Bio1220L: Practical One
Unit 1: Dichotomous keys
Dichotomous keys: Organized couplets that consist of mutually exclusive characteristics
two types of dichotomous keys
Bracketed Keys
1. Flowers Red…. …… …… ……2
1’ Flowers not Red…. ….. ….. ….3
2. Plant Herbaceous ………Species A
2’ Plant Woody………………Species b
Indented Keys
1. Flowers red
2.Plant herbaceous ………..Species A
2’ Plant Woody…………….Species B
1’Flowers not red
3. Leaves simple…………..Species C
3’ Leaves compound……..Species D
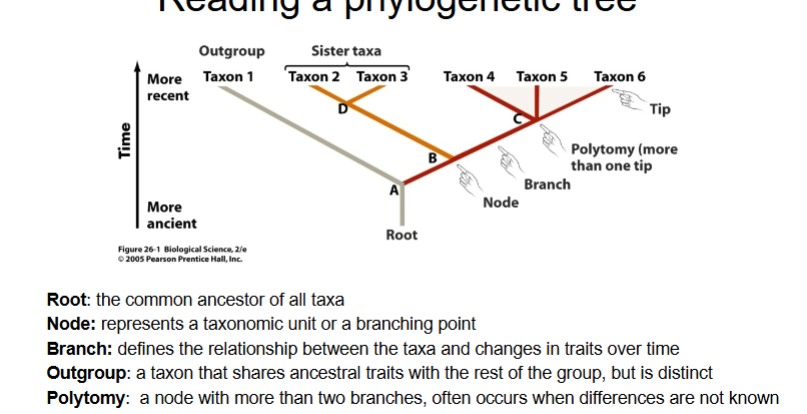
Unit 2: Phylogenetic Trees and Microscopes
Phylogenetic trees aid in inferring phylogenies based on these characteristics:
morphological
anatomical
reproductive
developmental
molecular
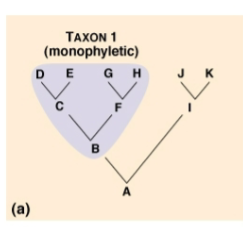
Monophyletic Groups
also called Clades
Group of organisms that descended from the same common ancestor
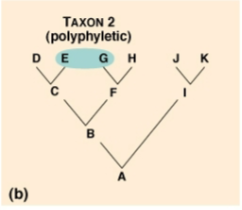
Polyphyletic Group
group of organisms descended from different common ancestors
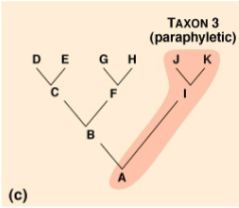
Paraphyletic Group
group of organisms descended from a common ancestor but does
not include all descendants of the common ancestor
Homologous traits/synapomorphies
traits that are shared between organisms that derived from the same common ancestors
Symplesiomorphies
traits shared between all organisms in a given phylogenetic tree
RNA, DNA, Proteins, Cell Membranes
Analogous Traits
convergent evolution
Occurs when organisms share traits, but not the same common ancestor
Microscopes
Compound Microscope (what we use)
magnifies up to 2000x
has two lenses
transmits a focused light through a specimen
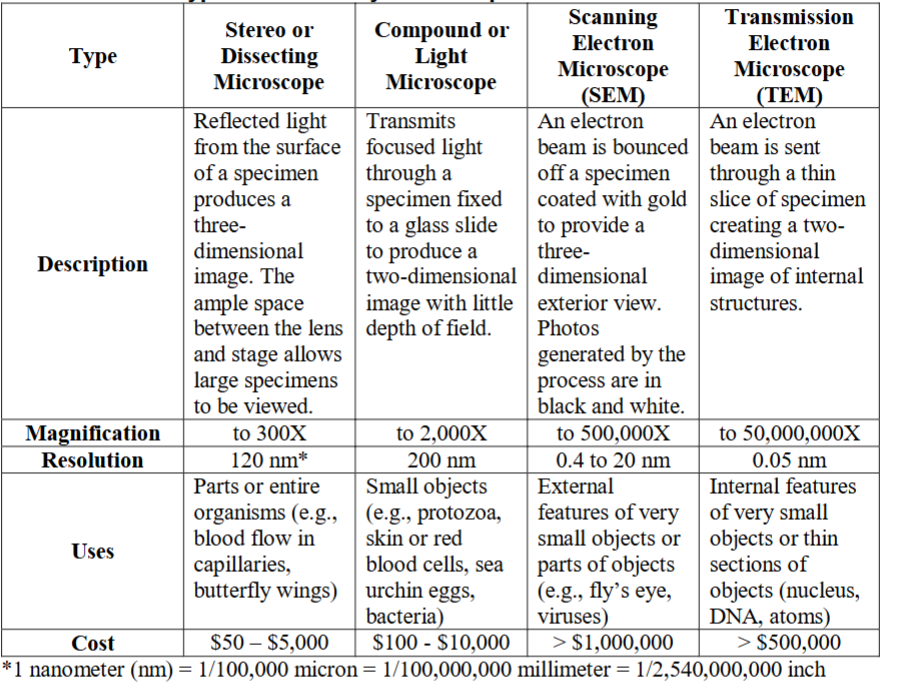
In order to calculate magnification
10 x lens magnification
Unit 3: Population Genetics
Evolution: a change in the genetic composition of a population over time
Population: a group of organisms of the same species that occur in the same area and interbreed or share a common gene pool
Gene Pool: genes available in a population
Genetics: study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
a model showing the frequencies of alleles in a population will stay the same regardless of starting frequencies under 5 certain conditions
1. No mutation of genes
2. Completely random mating
3. Large population size
4. No gene flow
5. No natural selection
Allelic frequency
p + q = 1
p = frequency of dominant allele
q = frequency of recessive alleles
Genotypic Frequency
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p² = frequency for homozygous dominant
2pq = frequency for heterozygous
q² = homozygous recessive
Evolutionary Forces: natural selection, mutations, genetic flow
Occurs due to outside stimulus and new characteristics are maintained because traits are beneficial for a species
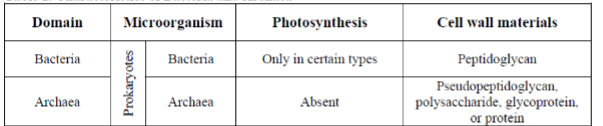
Unit 4: Bacteria & Archaea
Gram Negative
Stains pink due to low peptidoglycan poor walls
Gram positive
Stains purple due to peptidoglycan rich walls
Shannon Index
Checks how diverse an ecosystem is
H’ = sum of p ln(p)
Species Richness
Are there many species
S = sum of all species
H max = ln(S)
The higher the number, the higher the species richness
Species Evenness
Are the species well spread out
Checks for abundance of each species
J = H’/Hmax
species diversity
Dependent on species evenness and species richness
If species richness and species evenness are both high, then high species diversity
Low species diversity exists if:
There is low species richness
high species richness and low species evenness
Similarities between bacteria and archaea
No cell walls, just cell membranes
Typically use cilia or flagella to move around
they are smaller than eukaryotes
they are extremophiles
use a variety of metabolic process for acquiring carbon and energy
unicellular with very little cell specialization, decompartmemtalized
known as generalists
Differences between bacteria and archaea
Types of bacteria we need to know
Clostridium
Gram positive or gram negative, rod shaped
Mostly gram positive
Perfectly rod shaped
Colonies: Feathery or a perfectly round circle
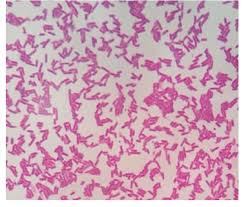
Streptococcus
Gram positive, ball/round shaped
Bacillus
Gram positive, rod shaped, shorter, put in chains
Looks like a tennis racquet
Colonies: smoother, irregular shaped
Spirillum
Gram negative, spiral shaped, long and spirally

Anabaena
Green, ball shaped, like a caterpillar
Cyanobacteria

Mixed archaea
A mixture of both
Unit 5
Climate Change
Caused by CO2 trapped in the atmosphere
Acidification of the ocean
Pace quickened due to human intervention
Fossil fuels
Effects
Loss of biodiversity
Species loss
More extreme weather
Unit 7
Phenology
the timing of events in an organism’s life cycle
important events are timed to match resources
Can be annual, biennial, or perennial
Annual: They grow in one year before dying
Biennial: Complete life cycle in two years
Perennial: they live more than two years
R² = how well data fits regression model
Coefficient of determination, determines how well y-hat can predict a new data point
p-value
ANOVA test
Tells us if changes in data are due to chance or not
If less than 0.05
We reject null hypothesis
H_0
If greater than 0.05
We fail to reject the null hypothesis
H_A
Accepting the alternate hypothesis
Correlation is the relationship between variables
Regression describes how well y-hat can predict future data
Unit 8: Protists
Protists are currently placed in Eukaryote Domain
Three types of Protists
Animal Like
Heterotrophs
Unicellular
Found in freshwater habitats, sometimes marine or damp terrestrial
4 main types based on movement
Fungus-Like
heterotrophs that feed on decompose organic matter
can be unicellular and multicellular
Terrestrial
found in shady and moist locations
Plant-Like
Autotrophic (photosynthesis)
Consists of unicellular
Animal Like
Ciliated Protozoans (Paramecium)
Cilia for movement
Contractile Vacuole for expelling water from the cell
Flagellated Protozoans (Trichonympha)
Move by beating their flagella
special because it has thousands of flagella
Amoeboid Protozoans (Amoeba)
lack cell walls, very flexible
move and feed by extending pseudopodia (pseudopods)
Eat via phagocytosis
Spore-Forming Protozoans (Plasmodium)
Parasites
are transferred from host to host via vectors
This one spreads malaria
Fungus-Like
Plasmodial Slime Molds (Physarum)
Heterotrophs that feed on and decompose dead organic matter
2 main types
cellular slime molds
plasmodial slime molds (This is our example)

Plant-Like
Euglenids (Euglena)
Unicellular freshwater algae
autotrophic organisms
one flagellum
have a eyespot (stigma

Dinoflagellates
Unicellular marine algae
two flagella
protective layer of cellulose
Diatoms
Unicellular marine and freshwater algae
assume different body shapes
made of silica (glass)
forms chains or colonies
Green Algae - Chlorophyta
Unicellular Freshwater (chlamydomonas)
Marine Multicellular (Ulva)
known as sea lettuce

Marine multinucleate (Codium)
known as dead man’s fingers

Multicellular Freshwater (Spirogyra, Cladophora)
Have filamentous morphology


Freshwater Colonial (Volvox)
each cell in the colony is identical, and could live independently of each other
Reproduces sexually and asexually
Brown Algae (Phaeophyta)
Multicellular marine organisms
Kelp
Largest of all protists
grow in large kelp forests near the shore

Rockweeds
Grow in mats that can be seen draped

Red Algae (Rhodophyta)
Multicellular marine organisms
often found deeper in the ocean than other algae