same plane.
Types of Mirrors:
Concave Mirrors: Curve inward, can create real or virtual images depending on object position. Used in telescopes, headlights, and makeup mirrors.
Image formation:
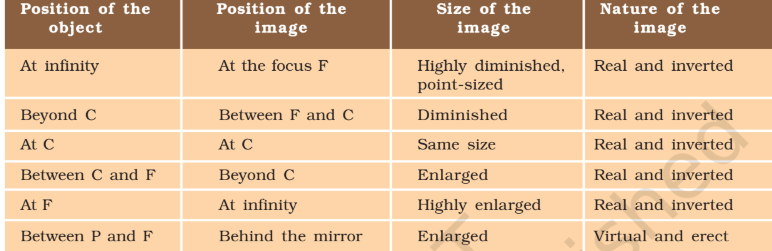
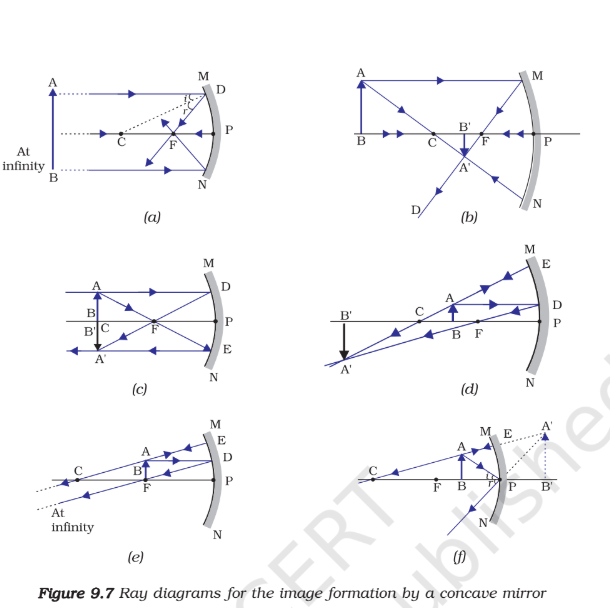
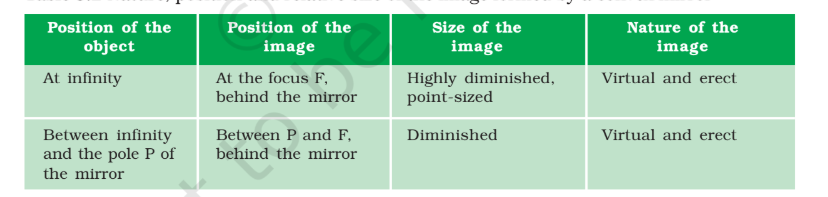
Convex Mirrors: Curve outward, always create virtual, upright, and smaller images. Used for security mirrors, car side mirrors for a wider field of view.
Image formation:
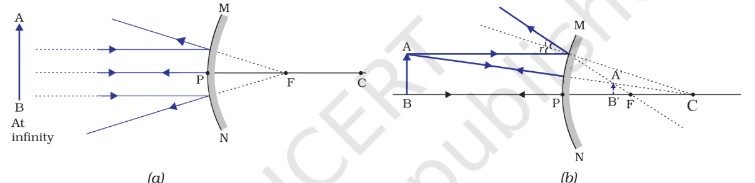
Refraction of Light: The bending of light as it passes from one medium (like air) to another (like water) is called refraction. This happens because light changes speed in different media.
Laws of Refraction (Snell's Law):
Similar to reflection, the incident ray, refracted ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of media.
Refractive Index: A measure of how much a substance can bend light. Higher refractive index means light slows down more and bends more.
Lenses: Lenses are curved pieces of glass or plastic that refract light to form images.
Types of Lenses:
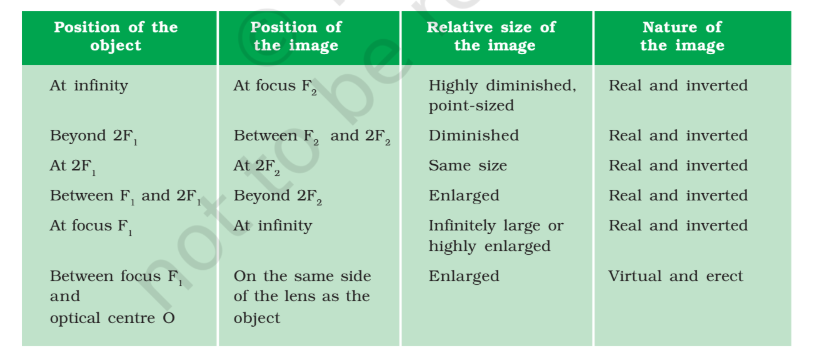
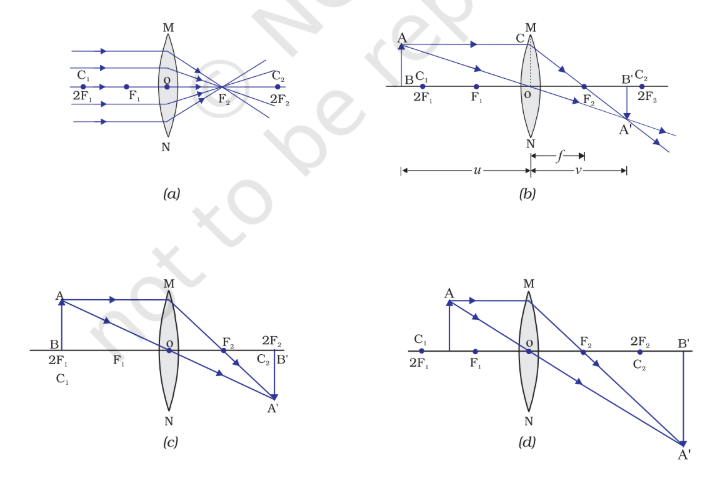
Convex Lenses: Thicker in the middle, converge (bring together) light rays. Used in magnifying glasses, cameras, and eyeglasses for farsightedness.
Image formation:
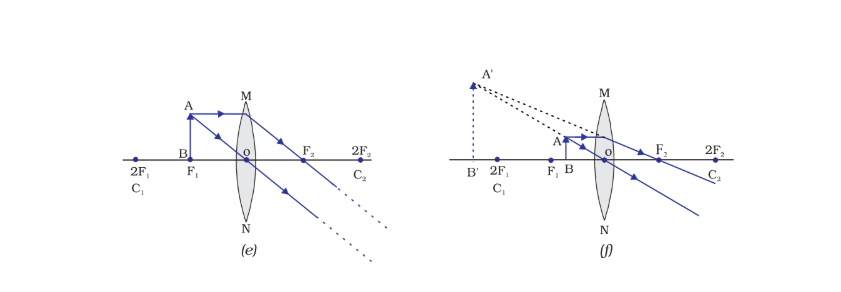
Concave Lenses: Thicker at the edges, diverge (spread out) light rays. Used in eyeglasses for nearsightedness and some telescopes.
Image formation:F
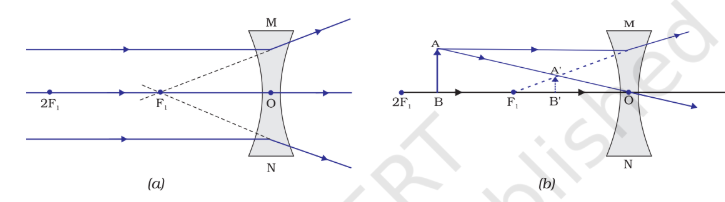
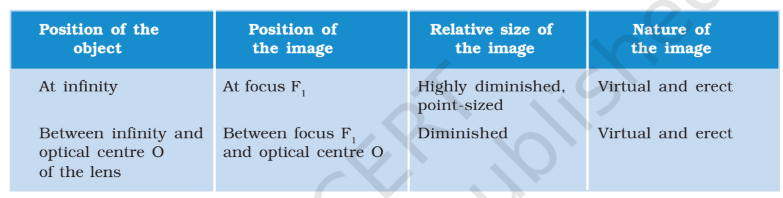
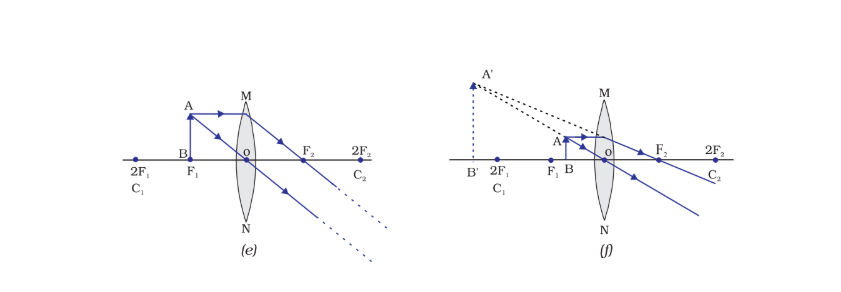
Lenses form images based on the object's position and the lens's shape. Images can be real or virtual, upright or inverted, magnified or diminished.
Power of a Lens: Measured in diopters, it indicates how strongly a lens converges or diverges light. It's the reciprocal of the focal length (the distance between the lens and where it focuses parallel rays).
FORMULAS:
Mirrors:
Mirror Formula: (Very similar to the lens formula)
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
Where:
f = Focal length of the mirror
v = Distance of the image from the mirror
u = Distance of the object from the mirror
Magnification (m):
m = hᵢ/h₀ = -v/u
Where:
m = Magnification
hᵢ = Height of the image
h₀ = Height of the object
Lenses:
Lens Formula (Thin Lens Equation):
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
Where:
f = Focal length of the lens
v = Distance of the image from the lens
u = Distance of the object from the lens
Magnification (m):
m = hᵢ/h₀ = -v/u
Where:
m = Magnification
hᵢ = Height of the image
h₀ = Height of the object
Power of a Lens (P):
P = 1/f (in diopters)
Where:
f = Focal length of the lens (in meters)