
HEART ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
HEART
Located at the left side of mediastinum
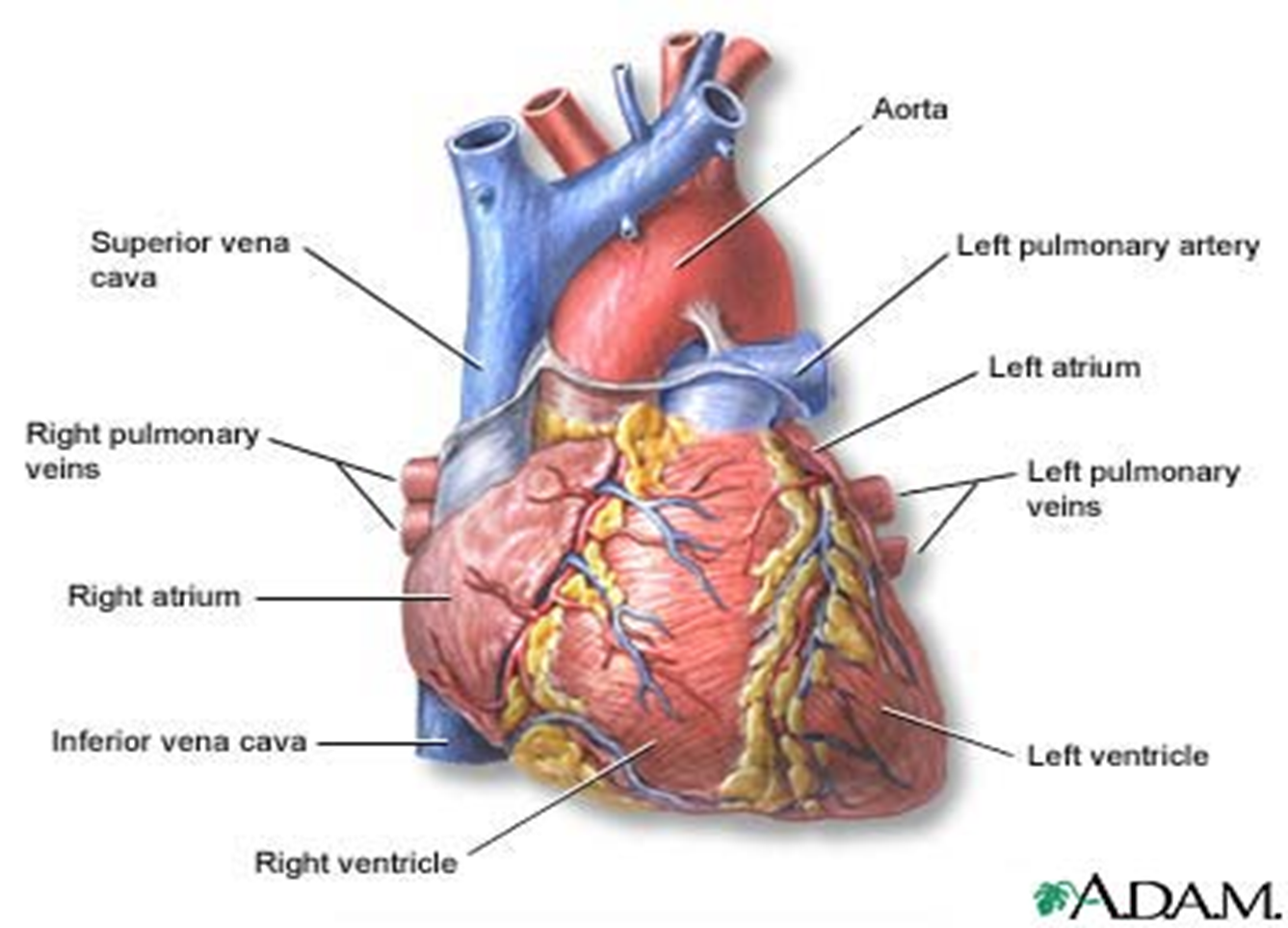
A. LAYERS
Epicardium - covers the outer surface of the heart
Myocardium - middle layers; contracting muscle
Endocardium - innermost layer; lines inner chamber and heart valves
B. PERICARDIUM - encases and protects the heart from trauma and infection
Parietal Pericardium - Tough fibrous membrane that attach to the sternum, thoracic vertebrae and diaphragm
Visceral Pericardium - Thin membrane that attach to the heart
Pericardial Space - In between: holds 5-20 ml 0f fluid which lubricates the pericardial surfaces
C. HEART CHAMBERS
Right Atrium - receives deoxygenated blood from the body via SVC and IVC
Right Ventricle - receives blood from the RA and pumps it to the lungs via Pulmonary Artery
Left Atrium - Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the 4 pulmonary veins
Left Ventricle - largest and most muscular chamber and receives oxygenated blood from the LA and pumps blood into the systemic circulation via aorta
D. HEART VALVES
Atrio-Ventricular Valves - lies between the atria and the ventricles Closed at the beginning of ventricular contraction and prevents blood from flowing back to the atria, Opens when ventricles relax
Semilunar Valves - Opens when ventricles contact and prevent blood from flowing back into ventricles, Closed when ventricles relax
Bicuspid or Mitral Valve - located at the left side of the heart
Tricuspid Valve - located at right side of the heart
Pulmonic Valve - Between RV and Pulmonary Artery
Aortic Semilunar Valve - Between LV and Aorta
E. ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF THE HEART
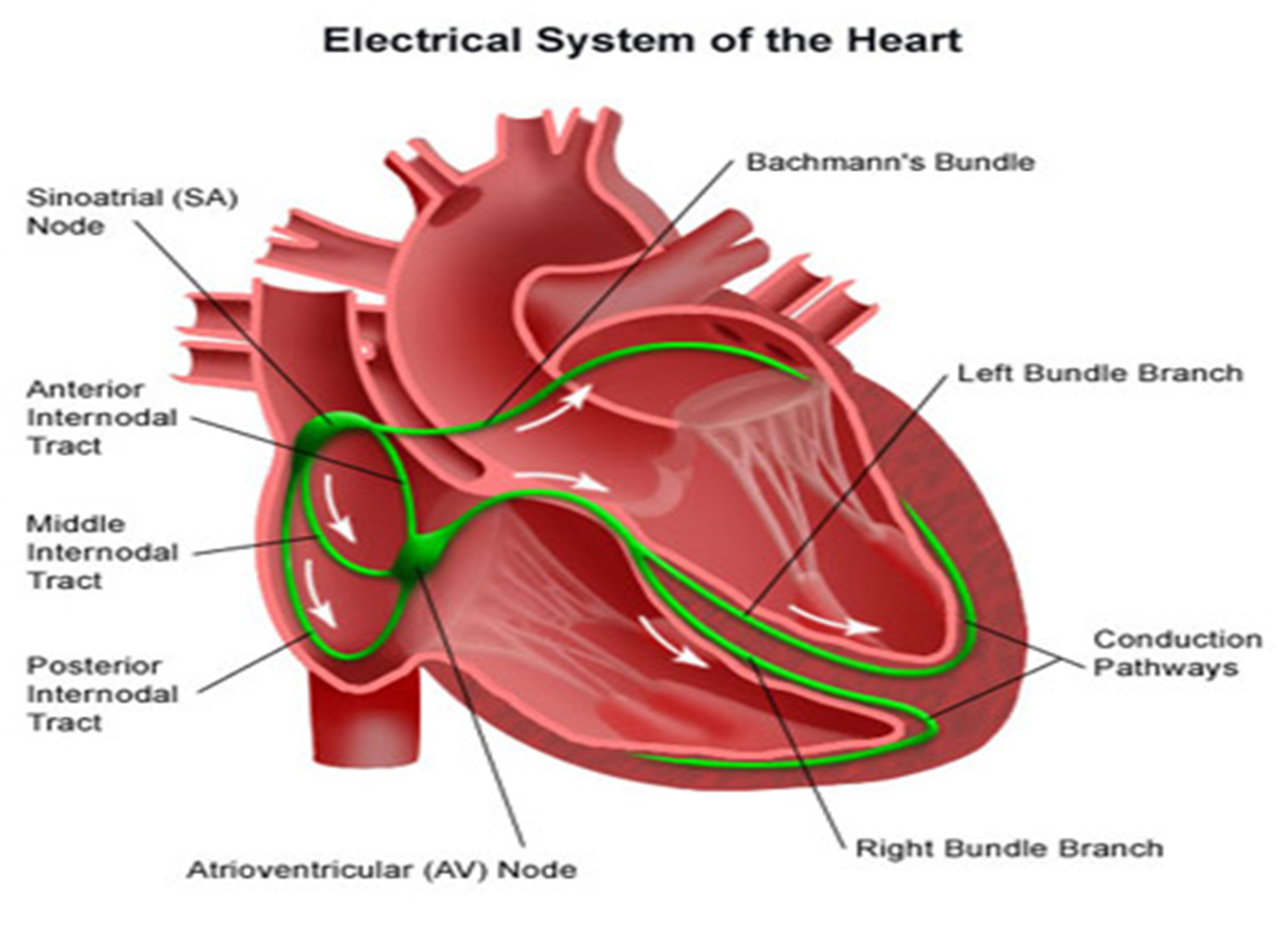
Sinoatrial Node (SA node) - Pacemaker of the Heart; initiates each heart beat
Located at junction of SVC and RA
Generates electrical impulse at 60-100 times/ min
Atrioventricular Node (AV node) - Located at the lower aspect of the atrial septum
Receives electrical impulse from the SA node
Bundle of HIS (AV Bundle) - Fuses with AV node to form another pacemaker site
Branches into the left and right Bundle Branch and terminates into Purkinjie Fibers
If SA node fails it can initiate and sustain HR of 40-60bpm
Purkinjie Fibers - Spread waves of depolarization through ventricles
F. CORONARY ARTERIES - Supply the myocardium with blood
G. HEART SOUNDS
S11st heart sound - heard when AV valve closed
S2 2nd heart sound - heard when semilunar valve closed
S3 3rd heart sound - CHF
S4 4rth heart sound - HTN
HEART ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
HEART
Located at the left side of mediastinum

A. LAYERS
Epicardium - covers the outer surface of the heart
Myocardium - middle layers; contracting muscle
Endocardium - innermost layer; lines inner chamber and heart valves
B. PERICARDIUM - encases and protects the heart from trauma and infection
Parietal Pericardium - Tough fibrous membrane that attach to the sternum, thoracic vertebrae and diaphragm
Visceral Pericardium - Thin membrane that attach to the heart
Pericardial Space - In between: holds 5-20 ml 0f fluid which lubricates the pericardial surfaces
C. HEART CHAMBERS
Right Atrium - receives deoxygenated blood from the body via SVC and IVC
Right Ventricle - receives blood from the RA and pumps it to the lungs via Pulmonary Artery
Left Atrium - Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the 4 pulmonary veins
Left Ventricle - largest and most muscular chamber and receives oxygenated blood from the LA and pumps blood into the systemic circulation via aorta
D. HEART VALVES
Atrio-Ventricular Valves - lies between the atria and the ventricles Closed at the beginning of ventricular contraction and prevents blood from flowing back to the atria, Opens when ventricles relax
Semilunar Valves - Opens when ventricles contact and prevent blood from flowing back into ventricles, Closed when ventricles relax
Bicuspid or Mitral Valve - located at the left side of the heart
Tricuspid Valve - located at right side of the heart
Pulmonic Valve - Between RV and Pulmonary Artery
Aortic Semilunar Valve - Between LV and Aorta
E. ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF THE HEART

Sinoatrial Node (SA node) - Pacemaker of the Heart; initiates each heart beat
Located at junction of SVC and RA
Generates electrical impulse at 60-100 times/ min
Atrioventricular Node (AV node) - Located at the lower aspect of the atrial septum
Receives electrical impulse from the SA node
Bundle of HIS (AV Bundle) - Fuses with AV node to form another pacemaker site
Branches into the left and right Bundle Branch and terminates into Purkinjie Fibers
If SA node fails it can initiate and sustain HR of 40-60bpm
Purkinjie Fibers - Spread waves of depolarization through ventricles
F. CORONARY ARTERIES - Supply the myocardium with blood
G. HEART SOUNDS
S11st heart sound - heard when AV valve closed
S2 2nd heart sound - heard when semilunar valve closed
S3 3rd heart sound - CHF
S4 4rth heart sound - HTN
 Knowt
Knowt