Biology Unit 11 - Evolution
EVOLUTION
What is evolution?
slow adaptations to someone/something, so that they can survive longer
effective natural selection
Who is Darwin?
he studied genetics and animals; studied how traits were passed on
he studied on a isolated island so he could really notice the new traits in animals
DEVELOPMENT OF THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION
Scientific theory: a theory is an explanation of a set of related observations or events based upon proven hypotheses and verified multiple times by a detached groups of researchers
EVOLUTION DUE TO THE PROCESS OF NATURAL SELECTION
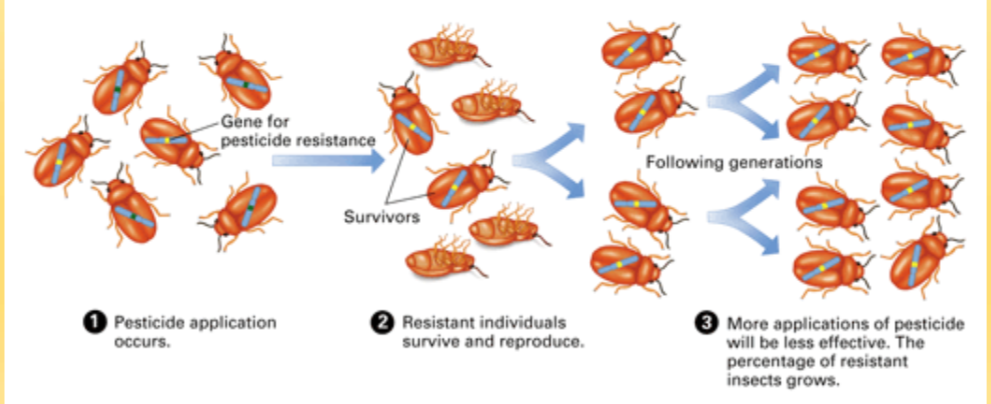
What does evolution due to the process of natural selection mean?
differences in survival and reproduction (you have to be able to reproduce to move along the trait) among individuals due to environmental conditions
What are some environmental conditions that could affect reproductive success?
climate, predators, habitat, food/water
NATURAL SELECTION IS THE MECHANISM OF EVOLUTION
interaction between environment & variability within population
variation by chance
natural selection NOT chance
FOUR POSTULATES OF NATURAL SELECTIONS
Variation
Heredity
Selective Pressure
Reproductive Success
POSTULATE 1 - VARIATION
individuals within a population vary in their traits
genetic variation
variations arise by chance from ransom mutations in DNA

POSTULATE 2 - HEREDITY
some of these variations/traits are hereditable
traits are passed from parent to offspring

POSTULATE 3 - SELECTIVE PRESSURE
a population can produce more individuals than can survive
resources are limited
individuals compete for survival
in each generation, some survive and others don’t

POSTUATE 4 - REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS
individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce over time.
evolution occurs as advantageous traits accumulate
natural selection selects for organisms that are best adapted to a particular environment (high fitness vs. low fitness)
survival and reproduction are NOT determined by chance; they are determined by the traits an organism possesses

EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
1 - GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION
Looks at geographical distribution of animals and plants.
Species that are closer in proximity to one another are usually more closely related.
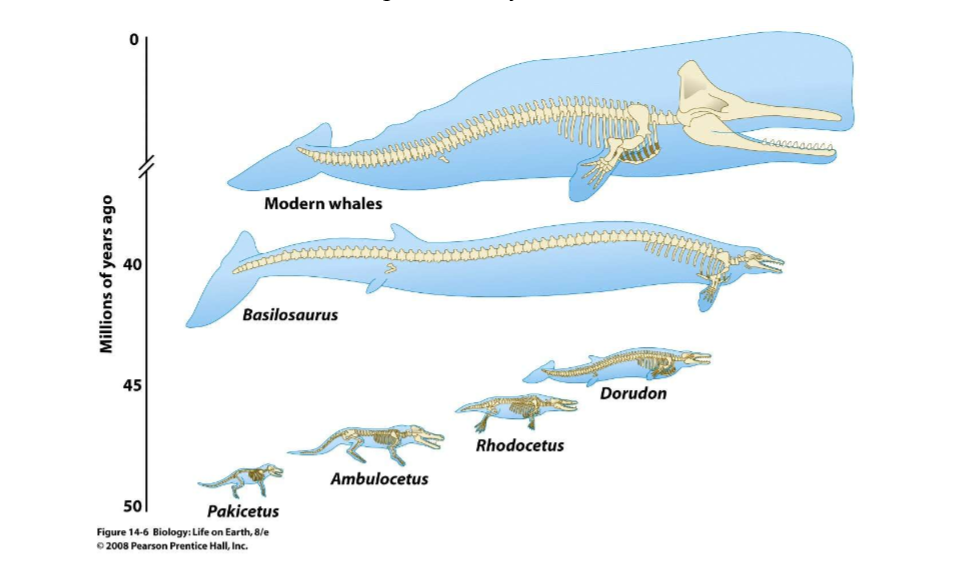
2 - FOSSIL EVIDENCE
fossil: any part or trace of an organism that is preserved in rock or sediments
fossils of an ancient species tend to be simpler in form than modern species
Transitional fossils - fossils or organisms that show the intermediate states between an ancestral form that of its descendants
3 - COMPARATIVE ANATOMY
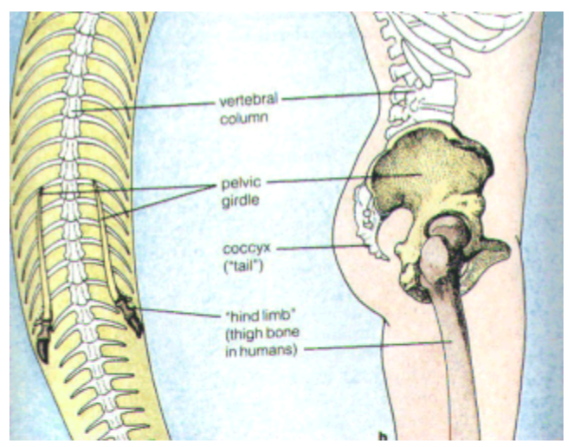
a. Vestigial Organs
remnants of structures that may have had important functions in an ancestral species, but have no clear function in modern descendants
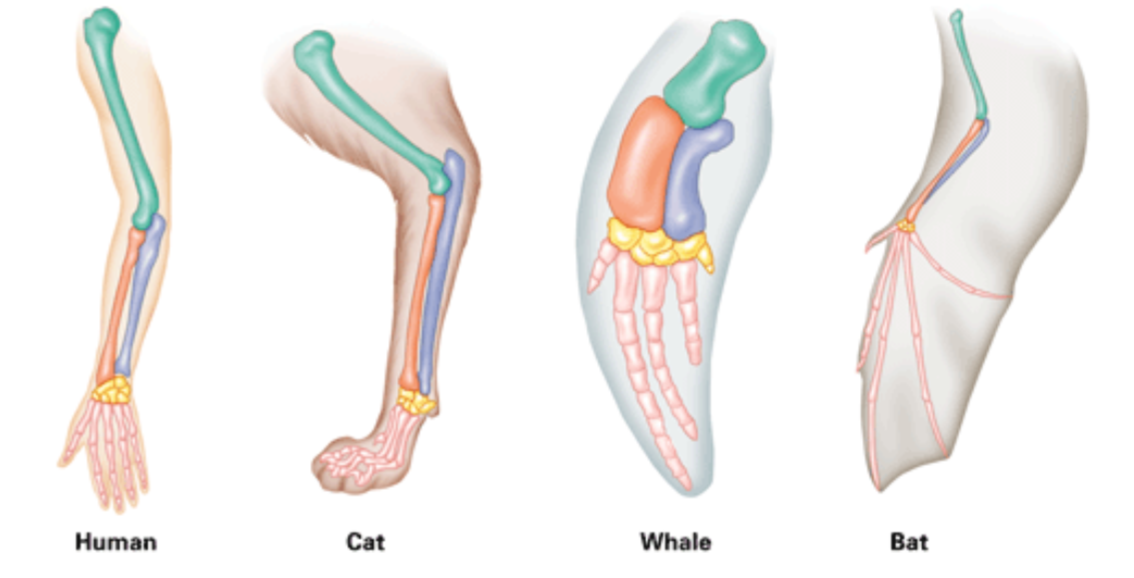
b. Homologous Structures
Body parts that have the same structural design and origin in different organisms
4 - COMPARATIVE EMRYOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT
More closely related species have embryological development that are more similar
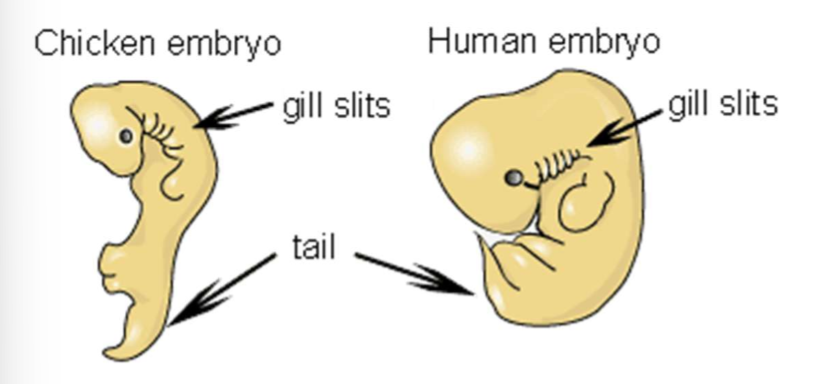
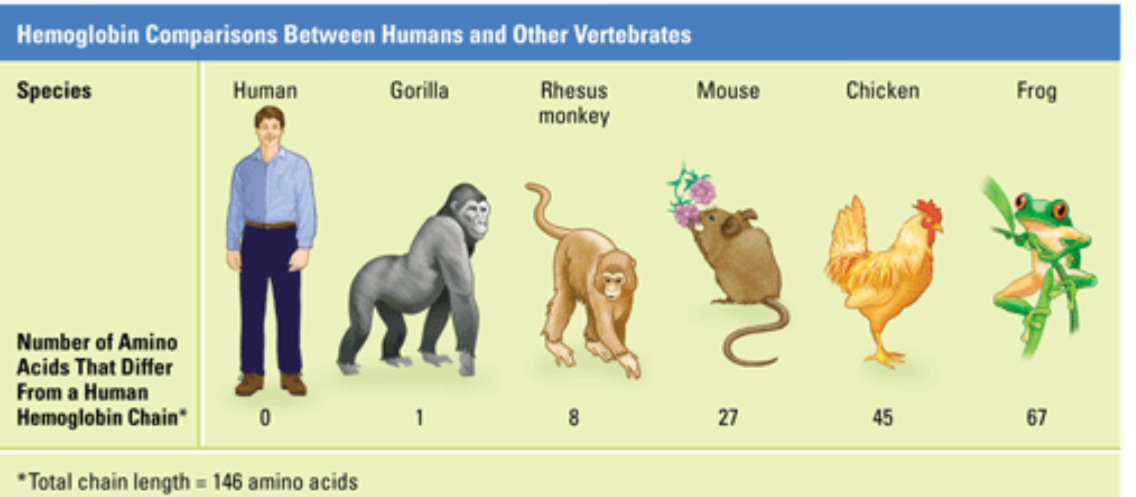
5 - CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR EVIDENCE
closely related species have similar molecular sequences

PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION
PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION
(what evolution looks like)
divergent evolution
one common ancestor evolves into two or more species
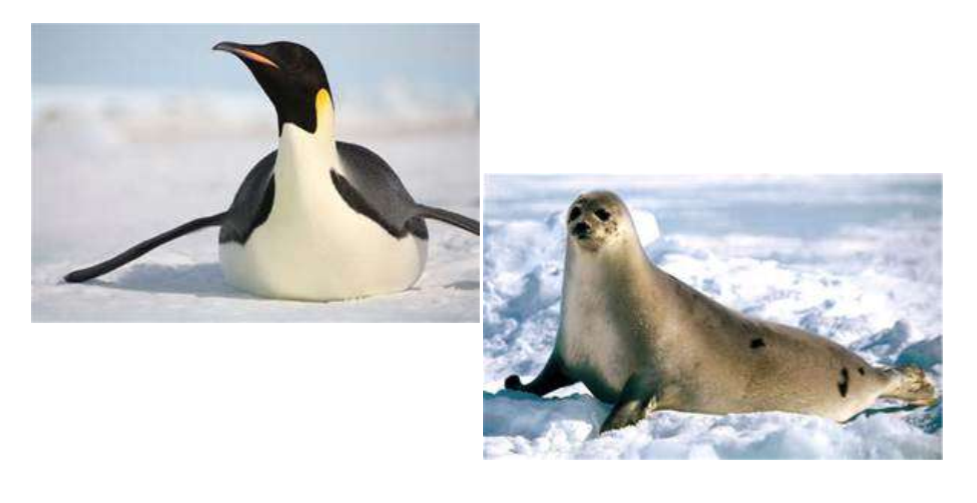
convergent evolution
two distinct species become more similar over time due to similar environments
coevolution
two species evolve in response to one another
EXAMPLES
divergent evolution →

convergent evolution →

coevolution →

POPULATION EVOLUTION
HOW CAN GENETIC CHANGE HAPPEN IN A POPULATION?
Population Evolution
natural selection - not random
gene flow - random
immigration
emigration
genetic drift - random
bottleneck effect
founder effect
mutation
NATURAL SELECTION
successful organisms are those that have the best adaptations to their present environment
adaptations = “more fit”
example of natural selection → tuberculosis
variation → bacteria are resistant or not
heredity → resistant bacteria pass on trait
selective pressure → antibiotics
reproductive success → resistant trait allows bacteria to survive and reproduce over time so whole population can become resistant very quickly
GENE FLOW
the movement of alleles from one population to another
immigration adds alleles to a population → increase genetic variation
emigration removes alleles from a population → decrease genetic variation
GENETIC DRIFT
random changes in allele frequency that happens by chance
2 main causes of genetic drift:
bottleneck effect
the reduction of a population’s size that randomly changes the distribution of alleles
big decrease in genetic variation
founder effect
occurs when individuals that colonize a new area do not accurately represent the gene frequency of the parent population
MUTATION
increases variations in gene pool by randomly creating new alleles
could be good or bad
THE ROLE OF REPRODUCTION IN POPULATION EVOLUTION
the sexual reproductive strategy was the most successful because it allowed more genetic variation
the role of sex in evolution is too create more genetic variation/ diversity so a species can keep up with the environment
the red queen hypothesis is that species must adapt and create in order to survive
Advantage of producing Asexually:
you don’t have to find a mate
guarantied that you will reproduce
Disadvantages of producing Asexually:
no variation
accumulate mutation faster in a population
Advantages of producing Sexually:
variation in offsprings
weed out harmful mutations
Disadvantages of producing Asexually:
less efficient- more energy used
have to find a mate