Functions of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules made out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio.
Functions of Carbohydrates
Structural Component
Structural Building Material
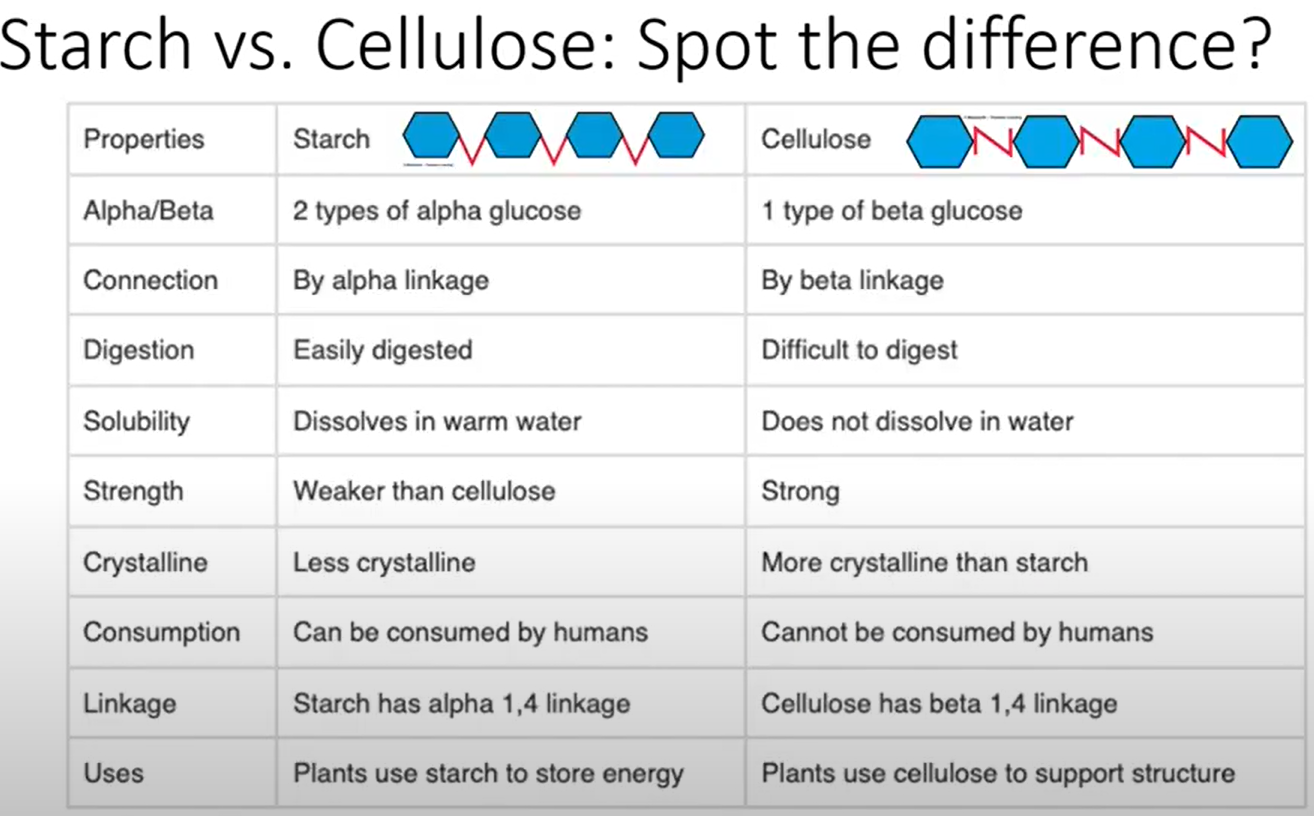
Plants build their cell walls with a complex carbohydrate called cellulose.
Animals such as arthropods build their exoskeletons with a complex carbohydrate called chitin.
Protein Spare
Nervous system uses carbohydrates
Lack of carbohydrates causes protein to go through gluconeogenesis (glucose) and be metabolized.
Energy Source
Fuel for activity
Immediate fuel for activity.
Sustained energy for aerobic activity.
Major energy for high intense activity like weight training or sprinting.
Metabolic Primer
Carbohydrates are metabolic primers, they are needed to completely burn fat.
Incomplete combustion of fat will result in ketone bodies.
Fat burns in flame of carbohydrates.
CNS Fuel
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel of CNS.
Acute carbohydrate depletion may cause tunnel vision, nausea, and irritability.
Metabolism can adopt to low carb, high fat / protein diet.
FUNCTION: Role in Different Biological Processes
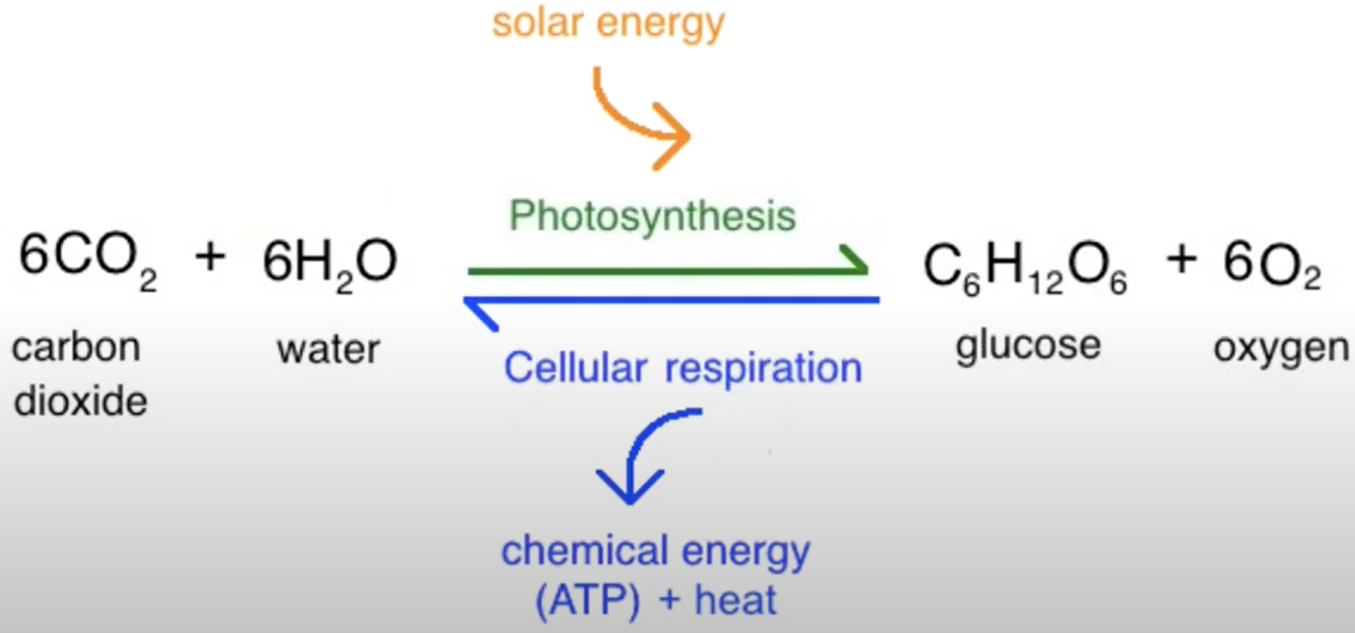
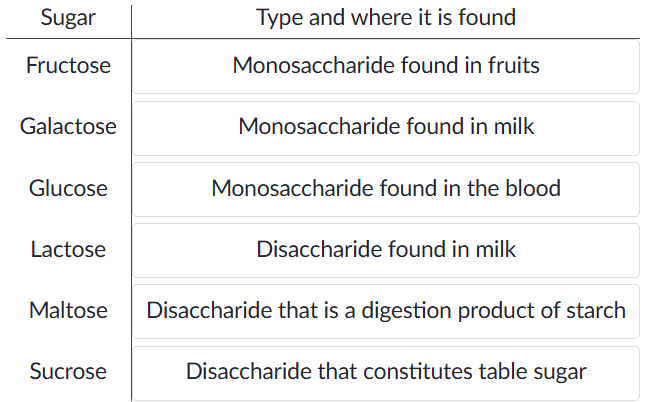
CLASSES OF SUGARS
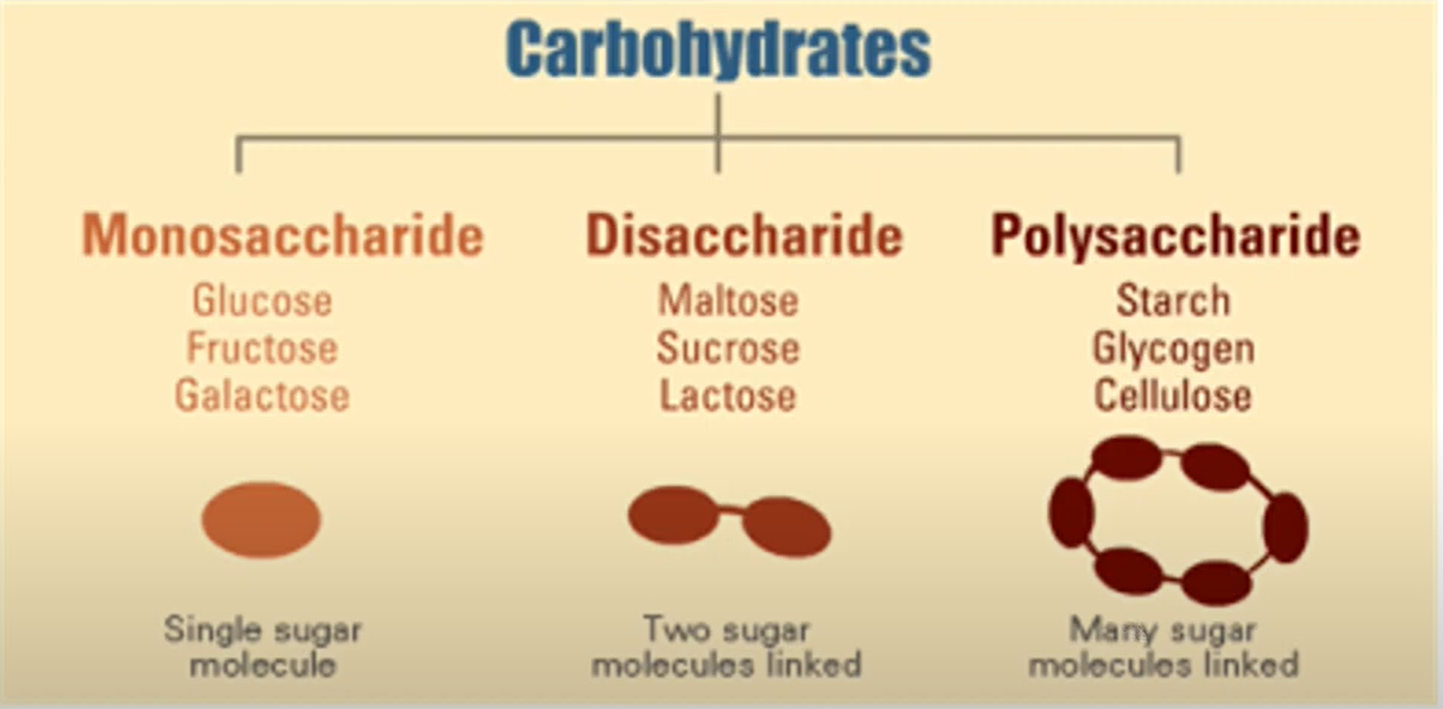
SIMPLE Carbohydrates
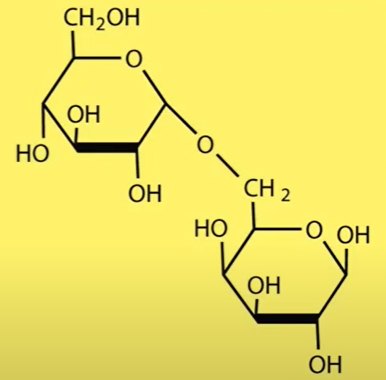
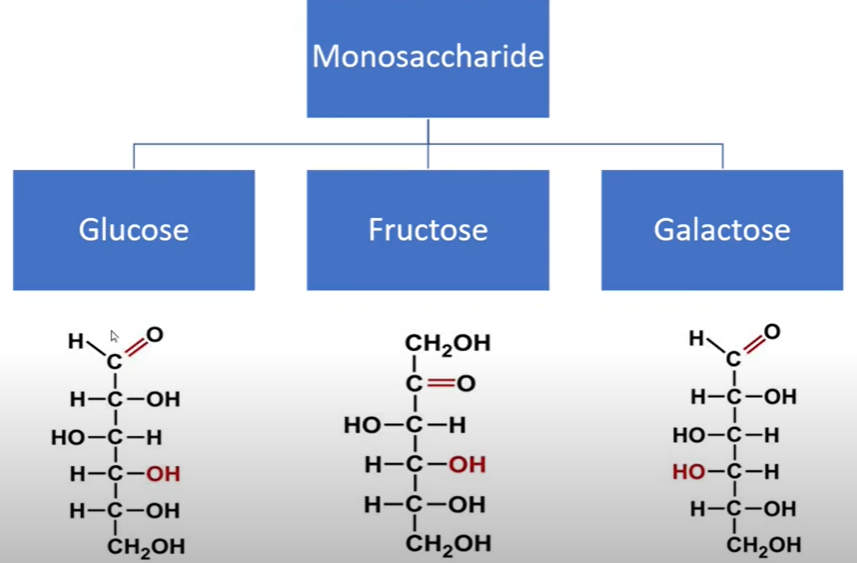
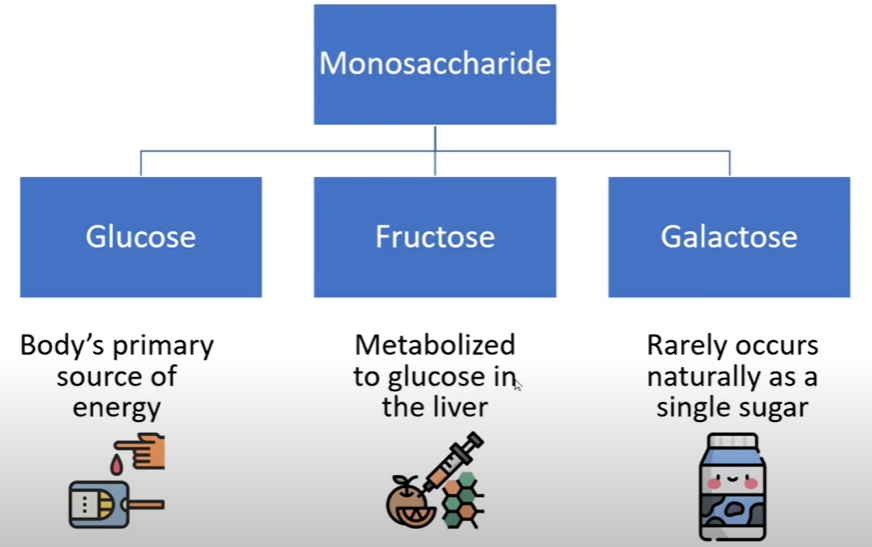
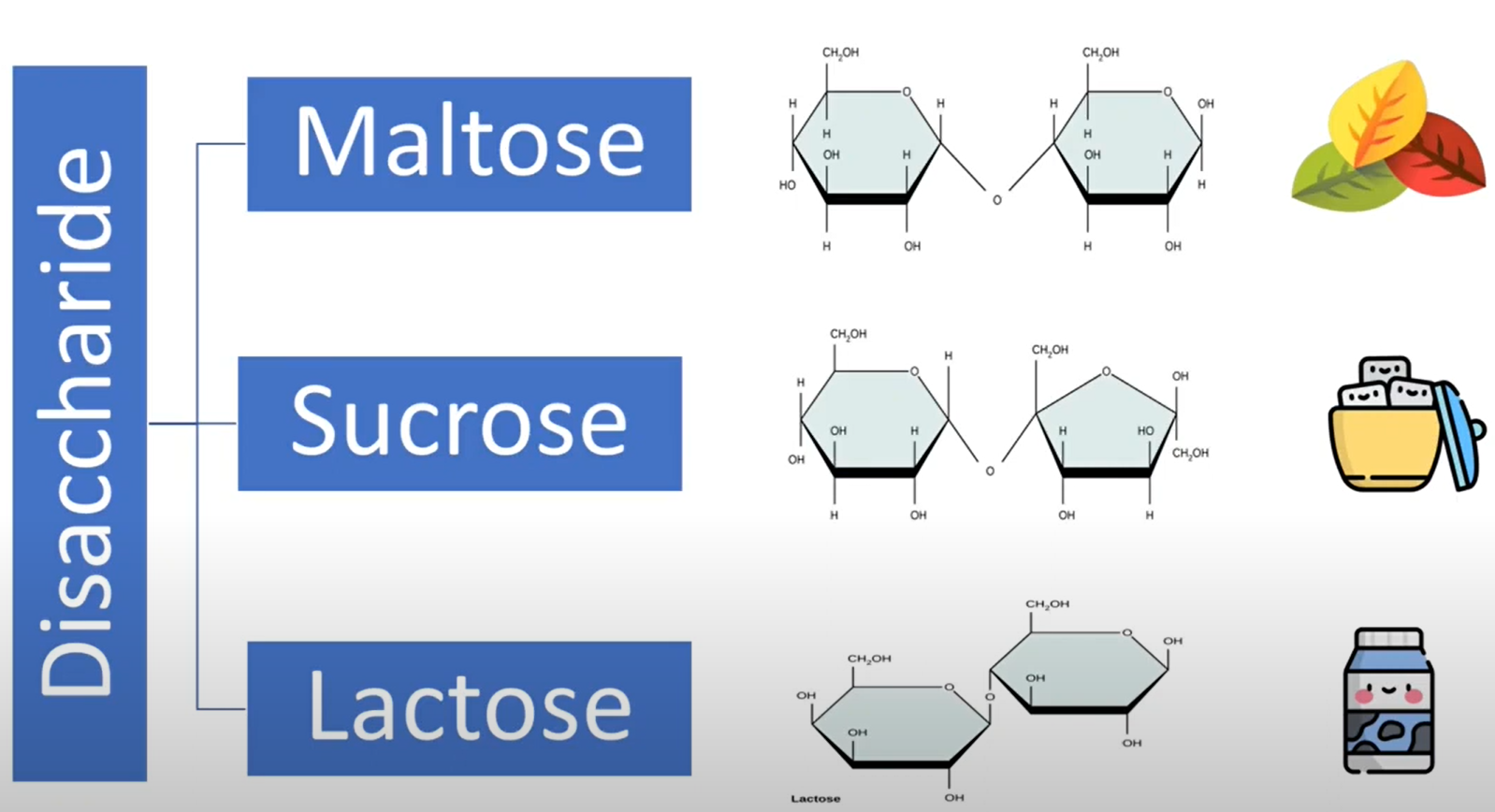
Sugars and their Type + Origin
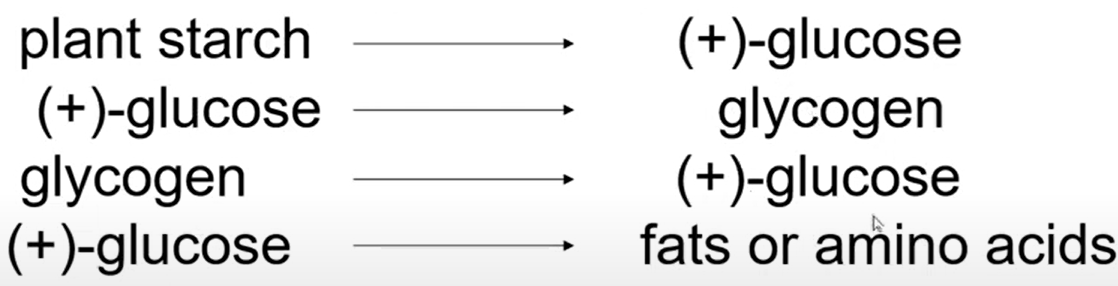
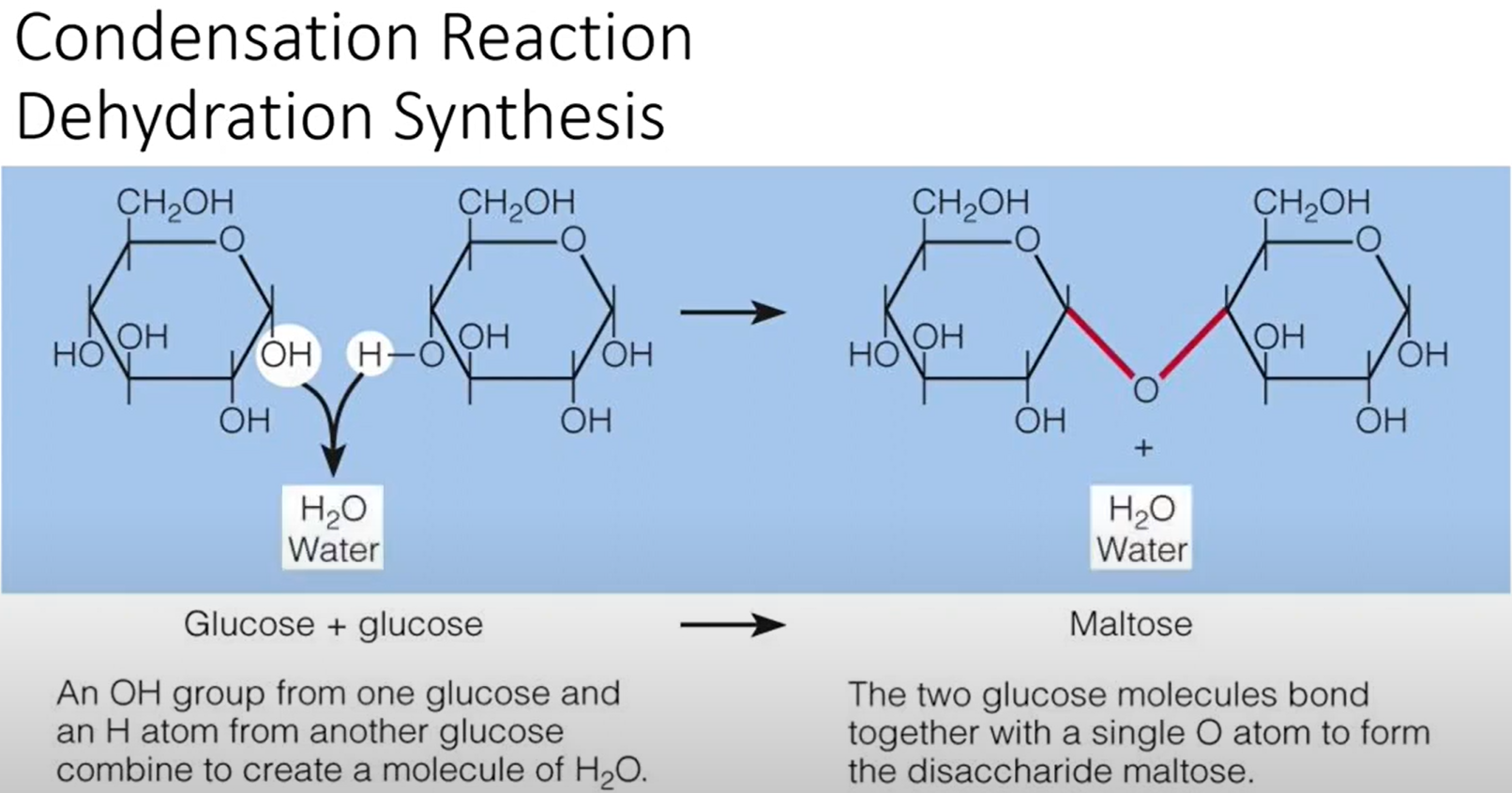
The Process That Combines Monosaccharides
The Process That Decomposes Polysaccharides (or Polymers in General)

COMPLEX Carbohydrates
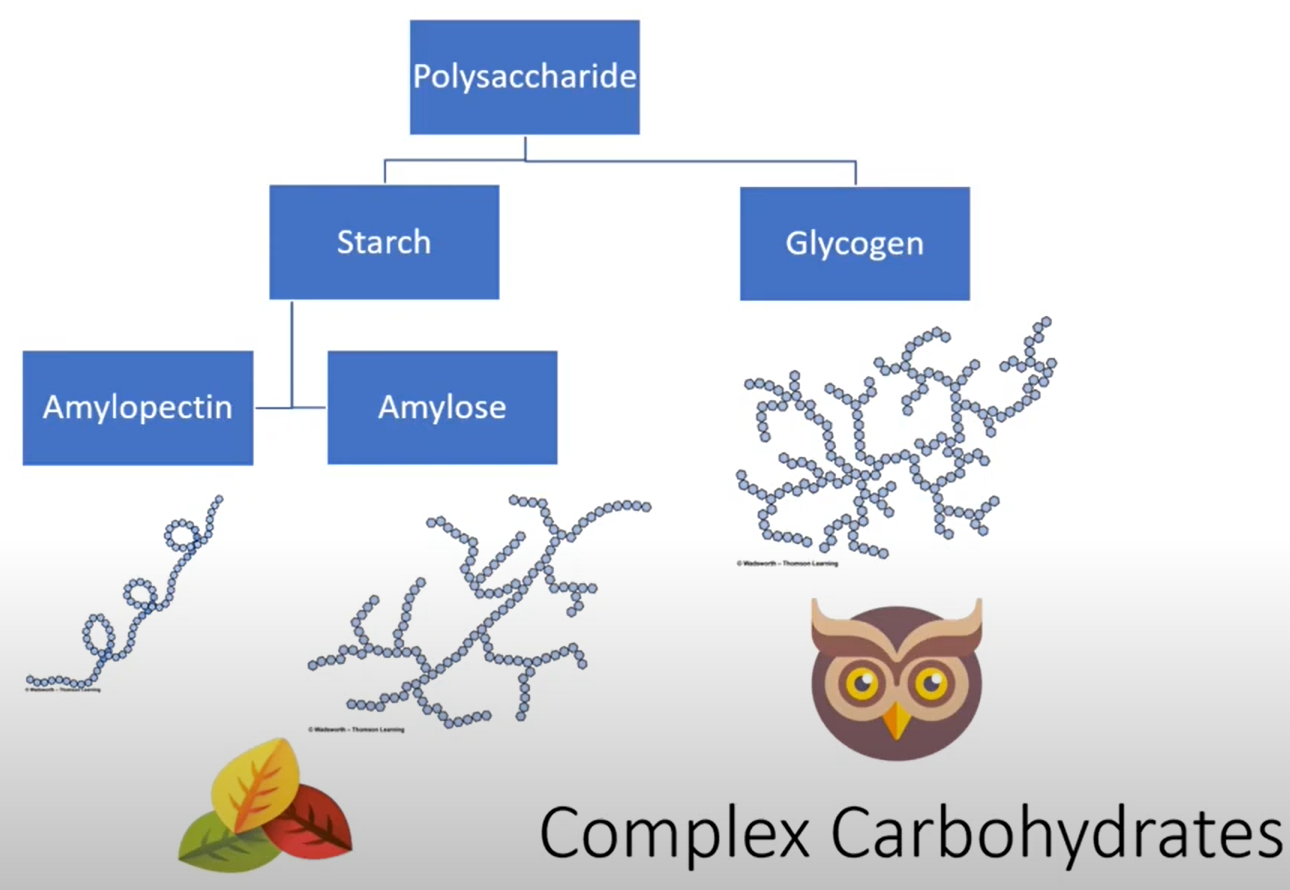
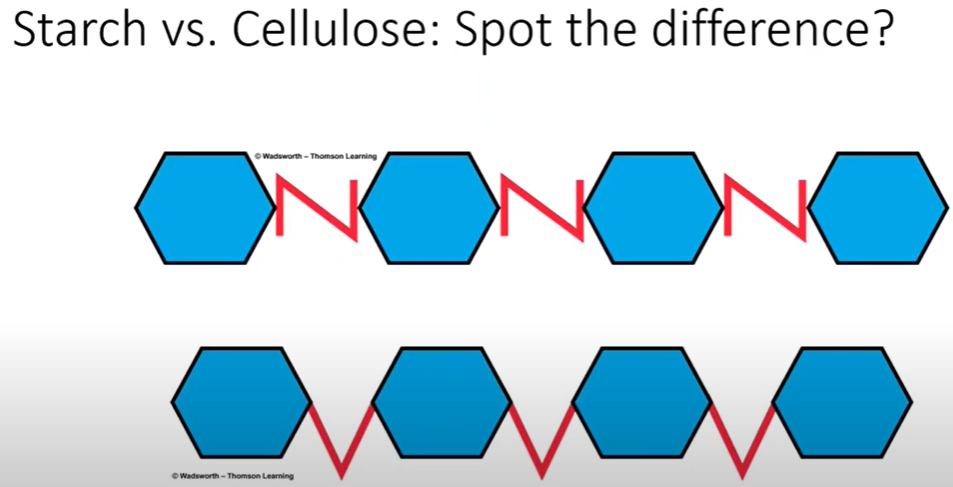
Polysaccharides and their Structure Description
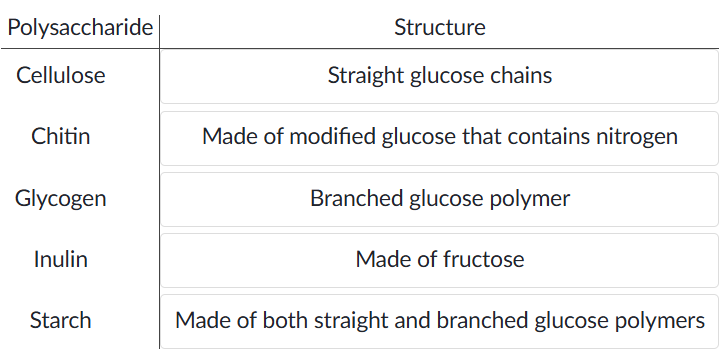
Fibers
Are usually found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains.
Indigestible Polysaccharides
Structural parts of plants
Indigestible to humans; lack enzymes to break down bonds
Fiber is lost in refined grain products
Health Benefits of Dietary Fiber
Protects against colon cancer
Prevents gastrointestinal disease
Controls high cholesterol
Reduces inflammation
Aids in weight loss
Treats piles
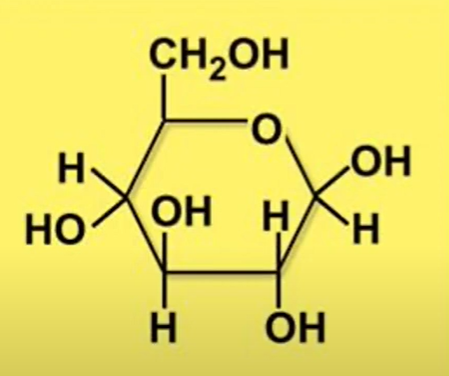
SUGAR STRUCTURE
Organic Compounds
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
General Formula: (CH2O)n
Classes
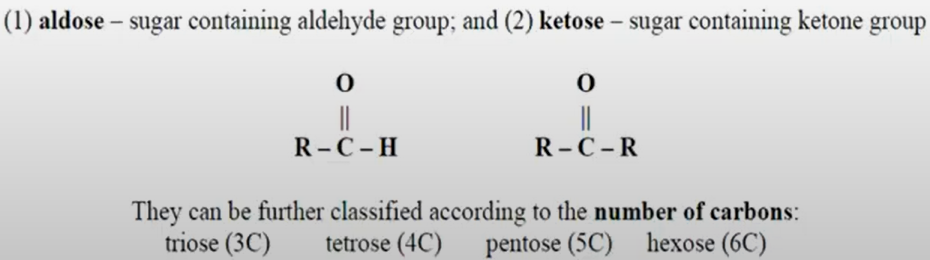
Aldose — sugar containing aldehyde group
Ketose — sugar containing ketone group
 Fun fact:
Fun fact:
"tri, tetr, pent, hex" indicates the number of carbons (based on the Greek language)
"ose" indicates sugar
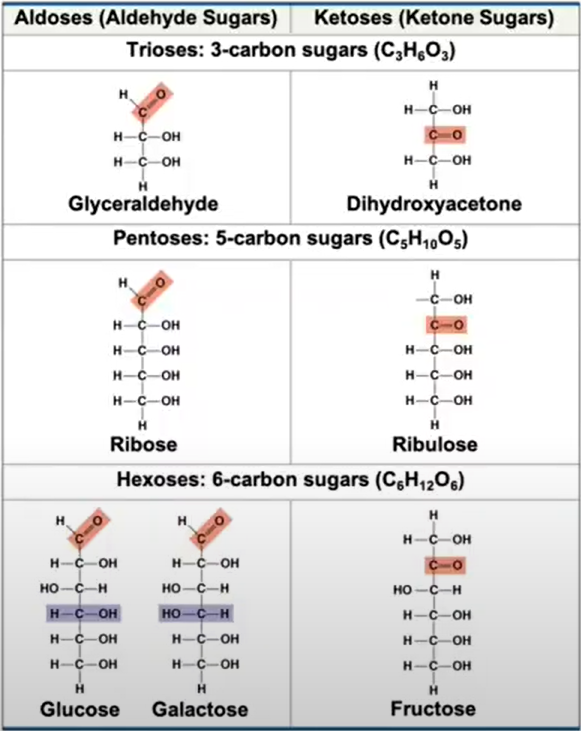
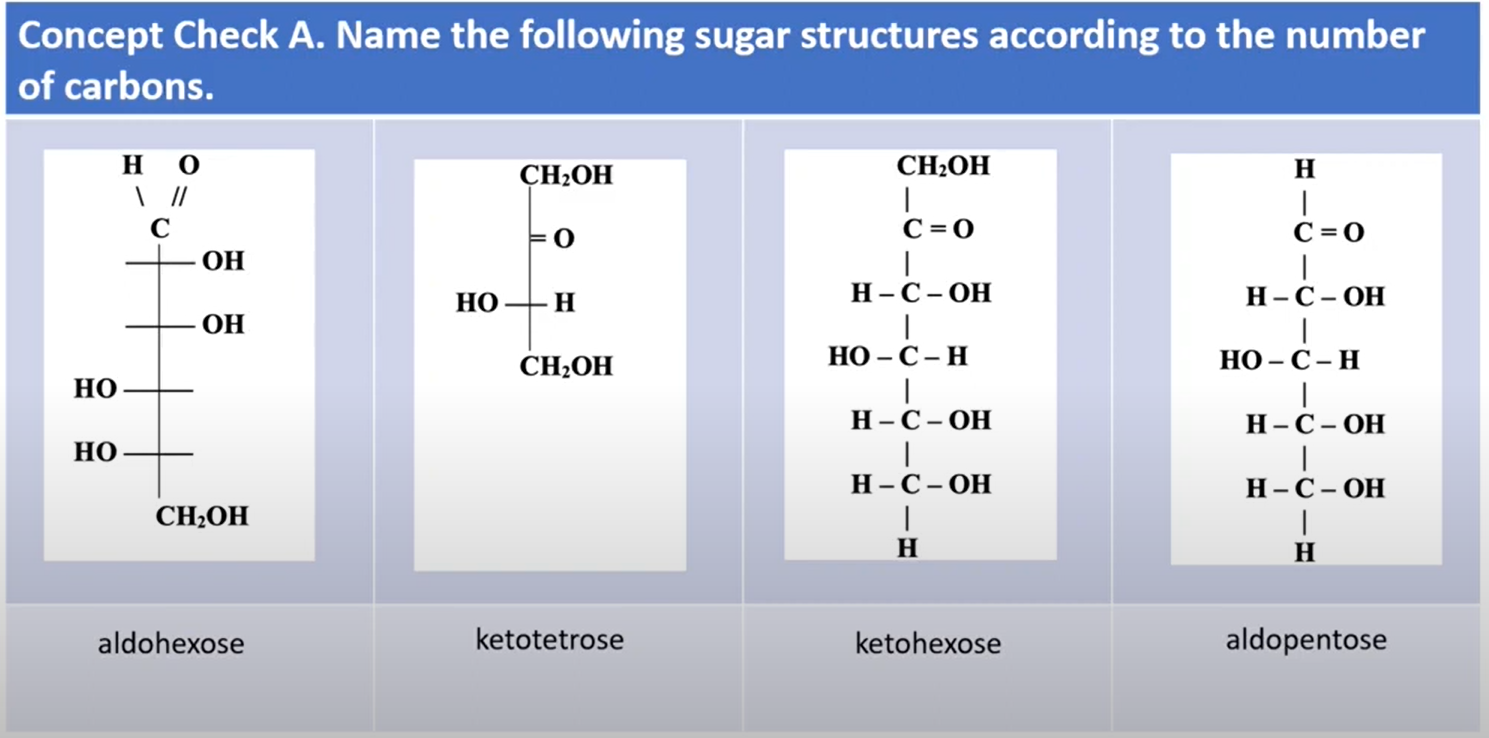 Naming sugar structures according to the number of carbons in the structure:
Naming sugar structures according to the number of carbons in the structure:
“Aldo”
— if the covalent bond of O is in the end of the structure (is not in between two Cs)
“Keto“
— if the covalent bond of O is in between two Cs
“tri (3), tetr(4), pent(5), hex(6)”
— states the number of Cs in the structure
“ose”
— add this at the end to convey that the structure is a sugar structure