Unit E: Integumentary System
Day 1
Skin
Subcutaneous (Hypodermis)
Melanocyte
Sudoriferous (Sweat Gland)
Sebaceous (Oil) Gland
Pacinian (Nerve Receptors) Corpuscle
Dermis
Hair Shaft
Hair follicle
Arrector (Erector Muscle0
Epidermis - 5 layers
Overall 7 Functions of Integumentary System
Protection - dehydration, injury, germ invasion
Regulation - body temperature (sweat/shiver)
Manufacture Vitamin D - (bones / teeth development - calcium/phosphorus metabolism)
Supports nerve receptors for sensory - pain/temperature
Storage - fat, glucose, water, minerals (salt)
Absorption - drugs, chemicals, lotion
Screening UV Rays from sunlight
Structure: (Epidermis → Dermis → Hypodermis)
Epidermis Structure and Function
Outermost Covering
Made of dead epithelial cells
Avascular (no blood vessels)
Keratin protein keeps skin dry, waterproof, and barrier from outside pathogens
Merkel cells - sensory receptors
Contain melanocytes make melanin (skin color) important in UV protection
Langerhans cells - macrophages that fight infections and protect skin
5 Layers: Stratum Corneum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum basale
Dermis Structure (True Layer)
Connective Tissue
Collagen Tissue bands
Elastic Fibers
Numerous blood vessels
Nerve endings
Muscles
Hair Follicles
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
Sidoferous (Sweat) Glands
Fat (Adipose) Tissue
Function
Middle Layer
Makes sweat and oil
Responds to injury, infection, or allergy (histamine - response to allergy and heparin - blood clotting)
Allows for senses due to nerve receptor
Subcutaneous Layer Structure and Function
Superficial Fascia
Hypodermis
Loose connective tissue
Stores ½ of the body’s stored adipose (fat) tissue
Controlling body temp
Attaches skin to muscle and bone
With age, the subcutaneous layer begins to disappear (causing the skin to sag and wrinkle)
Day 2
Overall Functions of the Integumentary
Protection- dehydration, injury, germ invasion
Regulation- body temperature (sweat/shiver)
Manufacture Vitamin D-(bones/teeth development-calcium/phosphorus metabolism)
Supports nerve receptors for sensory- pain/temperature
Storage-fat, glucose, water, minerals (salt)
Absorption- drugs, chemicals, lotion
Screening UV rays from sunlight
Appendages:
Hair
Nails
Glands
Sudoriferous (Sweat) Glands
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
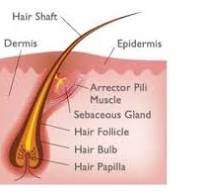
Hair Structure
Shaft
Cortex
Root
Hair follicle
Papilla
Arrector (erector) pili muscle
Sebaceous (oil) Gland
Hair Functions
What is the function of hair?
protection, regulation of body temperature, and perspiration
What factors influence hair type and color?
Shape of hair follicle determines type
Cortex contains pigments to determine color
What happens to your hair when you are cold? Why?
From a chill skin will surround hair raising it from the skin's surface
Nail Structure
Nail body made of keratin
Nail Body forms over Nail Bed to protect it
Originate from the nail root or nail Matrix
Nails Functions
What does the condition of a person’s nails tell about their general health?
One's habits
Anxiety level
Other health problems
Sudoriferous(Sweat) Glands of the Integumentary System
Sweat glands
Present in large numbers under arms, palms of hands, and soles of feet
Why does sweat smell bad?
Type of sweat produced in your armpits and groin combines with bacteria found normally on your skin breaking down sweat into acids
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands of the Integumentary System
Where are they located?
Microscopic glands next to hair follicle
What is their function?
Make sebum (oil) fluid that lubricates the skin and hair
The skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself.
Day 3
Skin Lesions:
Macule
Flat area with a noticeable change in color
Ex: Freckle, Birthmark, Su Spot
Ulcer
Deep loss to skin surface into dermis
Can bleed or scar
Example: Decubitus Ulcuer
Pressure Ulers / Bed Sore
Treatment: Prevention, Avoid infection
Prevention: Frequent Turning / Movement
Papule
Elevated Solid Area
Example: Nevi (mole)
Pustule
Pus filled raised area
Example: Pimple, Acne
Example: Chicken Pox, Shingles, Insect Bite, Herpes
Burns
1st degree
Superficial
Dry
Red
Treat: Cold Water or Compress
2nd Degree
Partial thickness
Blistered
Moist
Red & Pink
Treat: meds & sterile dressing changes
3rd Degree
Full thickness
Eschar (Charring)
Black, Red, Brown
Treat: Life threatening
Risk of
Fluid loss
Infection
Deformity
Acne Vulgaris
Non Contagious chronic disorder of the sebaceous (oil glands)
Oil becomes hard and clogs pore openings leading to accumulation of leukocytes and pus
Treatment: Topical medications or antibiotics if skin infected
Prevention: Wash face 2 times a day
Athletes Foot
Cause: Contagious fungal infection on the superficial layer of skin
Symptoms: Small blister between fingers/toes
Cracking and scaling
Where do you get it: Public locker rooms or showers
Treatment: Antifungal creams and powders
Dermatitis / Eczema: How are dermatitis and eczema similar
SImilarities
Inflammation of the skin
Cause a rash red, raised, dry
Urticaria (hives) - intense itchy wheels or welts, scaly or bumpy vskin
Different
Dermatitis develops from stress or irritant
Eczema develops from allergic reactions in 1st year of life
Treatment: Topical medications with hydrocortisone
Herpes
Cause: Viral Contagious
HSV Type 1: Herpes SImplex: Blisters on mouth
HSV Type 2: Blisters on genitals
Spread: Oral contact treated with antiviral (Valtrex / Zovirax) or creams
Prognosis
Active and Remission of symptoms
Life Long No Cure
What two bacteria cause Impetigo
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Symptoms: Ruptures vesicles with yellow crusty lesions
Risk Factors
Young Children 2 - 5
Daycare Cildren
Treatment: Antibacterial Creams
Antibiotic Medications
Psoriasis
Autoimmune disorder
Red patches covered with white scales
Usually occurs on knees, shins, scalp, & elbows
Who is likely to have psoriasis?
Stress
Obesity
What is the treatment?
Humira
Moisturizers
Ringworm
How is it spread?
Contagious
Locker Rooms
Pool decks
Pets
What causes ringworm?
Fungus
What is the medical term?
Tinea
How is it treated?
Antifungal drugs (Diflucan)
Antifungal creams (Lamisil)
Scabies
What is the cause of scabies?
Tiny burrowing mite
Is it contagious: Highly
How is it treated?
Scabicide Meds by prescription only
Deep clean clothes, sheets, etc.
How is it prevented?
Avoid skin-to-skin contact
Shingles
Cause: Virus similar to Herpes simplex
Caused by Herpes Zoster
Contagious: Yes when blisters present
Who is most at risk?
Elderly
Weakened immune system
Prevented with Vaccine
Three types of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Malignant melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most common and least malignant
Full recovery in 90% of patients
Most common to develop on the face
Treated with cryosurgery
Squamous Cell Carcimona
Treated with radiation
Surgical removal
Grows more rapidly
Common on face, head, tops of hands
Malignant Melanoma
Occurs in the melanocytes
Metastasize quickly
Color or size change in wart or mole (dark brown or black)
Surgical removal and chemotherapy
Warts
What causes warts?
Virus within the Human Papillomavirus virus (HPV)
Are they contagious?
Skin-to-skin contact with the virus
May or many not get a wart-unsure why
Can come back after heal
Can they be prevented?
Wash hands
Good hygiene in locker rooms and bathrooms