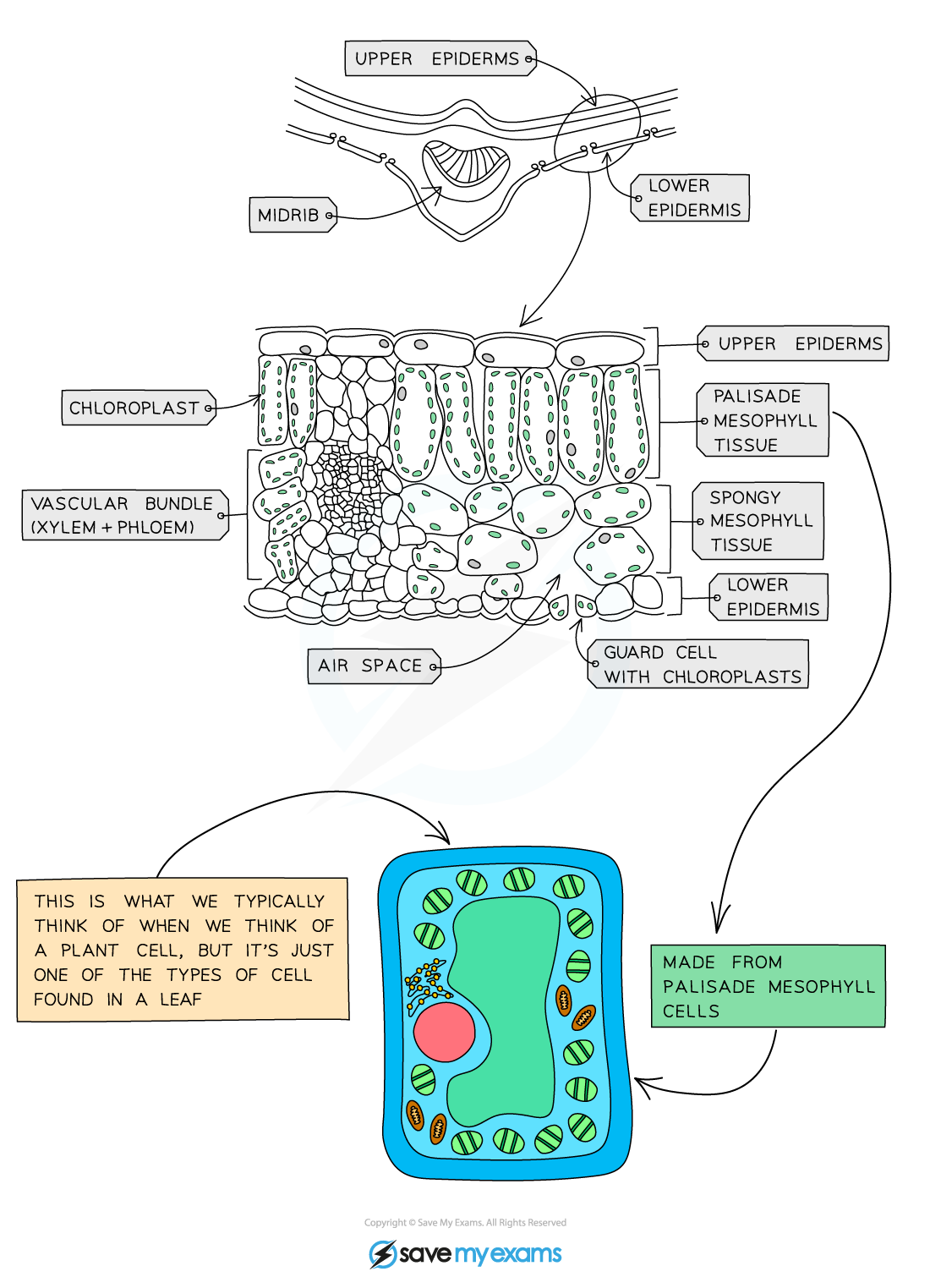
Gas Exchange (plants)
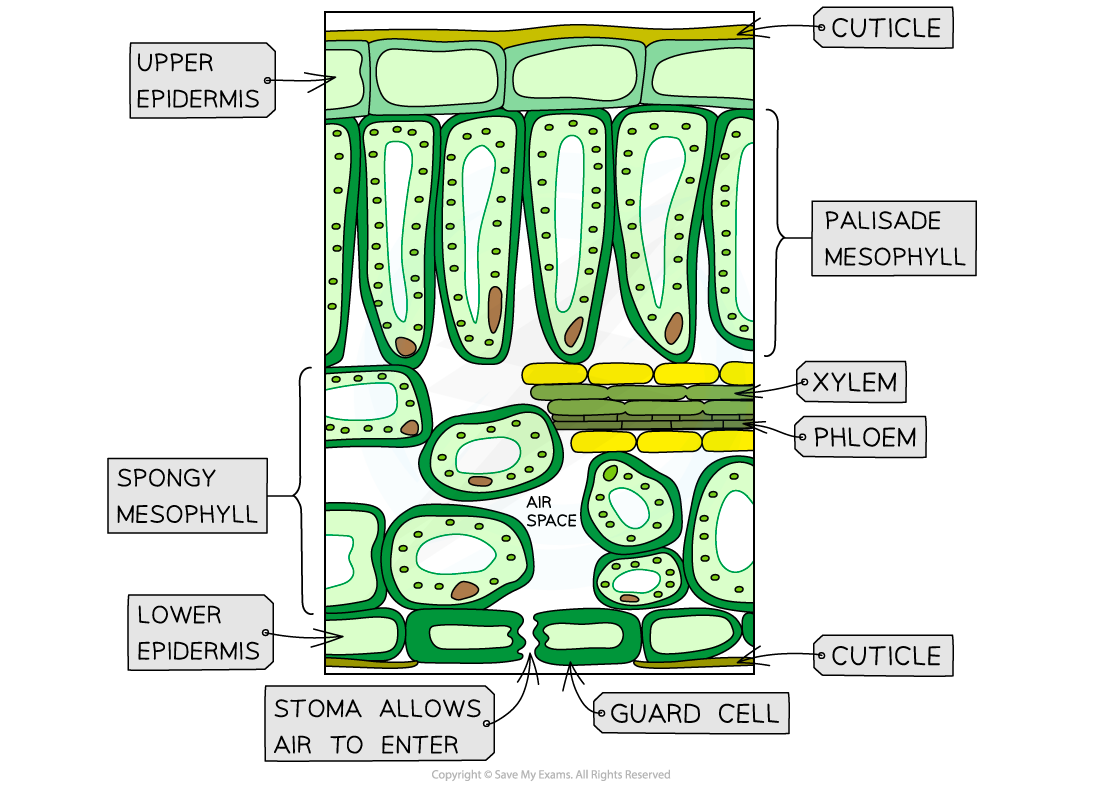
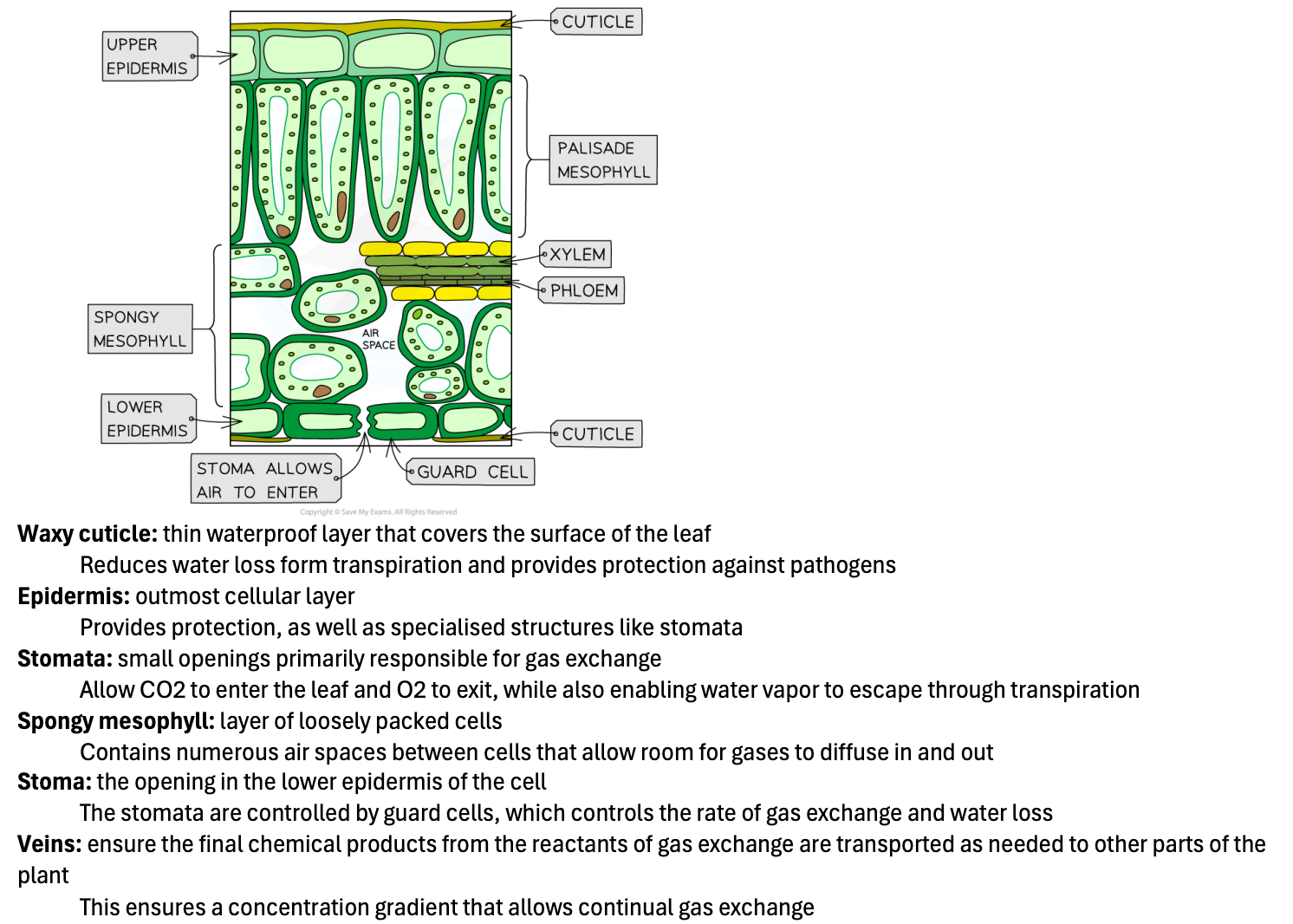
Waxy cuticle: thin waterproof layer that covers the surface of the leaf
Reduces water loss form transpiration and provides protection against pathogens
Epidermis: outmost cellular layer
Provides protection, as well as specialised structures like stomata
Stomata: small openings primarily responsible for gas exchange
Allow CO2 to enter the leaf and O2 to exit, while also enabling water vapor to escape through transpiration
Spongy mesophyll: layer of loosely packed cells
Contains numerous air spaces between cells that allow room for gases to diffuse in and out
Stoma: the opening in the lower epidermis of the cell
The stomata are controlled by guard cells, which controls the rate of gas exchange and water loss
Veins: ensure the final chemical products from the reactants of gas exchange are transported as needed to other parts of the plant
This ensures a concentration gradient that allows continual gas exchange