Unit 5: Agricultural Processes and Patterns
Types of Agriculture:
Intensive: requiring higher amounts of labor and investment
urban farming, greenhouse
Extensive: not requiring high amounts of labor and investment
larger pieces of land
uses natural fertilizer and climate
Commercial: Agriculture for profit and commercial selling
Subsistence: Agriculture to feed oneself, family, or village
Monocropping: the growth of a singular crop at a time
Irish Potatoes, Sri Lanka tea
Types of Agriculture II:
Market gardening: food producing plants grown in small plots of land
apples, lettuce, tomatoes
intensive, commercial
MDCs
Plantation: specialize in a specific crop
bananas, coffee, rubber
intensive, commercial
LDCs: Latin America, Africa, Asia
Mixed Crop/ Livestock: mixture of crop growing and livestock.
grains to feed animals, cash crops for money
extensive, commercial
MDCs, LDCs
Shifting Cultivation: short periods of cultivation are followed by relatively long periods of fallow
slash and burn
extensive, subsistence
SE Asia, Sub-Sahara Africa, South America
Nomadic Herding/ Pastoral Nomadism: Nomads herd animals to places where they can graze
extensive, subsistence
Uses little technology and lots of land
Nordic, East Africa, Saudi Arabia
Ranching: raise herds on large plots of land
extensive, commercial
South America, US, AUS
Wet Rice Dominant: Large amount of rice is grown in small area
intensive, subsistence
East, Southeast, South Asia
Grain Farming: grains are grown in large farms to make a profit
monocropping, extensive, commercial
USA, North EU, China, India
Agricultural Terracing:
Steps are built to farm more efficiently
environmental possiblism
intensive agriculture
Settlement Patterns:
Linear:
settlement along the river or road
access to transportation
France, Spain

Clustered:
settlement in close proximity
walk to farmland
used for defense
Europe

Dispersed:
isolated, spread out
privacy: individual land ownership
US: Westward expansion

Rural Survey Methods:
help divide up ownership of land and agriculture spaces
Metes and Bounds:
short distances
landmarks
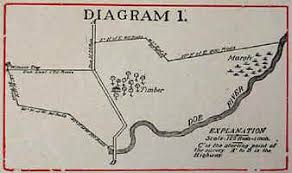
Township and Range:
Survey methods
Grid system
remote sensing
Long lot:
relationship to river

Agricultural Revolution(s):
First Agricultural Revolution (Neolithic Revolution):
Humans switched from hunter-gatherers to farmers
grew plants and domesticated animals
started settlements rather than be nomads
began independently around the globe
Second Agricultural Revolution:
Started by Industrial Revolution
Introduced new technology and techniques
Railroads & shipping canals for transportation of food\
Mechanized farming
Moved to stage 2 of DTM
Third Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution):
Scientists learned how to genetically engineer plants to produce a higher amount of field
High-yield seeds, chemicals, mechanized farming
Pros: Higher amounts of food, increased productivity
Cons: Pollution, Health risks
Von Thunen Model:
- 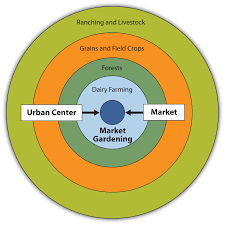
Utilizes bid-rent theory
Town/ Market: where fresh goods are sold
1. Intensive Agriculture & dairy:
produce perishable goods closer to market
dairy, fruits, veggies
2. Forest:
Timber for fuel and buildings
closer to market to offset high transit costs
3. Grain Crops:
extensive
crops don’t spoil as fast
4. Ranching/ Pasture:
extensive
crops don’t spoil as fast
5. Wilderness:
too far from market to profit
Global Farming:
Global supply chain: the network of individuals, organizations, resources, activities and technology involved in the production and sale of a product worldwide
Export commodity: a product that a state produces for exports rather than consumption
cocoa in cote d’ivoire
Commodity chain: A linked system of processes that gather resources, convert them into goods, package them for distribution, disperse them, and sell them on the market.
Inputs, Production, Processing, Marketing, Consumption
Economies of Scale: Agribusinesses can produce more for cheaper
puts agribusinesses in the leading position of sales
results in less family owned farms
Environmental Effects:
Land Cover Change: Humans change what an area of land is used for
land → urban farmland
United States
Desertification: fertile land becomes desert from drought or excessive agriculture
less fertile land
Africa
Soil salinization: increase in number of salt in the soil
lowers productivity of crop plants
Egypt, Argentina
Slash and burn agriculture: cutting and burning of plants in forest to create a field
soil fertility declines after a few years
weeds increase
Terracing: changing land to meet needs (creating steps)
reduces soil erosion
more cultivable land
SE Asia, Andes mountain
Deforestation: clearing of forested land
lost forests
Amazon Rainforest, SE Asia
Individual Food Choice:
Sustainable agriculture:
intended to satisfy human needs, minimize environmental impacts, promote fiar wages & worker treatment
Community supported agriculture:
prepaid subscriptions to receive food directly from farmers
MDCs
Urban farming:
intensive practices support growing city populations
growing on small plots in a city
Fair Trade:
a program that supports decent conditions for working & better wages
products cost more money
Farmed in LDCs, sold in MDCs

Food Insecurity: lack of regular access to enough safe & nutritious food
more common in LDCs, can happen anywhere
Food deserts: areas with limited access to fresh, nutritious foods
lack of stores or transportation
often in low-income areas
Women in Agriculture:
MDCs:
Few women working in agriculture
Due to increased opportunity for women, leading them to other jobs
LDCs:
Many women working in agriculture
rely more on subsistence and have less opportunities due to low education