Lesson 1.1 Beginning with Bones - Human Body Systems
Activity 1.1.4 Looking Inside of Bone
Bone’s Unique Architecture
Compact Bone: A solid/hard layer that makes up the shafts of long bones or the outer layer of all bones
Spongy Bone: A porous bone found in animals containing red bone marrow
Type of Bone | Description | Examples | Image |
Flat Bone | A layer of spongy between two thin layers of compact. Marrow exists, but there is no marrow cavity. | Occipital, Parietal, Frontal, Nasal, Lacriminal, Vomer, Sternum, Ribs, and Scapulae |  |
Long Bone | Consisting of a shaft with two ends (longer than wide). Thick outside layer with a marrow-filled cavity, with the ends containing spongy bone. | Clavicle, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Metacarpus, Phalanges, Femur, Tibi, Fibula, and Metaarsus |  |
Irregular Bone | Thin layers of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone (doesn’t fit previous descriptions) | Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Palatine, Temporal, Zygomatic, Maxilla, Mandible, Vertebrae, Saccrum, Coccyz, Hyoid, and Inferior Nasal Concha | 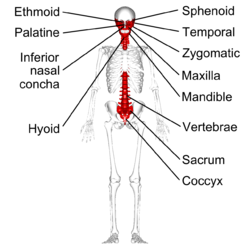 |
Short Bone | Roughly cube shape with vertical/horizontal dimension being equal. Mostly spongy, outside surface is a thin layer of compact. | Carpals, Tarsals, and Patella | 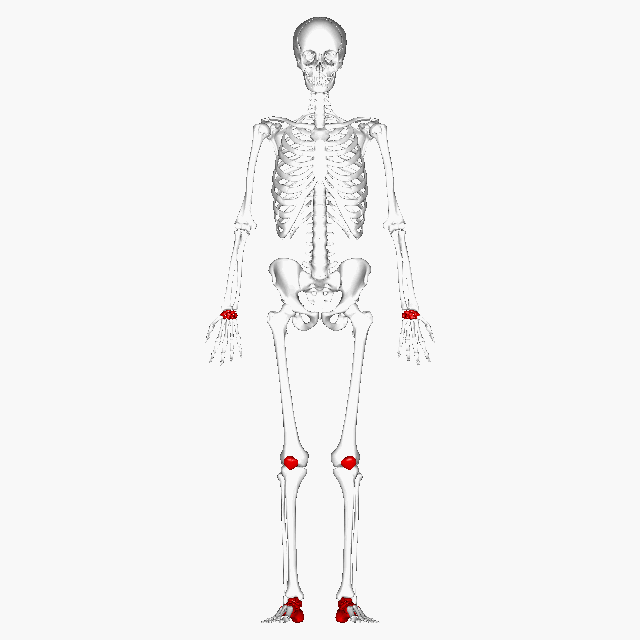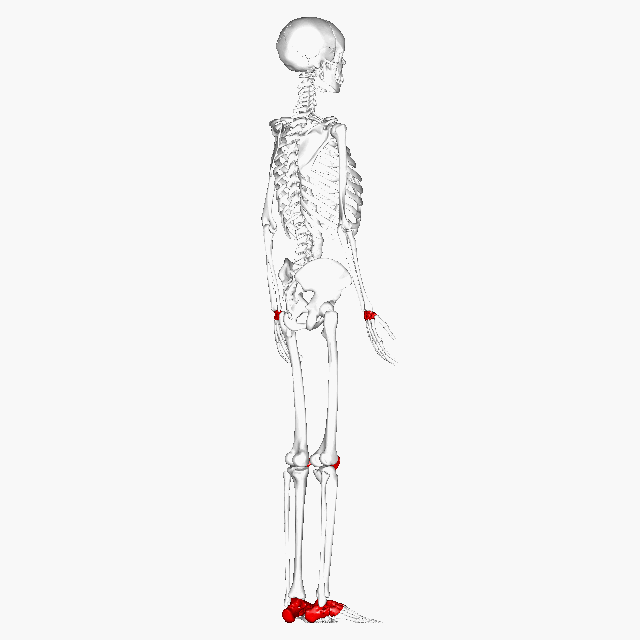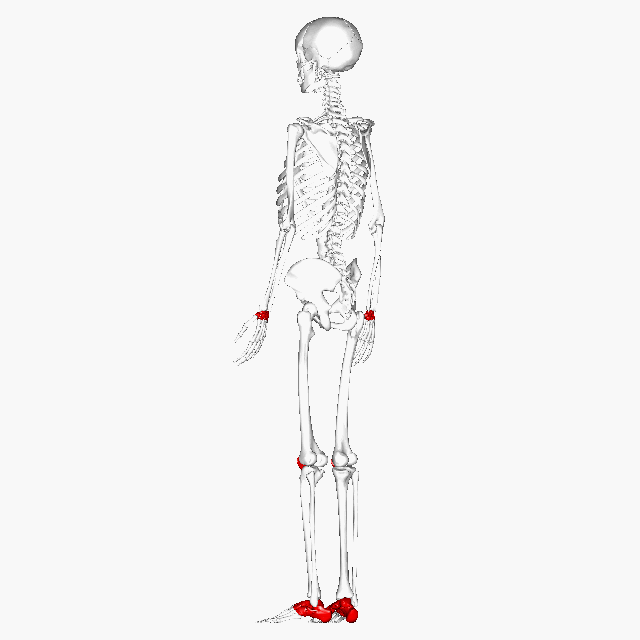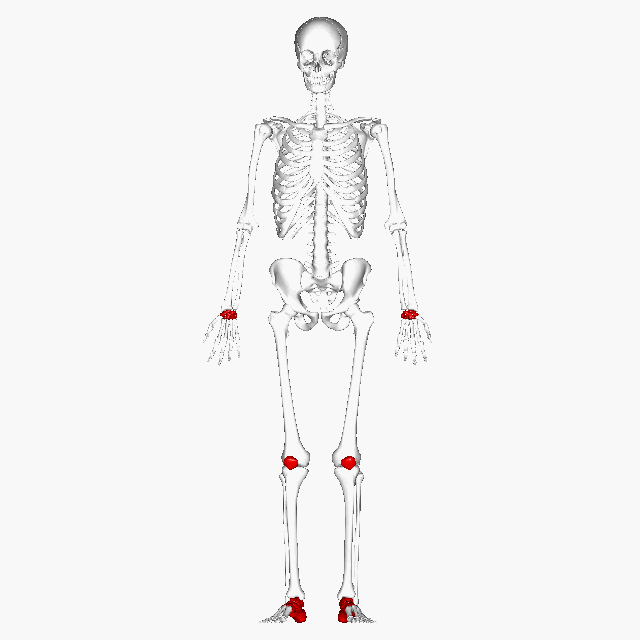 |
Upon Closer Examination

The femur has two heads (epiphyses), and a middle shaft (diaphysis)
Both epiphyses contain vessels and trabecular (spongy) bone
-trabecular is organized in a honeycomb-like framework, ideal for weight support
- red bone marrow is located in the epiphyses
The diaphysis contains the medullary cavity (long space filled with vessels/yellow bone marrow)
Compact or Cortical bone is located around the perimeter of the diaphysis/surrounds the medullary cavity (denser than spongy)