Assessment Methods for Selection & Placement
Assessment Methods for Hiring
The best predictor for future performance is past performance
ideally wed hire based on ^
but we rarely have that info
instead, we measure KSAOs as ‘predictors of criteria’
Psychological Tests
test: a standardized series of problems or questions that assess KSAOs
1. ability
2. psychomotor ability
3. personality
4. emotional intelligence
5. integrity
6. interests
Testing Formats
Speed vs Power
speed tests have strict time limits (e.g. typing tests, math attack)
Power tests, time is not a factor (e.g. first exam)
Individual vs Group
Individual tests require 1-1 test administration (e.g. driving tests)
groups test can be taken by multiple people at once (e.g. our fist exam, SAT)
Paper ‘n’ Pencil Tests
test takers respond to quesitons on paper (or computer screen)
e.g. fill-in-blank, multiple choice
Performance Tests
involves manipulating an object/equipment to test applied skills
e.g. flight simulators, computer programming
Key Issues to consider when using tests for hiring
Characteristics of good tests revisited:
how well does it predict job performance: criterion validity '
is the test free from random error: reliability
will the benefits of testing exceed the cost”: practicality
will the test disadvantage anyone: fairness
does the test effectively capture individual differences: sensitivity
Combining multiple tests
incremental validity: the additional variance explained in an outcome by adding a predictor
ex) interview scores explain roughly 18% of total variance in job performance
that leaves around 82% unaccounted for
The Predictive validity of different assessment methods for job performance
results shown here here based on many meta-analyses
validity estimate = average correlation with job performance
although this is a very informative table, it does not show differences across jobs, organizations, contexts, etc.
General Cognitive Ability Tests
a common, relatively easy-to-adminster selection measure
cognitive ability is important for most jobs, but is a stronger predictor of performance in more complex jobs
began with Army Alpha and Beta (remember the WWI history)
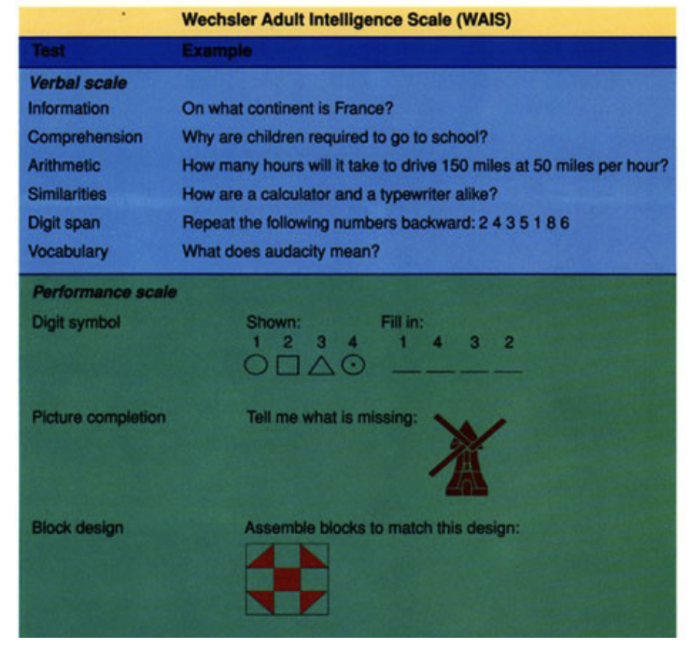
ex): WAIS, Wonderlic, Ravens Progressive Matricies
Issues with General Cognitive Ability Tests
group differences in scores across racial and socio-economic backgrounds
racial differences smaller in recent years, but still exist
test scores related to years of formal schooling and test prep
test-taking wiseness
On measuring ‘innate’ ability
you cant measure innate intelligence any more than you can measure the innate height of a stalk of corn
cognitive test scores are products of genes + enviornment
Specific cognitive ability tests
tests spedific abilities that are required on the job (vs. general capacity to learn)
more similar to job knowledge
r= .30 to .40 with performance
ex)
mechanical (bennet mechanical test)
spatial (Space relations test)
clerical (minnesota clerical test)
Psychomotor Ability Tests
assess speed and accuracy of mtor and sensory coordination
movement, vision, hearing, etc
e.g. Purdue Pegboard
r= .30 to .40 with performance
but only in jobs that require these abilities = job analysis
 Knowt
Knowt