Naturally occurring elements in the body
Major Elements = 96%
Oxygen 65%
Carbon 18.5%
Hydrogen 9.5%
Nitrogen 3.3%
Essential Elements = 4%
Calcium
Phosphorus
Potassium
Sulfur
Sodium
Chlorine
Magnesium
Trace Elements = 0.01%
Copper: hair and skin
Zinc: enzyme function
Iodine: salt good for thyroid
Iron: needed in transport O2 in blood
Cofactor: Allows enzymes to function
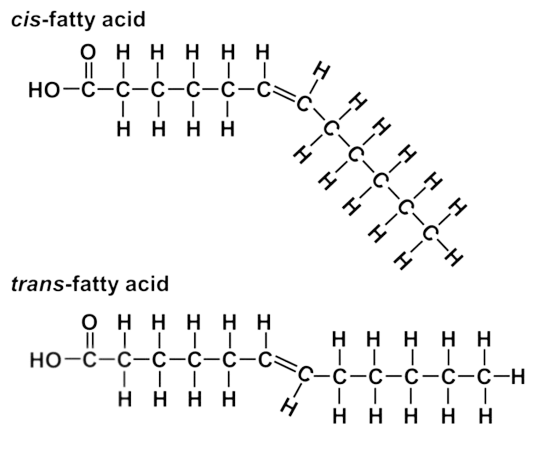
Poly unsaturated: plant fat with many double bonds
Monounsaturated: plant fat with one double bond
Dietary Fiber: need 6 g to feel full
Protein-rich: 5g-6g
BHT: to pressure food and persevere food. It gives things shelf life
Things to check on the nutrition label
Serving Size
Calories
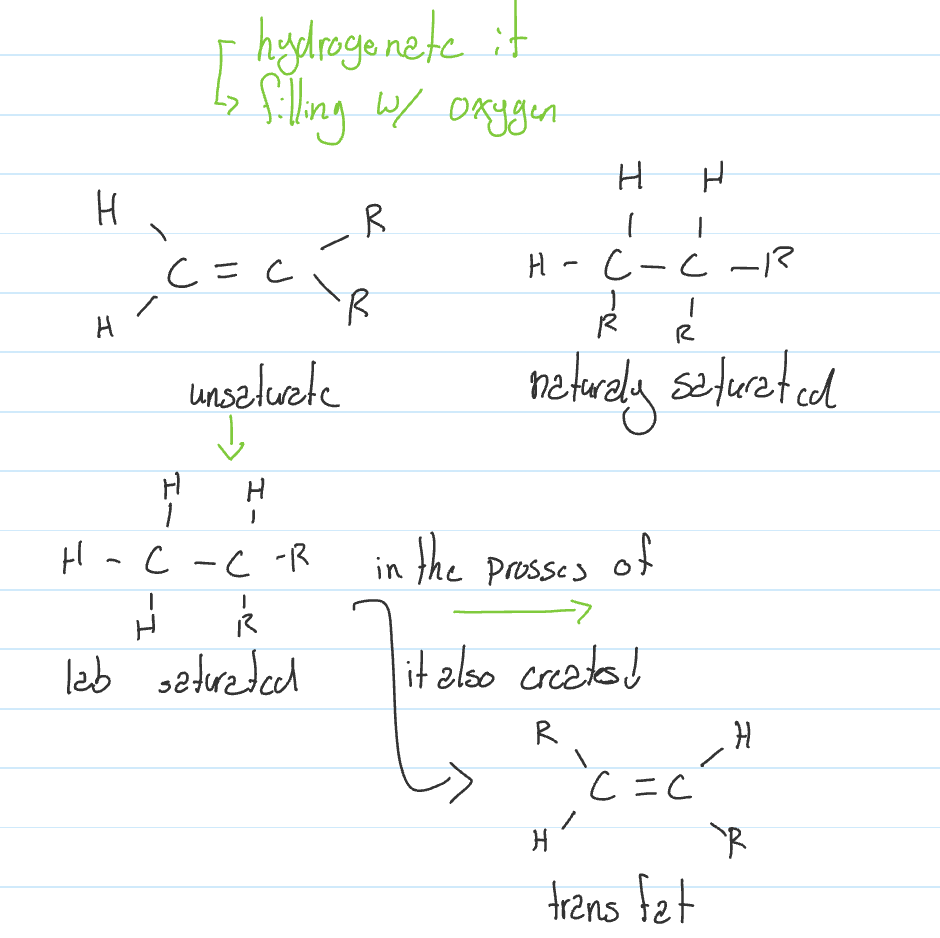
Trans fat; toxic & manmade
Radioisotope: an isotope of an element that has an unstable nuclei
Radioactive decay: the process by which an unstable nucleus rearranges itself
Electronegativity: Tendency of an atom to attract electrons
Partial charges: do not let electricity to pass through
Ionic bonds: Transfer of electrons between two unstable atoms
pH effect on the environment:
Acid Rain
Coral reef
Carbon
Element of life
Bonds:
Does not want to have charge; it only wants covalent bonds.
The double bond allows for fixed position
The single bond allows for rotation
Hydrocarbon properties:
Length
Double bonds
Branching
Rings
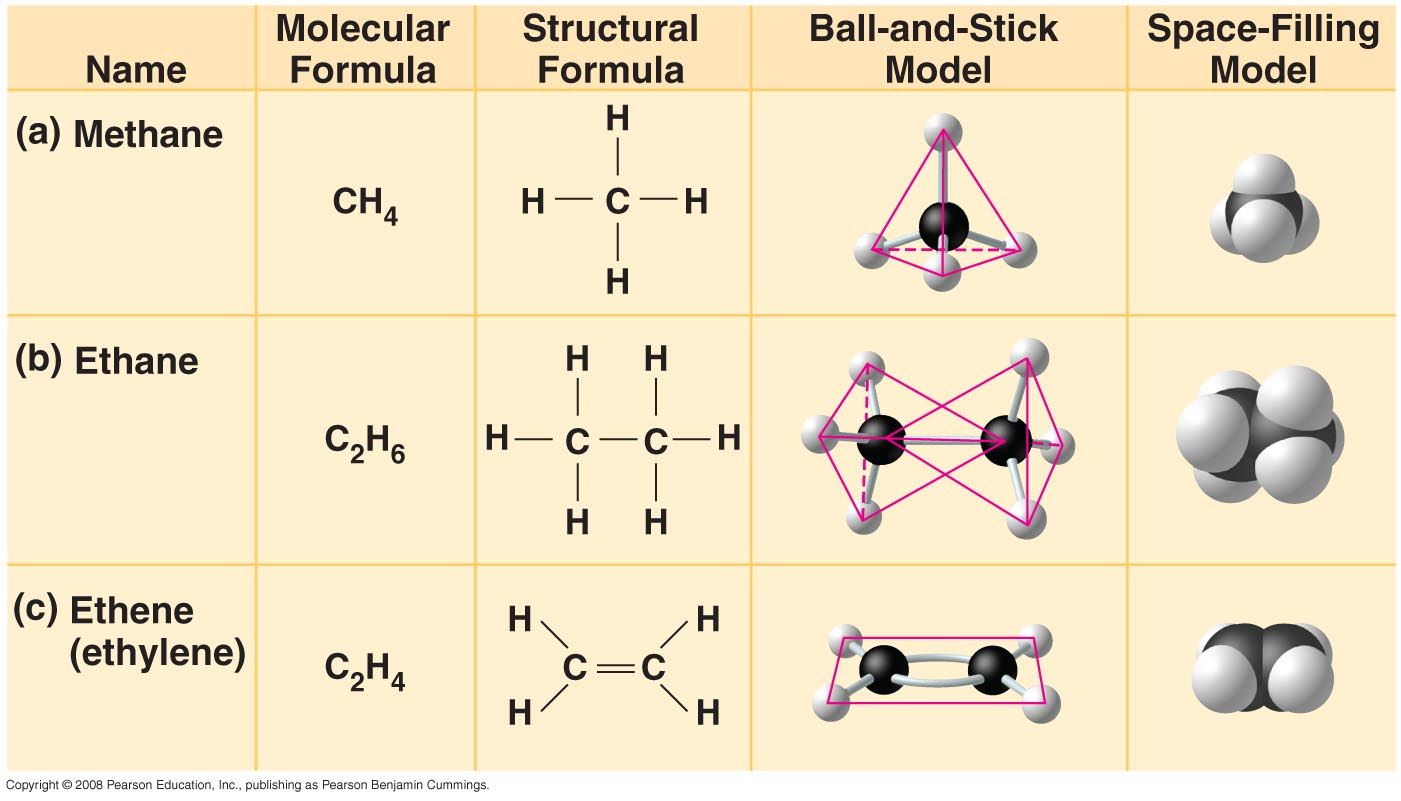
Methane: CH4
Ethane: C2H6
Ethene: C2H4
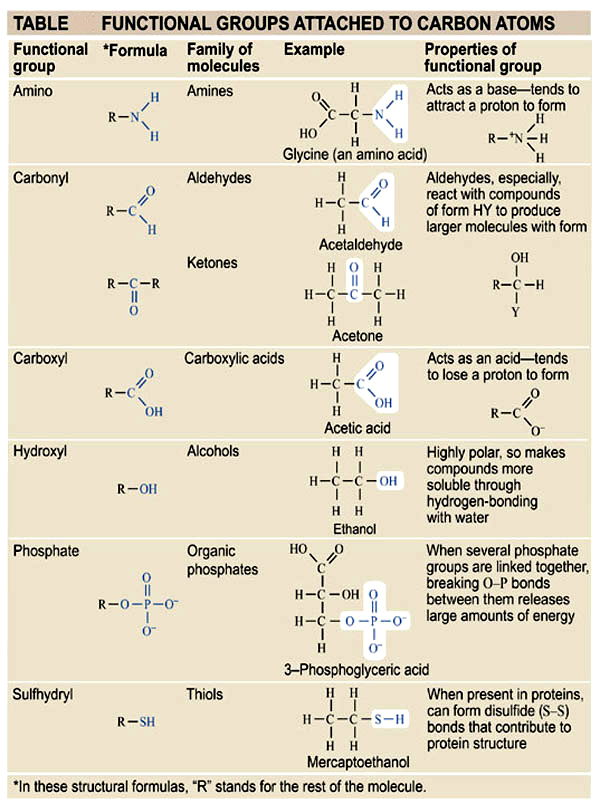
Most common Functional Groups attached to carbon
Methyl: R-CH3 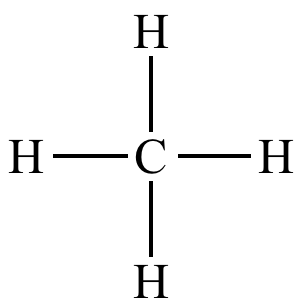
 Note
Note Studied by 19 people
Studied by 19 people Note
Note Studied by 49 people
Studied by 49 people Note
Note Studied by 14 people
Studied by 14 people Note
Note Studied by 164 people
Studied by 164 people Note
Note Studied by 7 people
Studied by 7 people Note
Note Studied by 22261 people
Studied by 22261 people Knowt
Knowt
