D.1
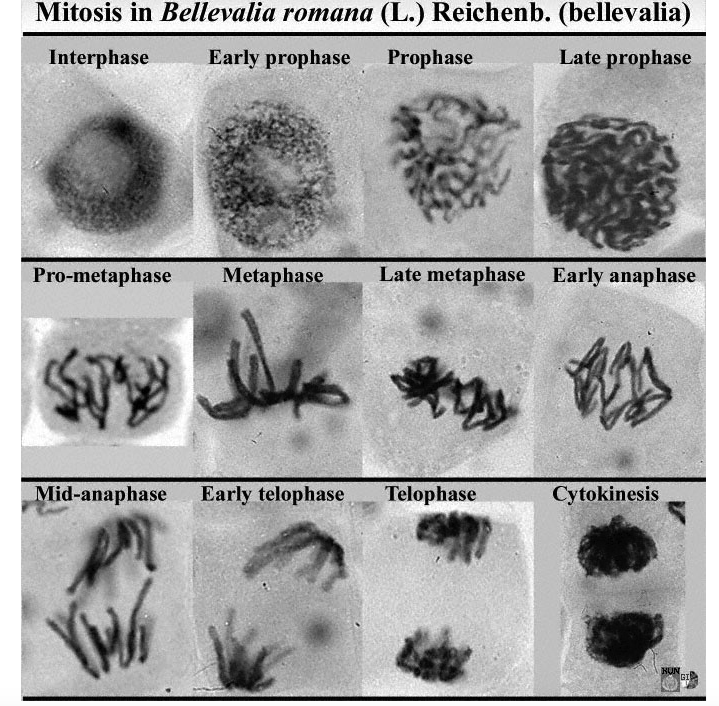
Mitosis
Interphase
To grow and heal and repair, you need more cells. Mitosis happens more frequently in embryos. We constantly need to create more cells. It also happens in asexual reproduction.
Proliferation: Rapid increase in cell number through mitosis.
Start with G1, which is growing and doing its job. The G stands for gap, but it basically means growth. Then you go through the synthesis, or s, phase, where you synthesize DNA (replicate it). After that, you go through another G phase, but you also start preparing for mitosis. This is all called interphase.
Interphase: The gap between mitosis where a cell grows, does its job, prepares for mitosis, and synthesizes proteins.
Chromosomes: Condensed form of DNA. If before S phase, looks like a chromatid
Chromatid: half of a chromosome. Only occurs after S phase.
Chromatin: Spaghetti for of DNA
Centromere: center of a chromosome
To count chromosomes, count centromeres
Diploid: 2 sets of each chromosome, somatic cells - mitosis
Haploid: 1 set of each chromosome, gametes - meiosis
Gamete: sex cell
What happens in interphase:
Metabolic reactions: respiration to produce ATP
Protein synthesis
Organelle numbers are increased
DNA is replicated
S phase goes from one chromosome to one chromosome (it now has two chromatids). The chromatids separate during mitosis.
We super coil (turn DNA from spaghetti to little bitty thing) so we can split it exactly and fit it inside the nucleus.
Mitosis
Mitosis: the division of the nucleus into two genetically identical nuclei
Cytokinesis: the splitting of the cell, not part of mitosis.
Prophase:
DNA condenses into chromosomes
the nuclear membrane breaks down
the centrioles start creating spindle fibers
the centrioles move to the poles
Metaphase
Chromosomes go to the middle of the cell
Spindles attach to the chromosomes at the centromere
Quick phase, visible by chromosomes in middle
The nucleus is completely gone
The equator is the middle of the cell (metaphase plate)
Kinetochore: when the spindles connect to the centromere, a kinetochore is formed
Anaphase
In a microscope, you see two distinct lines
The centrioles act like gears and pull the chromatids away from each other
Telophase
The nuclear membranes reappears
The spindle fibers detach and break down
DNA relaxes
You can’t see individual chromosomes in telophase
Late telophase is where the plasma membrane pinches
Cytokinesis is the splitting of the cell.
In animal cells: A microfilament ring forms around the equator, and it tightens into a cleavage furrow, and then you have two cells.
In plant cells: you form a cell plate and build the cell wall between both cells
Result of mitosis: Two identical diploid daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes in each and they have the same DNA
Mitotic Index = number of cells in mitosis / total number
Too much is cancer
Phases of Mitosis practice