L10: Fluorescence Spectroscopy
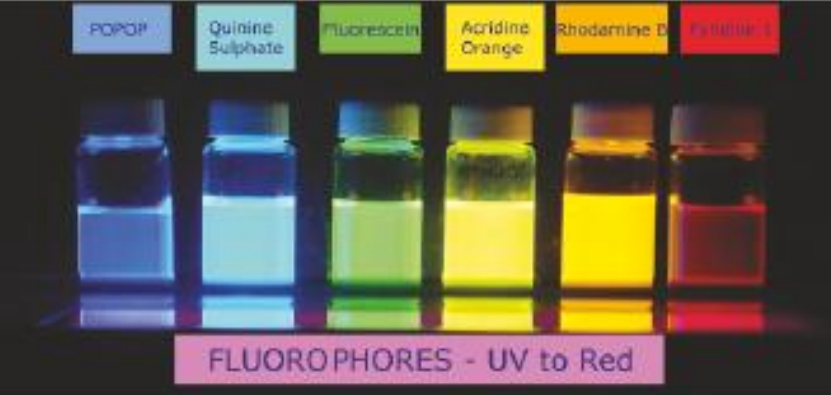
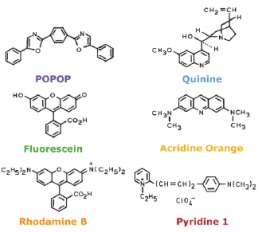
Discovery of fluorescence
aromatic, conjugated systems in particular environments
dyes - Ancient Egypt
Sir William Herschel -
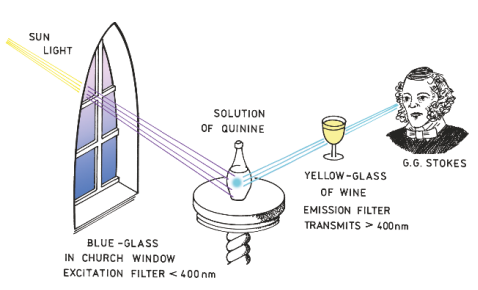
Characteristics of fluorescence emission
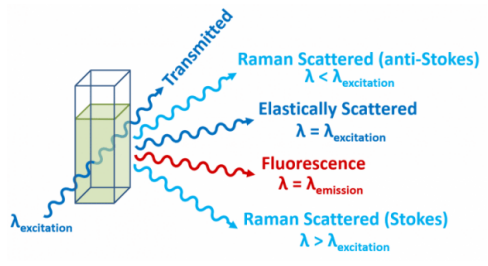
All emission is NOT fluorescence


Fluorescence & phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence (light from absorption of photons)
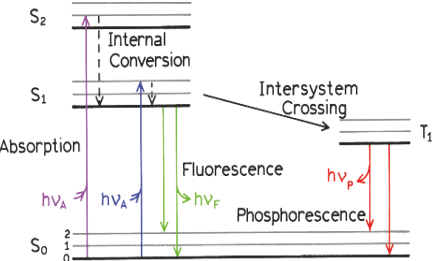
Jablonski diagram, Stokes shift
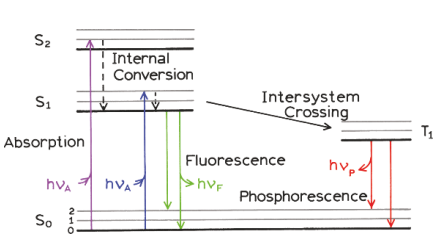
Stokes Shift: Emission occurs at longer wavelengths due to vibrational relaxation
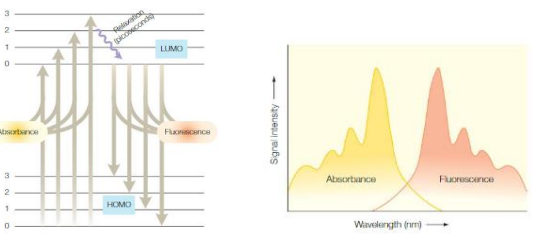
Excitation and emission spectrum
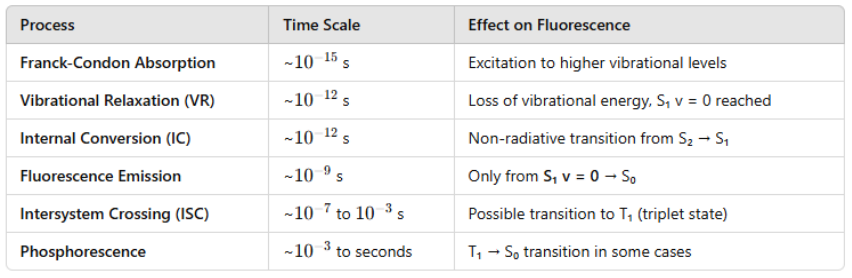
State transitions occur ~10-15s, too short a time of nuclei to move
Internal conversion ~ 10-12 s Vibrational relaxation ~ 10-12 s
Emission spectrum is the wavelength distribution of an emission measured at a single constant excitation wavelength.
Excitation spectrum is the dependence of emission intensity, measured at a single emission wavelength, upon scanning the excitation wavelength.
Absorption and Excitation:
Excitation process: Molecule absorbs a photon and is promoted to an excited electronic state (Sn).
Franck-Condon Principle: Transition occurs rapidly without nuclear motion
Vibrational Relaxation and Internal Conversion:
Excited molecules relax to the lowest vibrational level of S1 before emission (Kasha’s Rule).
Fluorescence Emission:
Molecule returns to the ground state by emitting a longer-wavelength photon (lower energy).
Kasha's rule
Same fluorescence emission spectrum is generally observed irrespective of the excitation wavelength.
QY, Lifetime, Anisotropy
Quantum Yield (Φ) Fraction of absorbed photons that result in fluorescence:
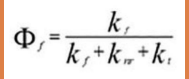
High Φ = Efficient fluorescence, Low Φ = Quenching or nonradiative decay
Fluorescence Lifetime (τ) = Average time a molecule stays in excited state before emitting a photon
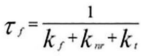
Measured using Time-Correlated Single-Photon Counting (TCSPC).