W3 L3: The microbiology of milk and honey
What is milk?
- Emulsion of fat & water containing dissolved carbohydrates, proteins, vits & minerals - that are produced in/ transported to mammary gland to provide complete nutrition & immunological protection to newborns
Components of milk:
- Water ~ 87%
- Protein ~ 3.5 %
- Fat ~ 4%
- Lactose ~ 4.7%
- Minerals ~ 0.8%
Water activity (aw) → 0.99
pH → 6.4-6.6
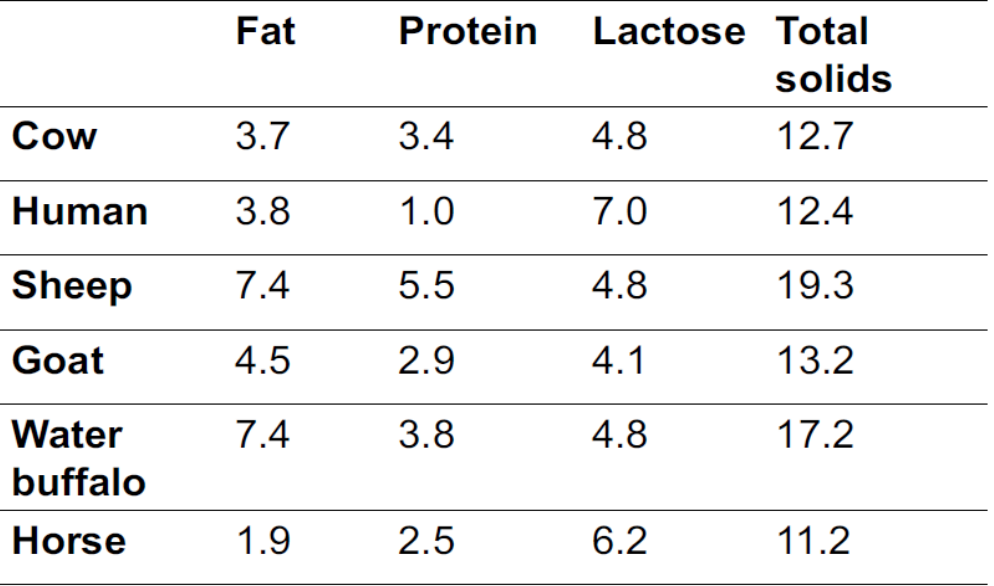
How is milk produced? lactation
Following digestion necessary nutrients are absorbed from intestines into blood stream
Nutrients are delivered to udder (high supply of blood) → allows large vol. of milk to be produced
Nutrients used to produce accumulated milk, then secreted
Udder is highly developed & modified sweat gland - in cattle is composed of 4 individual glands → quarters
Interior of each quarter comprises → teat cistern, gland cistern, milk ducts & glandular tissue
Glandular tissue→ contains millions of microscopic sacs - alveoli
- Each alveolus is lined w/ milk-producing epithelial cells & surrounded by muscle cells that contract to squeeze milk into milk ducts when stimulated during milking (calf sucking)
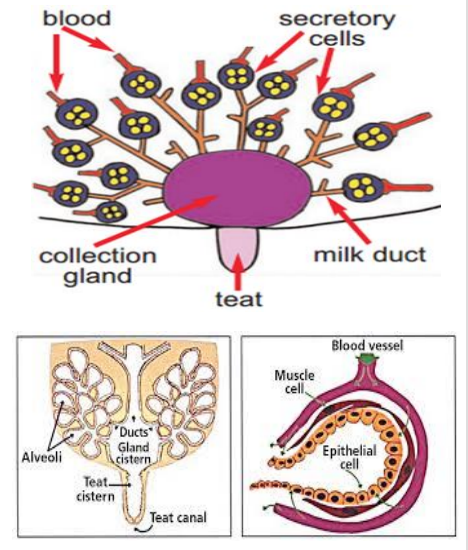
Milk formation
Milk secreted from epithelial cells into lumen of alveoli
Substances e.g. water, minerals, vits & immunoglobulins can pass cell membrane from blood stream
Substance inc. proteins, lactose & fat are produced in secretory cells - then transported into lumen
Amt. of milk regulated by lactose by influencing osmotic pressure b/w blood & alveoli
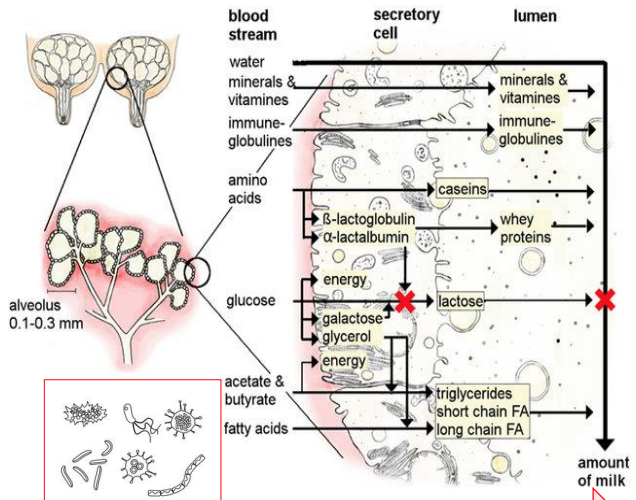
Bacteria in mammary gland
Cross-talk b/w milk microbiota, epithelial cells & immune cells maintain a balanced, healthy environment
Microbial imbalance that leads to infection→ commensal bacteria barely inhibit the pathogen (1); immune & epithelial cells only respond to the pathogen (2-3)
- results in massive production of pro-inflammatory mediators (cytokines, chemokines, AMPs)- causes the attraction of additional activated immune cells (4)→ leads to mastitis

Origin of human milk bacteria
Dendritic cells go across gut epithelium to directly take up bacteria from gut lumen
Once associated w/ dendritic cells, live bacteria spread to other locations through bloodstream
Dendritic cells migrate using enteromammary pathway via mesenteric lymph node, so bacteria arrive at mammary gland
- mechanism explains presence & abundance of maternal gut bacteria in colostrum & breast milk
Milk microbiota, breast milk microbiota & infant oral microbiota all continue travelling until infant gut is reached
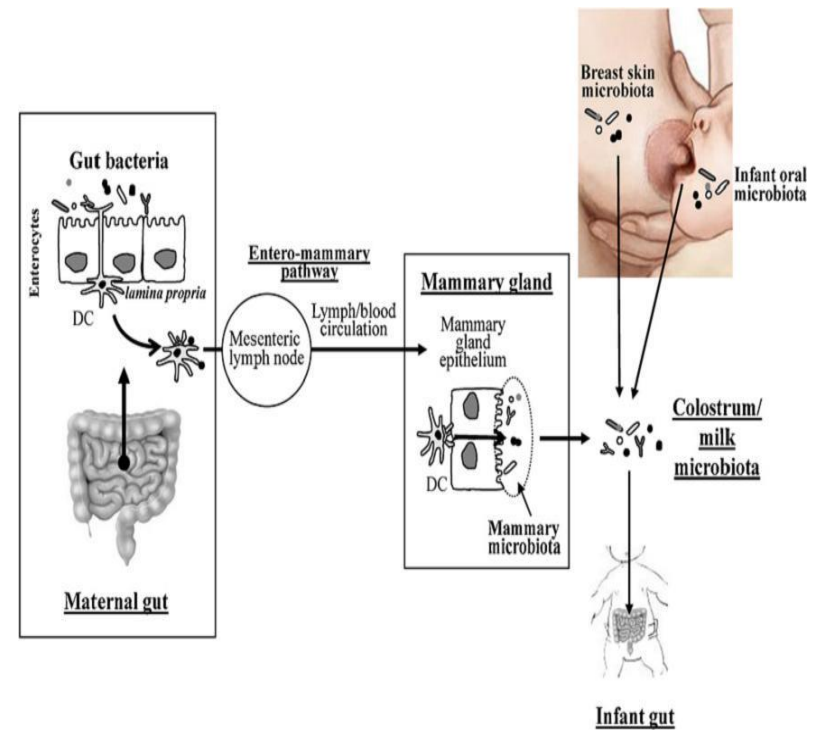
Enteromammary pathway
- When pathogen enters maternal gut, antigens are presented to immune cells that travel via blood
- IgA production induced at mammary cells & secreted as component of milk to protect infant
Maternal gut microbiome regulates neonatal gut microbiome via IgGs
Maternal antibodies transferred placentally before birth to fetus & via breast milk to neonate after birth
After birth, maternal milk provides 1st source of antibody-mediated protection in intestinal tract of infants against infection
Gut microbiome can induce antigen-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) → cross-reacts w/ pathogen antigens to promote systemic pathogen eradication in humans & animals
Gut microbiome-induced IgG antibodies exhibit bias against Gram -ve Enterobacteriaceae e.g. E.coli - common causative bacterium in neonatal infections
Maternal IgG antibodies cooperate w/ IgAs in neonatal gut
Recent studies → gut microbiome-induced IgG antibodies transferred from serum to maternal milk in process facilitated by neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)→ ↑ levels of IgG & IgA in neonatal intestine than in adult intestine & robust IgG & IgA coating of gut commensal bacteria
FcRn expressed at high levels in epithelial cells in human mammary glands → facilitates transfer of serum IgG to maternal milk & in neonatal intestinal enterocytes to facilitate uptake of maternal milk & transcytosis to circulation
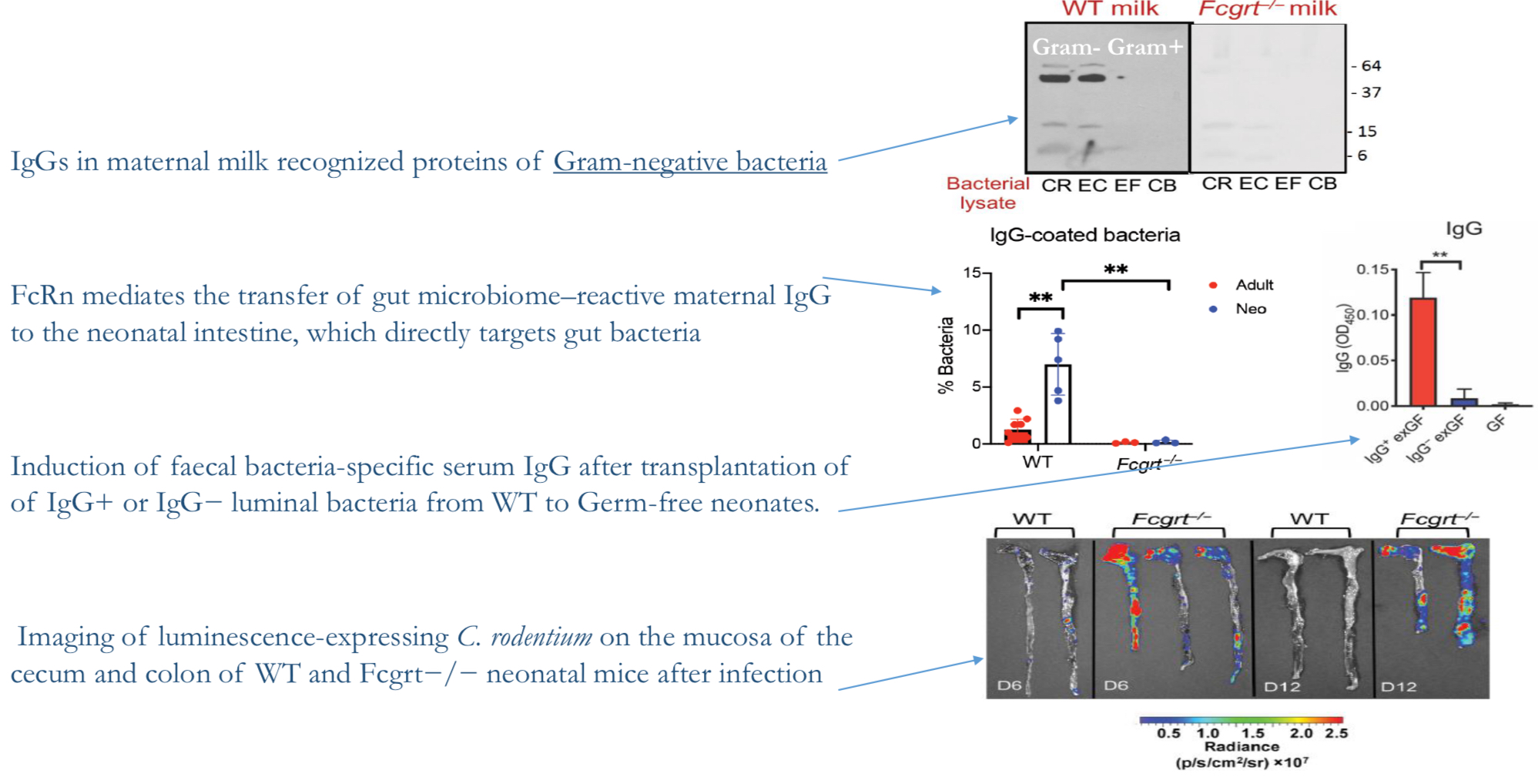
IgGs in maternal milk recognise proteins of Gram -ve bacteria
FcRn mediates transfer of gut microbiome-reactive maternal IgG to neonatal intestine- directly targets gut bacteria
Induction of faecal bacteria-specific serum IgG after transplantation of IgG+ or IgG- luminal bacteria from WT to germ-free neonates
Imaging of luminescence-expressing C rodentium on mucosa of cecum & colon of WT & Fcgrt -/- neonatal mice after infection
Milk natural antimicrobial systems
Antibodies→ IgA, IgG
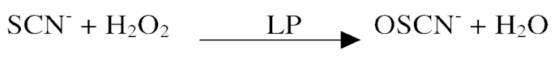
Lactoperoxidase→ generates short lived [O] intermediates e.g. hypothiocyanite - effective in killing aerobic & anaerobic bacteria
Xanthine oxidase→ produces antimicrobial radicals such as superoxide, nitric oxide and peroxynitrite
Lysozyme→ degrades bacterial cell wall of Gram-positives
Lactoferrin→ binds iron and withholds
Phagocytes
Milk Distribution
==Historically== Now
- ==No temperature control== → Industrialisation
- ==Short distribution chains== → Long distribution chains, from farms to urban centres
- ==Preservation not that important==→ preservation is essential
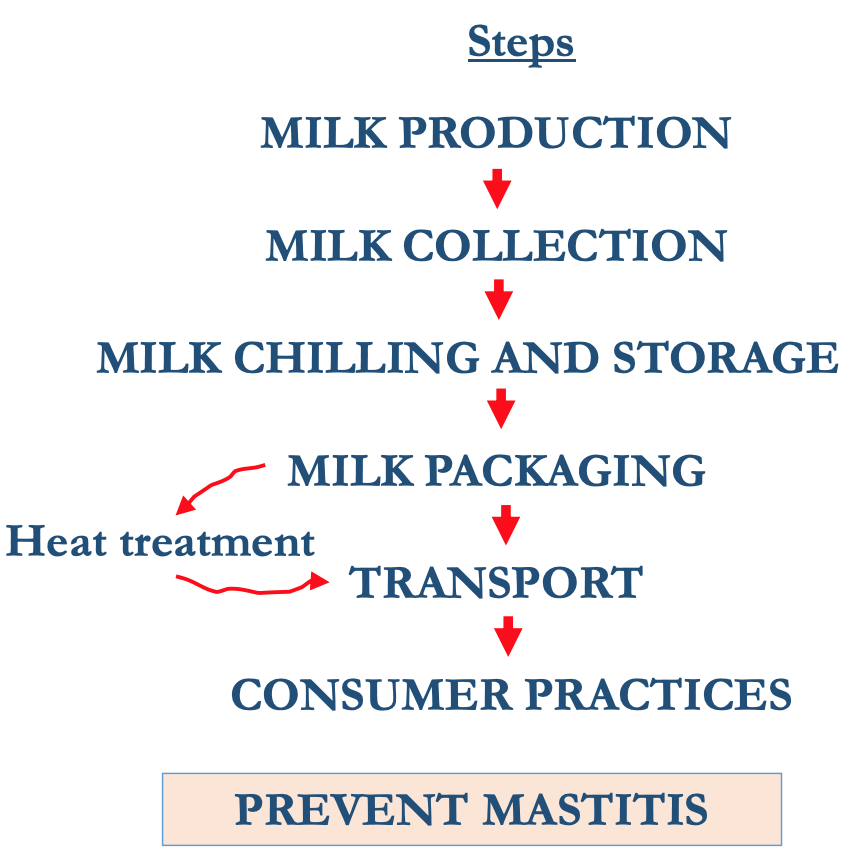
Milk distribution: factors affecting milk quality
MILK PRODUCTION→ MILK COLLECTION→ MILK CHILLING & STORAGE→ MILK PACKAGING→heat treatment→ TRANSPORT→ CONSUMER PRACTICES→ Prevent Mastitis
Important Risk Factors
Health status, housing & herd size, silage, water source & waste management
Milk practices, mastitis control measures, Equipment cleaning and maintenance
Efficiency of chilling practices, equipment, personnel hygiene & sanitation
Maintenance of chill temperatures equipment, personnel hygiene & sanitation
Efficiency of pasteurisation
Maintenance of chill temp- adherence to use-by-dates
→PREVENT MICROBIAL HAZARDS
Quality in distribution chain
- Mastitis prevention
- temp control
- heating
Mastitis
- Inflammation of mammary glands due to ↑ level of bacteria & somatic cells, w/ the subsequent ↓ in milk quality
- Causes major losses in milk production → clinical (25 cases per 100 cows/year) or subclinical (15-20% cows)
- Caused by 137 different organisms but 5 cause over 80% of infections:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Streptococcus dysgalactiae
- Streptococcus uberis
- E. coli
Methods to prevent mastitis
- Provision of clean litter
- Rapid removal of slurry
- Prevention of muddy areas
- Shave udders
- trim tails Wash teats with disinfectant
- Dry teats
- Keep parlour floor clean
- Clean teat cups
- Discard foremilk
Detection
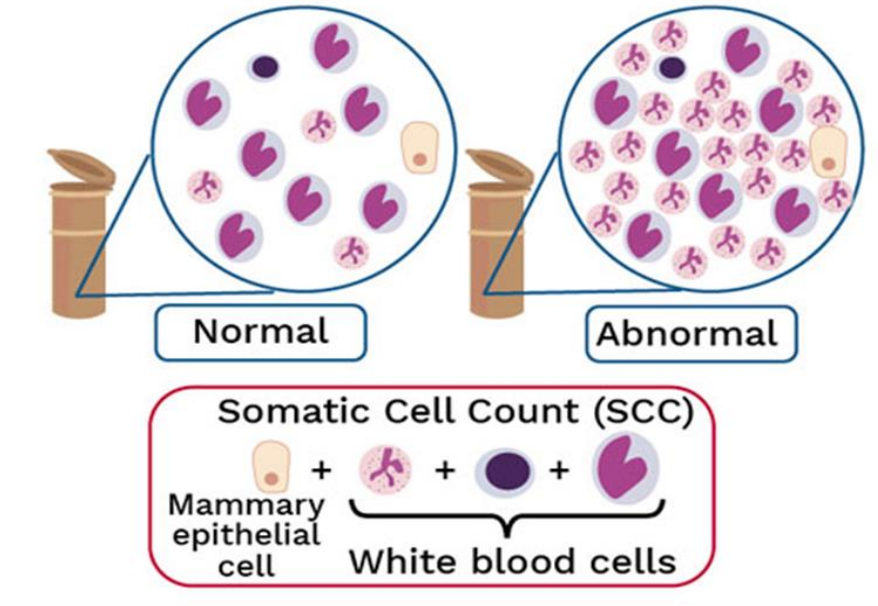
Main indicators of milk quality
- Somatic cell count (SCC) → Plate count (PC)
Somatic cells are a mixture of milk-producing cells (1-2%) & immune cells (98-99%)
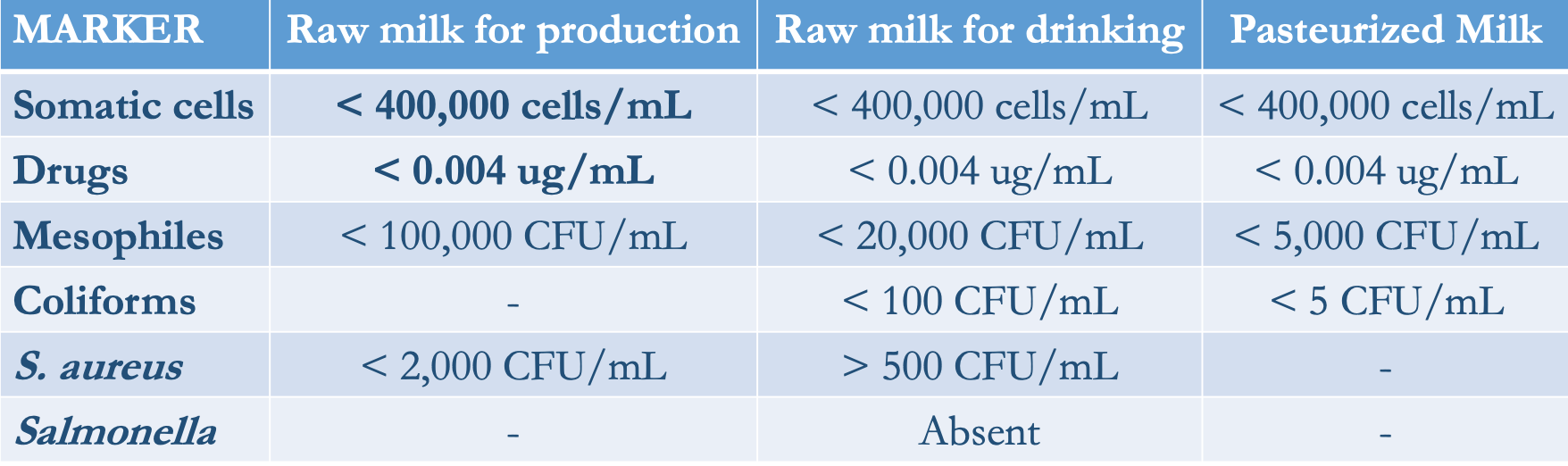
- SCC < 100,000 cells/mL = no infection
- 200,000 cells/mL = mastitis
EU regulations:
- PC < 100,000 mesophiles per mL
- SCC < 400,000 cells per mL
Milk buyers pay a premium of 3-5% of milk price below threshold of 200,000 and apply reductions of 5-10% if above
The influence of farm hygiene practice
Bacterial counts (CFU/ml)
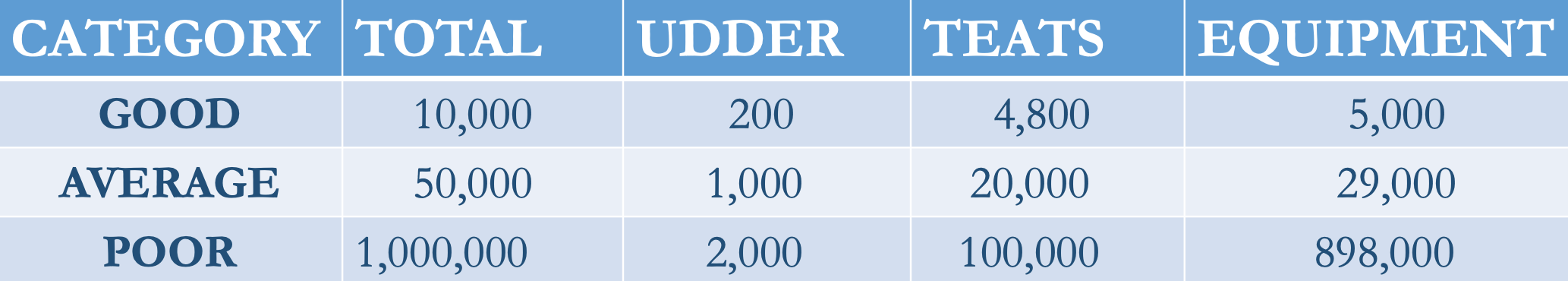
Temp control
- Farm bulk tank→ refrigerated (< 4ºC for < 48h) = 103 CFU/mL
- Road tanker→ insulated (< 6ºC for 1-8h) = 103 -104 CFU/mL
- Rejected if > 7ºC
- Silo at dairy→ insulated (6-8ºC) or refrigerated (2-4ºC)
- < 104 CFU/mL in the silo
- < 105 CFU/mL before pasteurisation
Heating: pasteurisation/UHT
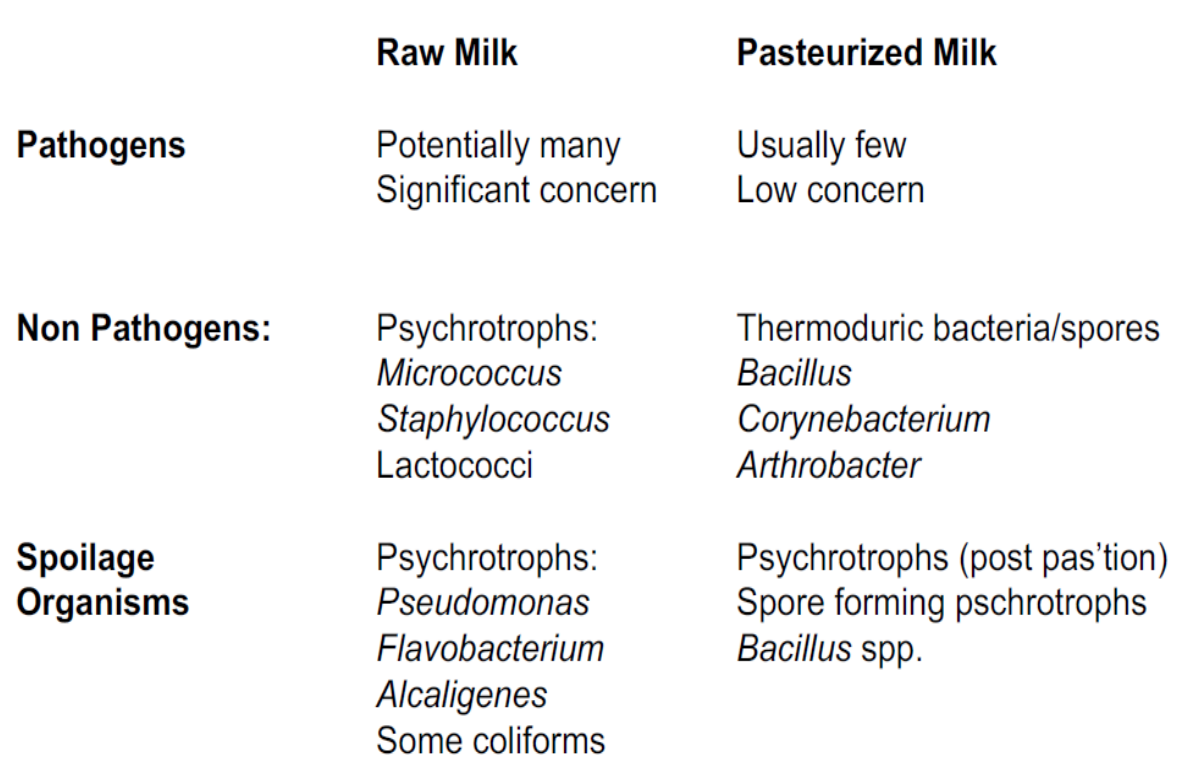
Milk spoilage → Psychrotrophic bacteria
- Refrigerated raw milk may contain psychrotrophic bacteria that produce thermoresistant exo-proteases and lipases → compromise the quality of dairy products during storage
- Carbohydrates
- 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘭𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘴 converts: lactose→ Lactic acid (produces sour taste/smell?)
- Proteins
- 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘌𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳, 𝘚𝘦𝘳𝘳𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘢, 𝘈𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴 converts: Caseins & whey proteins → Short peptides, amino acids, amines (produces bitter, putrid smell/ taste?)
- Lipids
- 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘈𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘈𝘤𝘪𝘯𝘦𝘵𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳 converts: Short-chain fatty acids (produces rancid flavour)
Microbial hazards in milk today
 \n
\n 
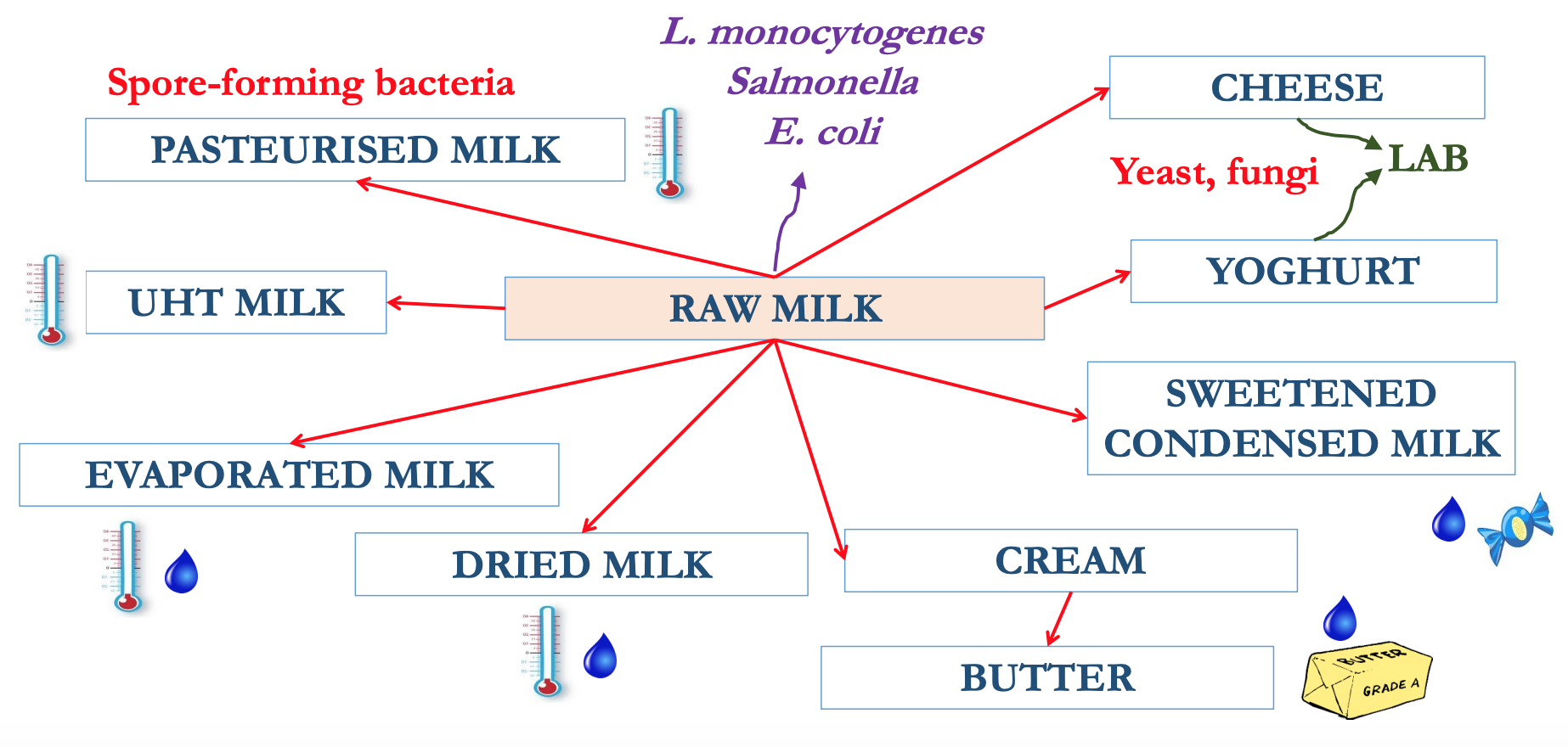
Milk legislations & testing
EU Council Directive 92/46/ECC lays down the health rules for the production and distribution of milk and dairy product on the market
Milk can only come from herds that are officially TB-free (and Brucellosis-free)
Pasteurised milk must pass the phosphatase test to assure the effectiveness of the process
Honey
Sweet, viscous substance made from floral nectar by bees & some related insects
Produced after ingestion, enzymatic activity, regurgitation & H2O evaporation
- Water~18%
- Fructose~40%
- Glucose~ 30%
- Other sugars~ 10%
- Minerals~ 2%
- water activity (aw) → 0.60
- pH → 3.4 - 5
History
- Earliest evidence of humans collecting honey is a cave-painting in Valencia, on Spain's eastern coast, thought to date from around 8000 BC
- Since about 4000 BC, the ancient Hindi medical theory of Ayurveda outlined honey's medicinal qualities in treating burns, allergies & infections
- Western cultures have eventually caught up by devising honey-based wound dressings & oral medicines.
- Composition of honey varies greatly - depends on the local flora in the bees' immediate environment
- Bees visit various flowers making honey w/ diff. healing properties - scope for finding new uses for honey is vast.
How is it produced?
- Bees collect nectar using their tongue
- It goes to their honey stomach (40 mg of nectar)
- Enzymes break down sucrose into glucose & fructose
- Digested nectar is regurgitated, placed in honeycomb cells & left unsealed
- Fermentation → LAB & yeasts (acidity)
- Bees flutter their wings to circulate air & evaporate H2O (sugar conc. ↑ & then sealed with wax)
- Food supply (E) or removed by beekeepers