Week 9 Vaginal DDS
Vaginal FloraVaginal and Urethral Drug Delivery Systems
Importance of maintaining a healthy vaginal pH (3.8-4.5), similar to that of a tomato.
Vaginal flora protect against reproductive system infections.
Health Statistics
42% of women report never being taught vaginal health care.
45% of women use soaps, which can disrupt natural pH.
Friendly Bacteria
L. reuteri RC-14® & L. rhamnosus GR-1®: Support vaginal health and balance flora.
Imbalance in Flora
Over 50% of women with bacterial vaginosis experience recurrent infections.
Learning Objectives
Describe the physiology of the vagina and urethra.
Explain physiological challenges to vaginal/urethral drug delivery.
List ideal physicochemical properties for vaginal drug delivery systems (DDS).
Identify ideal formulation factors for vaginal DDS.
Compare different types of vaginal DDS.
Discuss special patient conditions benefiting from vaginal/urethral routes.
Physiology of the Vagina
Vaginal Structure
Components: Ampulla, Isthmus, Infundibulum, Fimbriae, Ovary, Ovarian ligament.
Uterine Layers
Perimetrium: Outer layer of uterus.
Myometrium: Muscular middle layer.
Endometrium: Inner lining.
Physiological Factors for Vaginal DDS
Dimensions
Length: 8-10 cm; Width: 2 cm.
Fluid Volume
Vaginal fluids: 2-3 mL.
Vascularization
High vascular supply aiding absorption.
Surface Area
Increased by rugae and microridges; varies cyclically with hormones affecting drug dissolution and permeability.
Thickness of Epithelium
Thickness varies between menstruating (3.5-4.5) and non-menstruating (6-7) women; also affects buffering capacity.
Enzymatic Activity
Generally low, influencing drug metabolism.
Drug Transport
Primarily passive transcellular transport.
Physicochemical Factors for Vaginal DDS
Drug Molecular Weight
Low molecular weight (< 1,000 Da) is preferred for absorption.
Lipophilicity
Lipophilic drugs are absorbed more effectively than hydrophilic drugs.
Formulation Factors for Vaginal DDS
Mucoadhesives
Increase contact time and prevent dripping, critical due to lack of sphincters in the vagina.
Surfactants & Co-solvents
Aim to dissolve drugs slowly to avoid rapid leakage, which causes loss of dosage form.
Dissolution pH
Menstruating women: acidic; non-menstruating women: neutral.
Volume of Administration
Low
Dosage Forms for Vaginal DDS
Types
Suppositories: PEG bases.
Ointments, Creams, Gels: Potentially messy.
Vaginal Tablets.
Vaginal Rings: For sustained release.
NuvaRing®
Description
Non-biodegradable, flexible contraceptive vaginal ring.
Contains 0.12 mg etonogestrel and 0.015 mg ethinyl estradiol; releases drugs by diffusion.
Usage
Worn for 3 weeks; 1-week removal required.
Total drug content: 11.7 mg etonogestrel, 2.7 mg ethinyl estradiol.
Disposal
Must be discarded in waste, not in toilet.
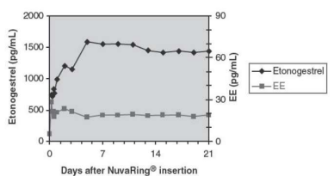
Pharmacokinetic Profile of NuvaRing®
Drug Concentration
Profiles for etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol during 3-week use.
Insertion and Removal of NuvaRing®
Insertion Steps
Remove from packaging, fold and insert gently into the vagina. Position is not crucial for effectiveness.
Removal Steps
To be done 3 weeks post-insertion; dispose responsibly.
Advantages of Vaginal DDS
Benefits
Large surface area, rich blood supply, low metabolic activity, and high permeability.
Easy administration and prolonged retention possible, enabling zero-order release.
Limitations
Effective mainly for potent molecules; may irritate vaginal tissue; prone to leakage; epithelium changes with hormones; not applicable to half the population.
Urethral DDS
Anatomy Overview
Male urethra ~20 cm; Female urethra ~4 cm.
Functionality
Site of action for urine excretion and conditions like catheter infections.
Medicated Urethral System for Erection (MUSE®)
Description
Trans-urethral suppository delivering alprostadil to erectile tissue.
Formulated in a pellet for easy insertion via an applicator.
Store in fridge
Advantages and Disadvantages of Urethral DDS
Advancements
Offers local effects.
Challenges
Unpopular and unsuitable for systemic delivery; requires different sizes for administration.
Review Quiz**
Determine if a weak base drug will be absorbed systemically or retained locally in the vagina based on the patient's reproductive status.
 Knowt
Knowt