2/18/25
VOICES!
blue jay
yellow rumped warbler
carolina chickadee
cricket frog
cardinal
tufted titmouse
mockingbird
- if we get cricket frog on the quiz, just put cricket frog
midterm is just lecture stuff (No ID)
Biology and Diversity of Mammals
Characteristics of mammals
uniquely modified skull (jaw, ear, zygomatic arch)
heterodont dentition
Specialized skeleton, especially feet
hair (another time of keratinized epidermis)
dermal muscles (also in birds)
like hair going up on a dogs back (the dermal muscle be doing that)
mammary glands (and other skin glands)
endothermy
Origin and diversity of mammals, class Mammalia
Mammal-like reptiles diverged from the stem reptiles about 300 mya
Theraspsida, a clade that includes mammals
reptilian vertebral column and ribs
mammalian limb orientation - under the trunk
mammalian and reptilian skull characteristics
Mammalian skull characteristics
zygomatic arch
coronoid process of dentary
heterodont dentition (teeth with different shapes)
Reptilian Skull characteristic
jaw articulation at the rear of the jaw on the articular
Evolution of the mammalian jaw
appearance of heterodont teeth, some with multiple roots
loss of jaw bones (articular moves to the middle ear, only dentary remains)
enlargement of coronoid process
Molecular phylogeny of the mammals
3 old clades
monotremes (platypus (egg-laying mammals))
marsupials
eutherians (true placentals)
Major eutherian clades
present by late cretaceous
Eutherian diversification
after K-Pg extinctions (65 mya)
Dentition and dental formulas
I = incisor
C = canine
P = premolar
M = molar
the amount of I, C, P, and M in the upper and lower jaws can be used to find out which animal, or what type (like carnivores, or bats)
Opossum - relatively primitive, lots of teeth (few in carnivores (eutherians))
Typical carnivore skull - specialized for tearing
carnassial tooth (long tooth for tearing) in canids is a premolar on the maxillia and a molar on the manible
White-tailed Deer - ungulate skull
highly specialized for plant diet
often lose upper incisors
usually lose canines
long, flat molars and premolars with irregular surfaces
More dentition
rodents have unique teeth
Armadillo skull - bizarre
peg-like, single-rooted teeth are often not classified as incisors
Hispid Cotton Rat skull - typical rodent
highly derived - loss of lots of teeth
elongated incisors (do keep growing)
no canines or premolars
few broad molars
Mammal feet
Plantigrade (primate) - primitive
Digitigrade (carnivores) - derived
Unguligrade (ungulates) - most derived
Skin glands unique to mammals
mammary glands - provide nourishment for young during postnatal growth (milk stimulated by endocrine system)
sweat glands - promotes evaporative cooling and eliminates waste - typically restricted in location
sebaceous glands - secretions lubricate hair and skin
Hair (also called pelage)
keratin-based product of epidermis
critical for endothermy
pelage patterns important for communication or crypsis
hair oriented by dermal muscles
Endothermy - circulatory system
complete separation of systemic and pulmonary circulation (4 chambered heart, 2 chambers receive blood and 2 pump blood)
many mammals can alter heart rate
hibernation
carnivore lethargy, alarm bradycardia (‘freezing’)
bats - resting and active heart rates differ by 500 beats per minute, and change within 1 second
Only in endotherms, with high oxygen demand, is it critical always to separate oxygenated blood (coming from the lung) from deoxygenated blood (coming from the body’s capillary beds)
Fat and energy storage
not unique to mammals, but important for energy storage, source of heat and water, and insulation
temperate mammals typically have localized fat storage
boreal and aquatic species store fat subcutaneously over the body
Respiratory system
disphragm - unique to mammals[
heart and particularly lungs are large relative to body surface - required for endothermy
exchange of gases occurs via alveoli, where oxygen enters bloodstream
lung surface - humans have 70 m² of lung surface, about 40x the surface area of the body
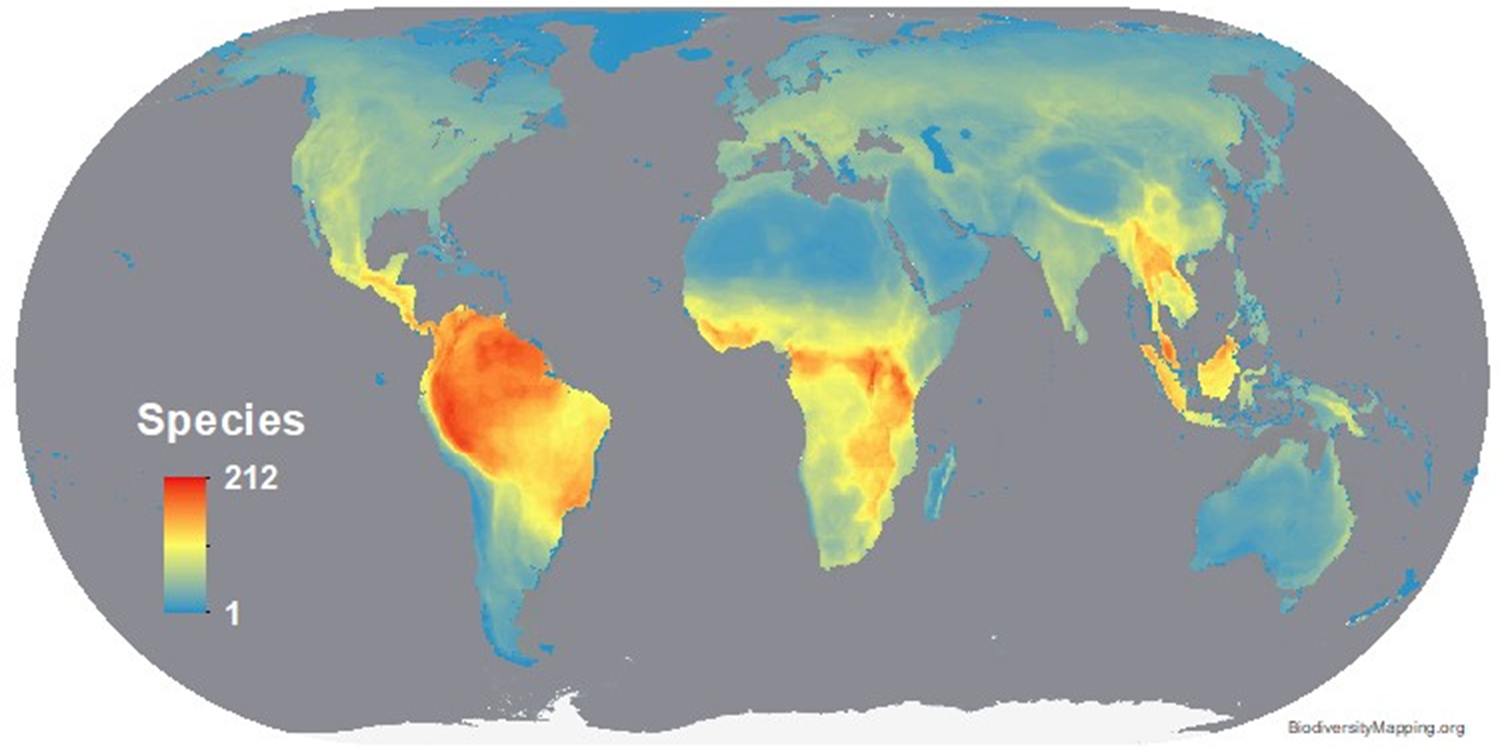
Worldwide terrestrial mammal diversity (~5400 species terrestrial + aquatic)
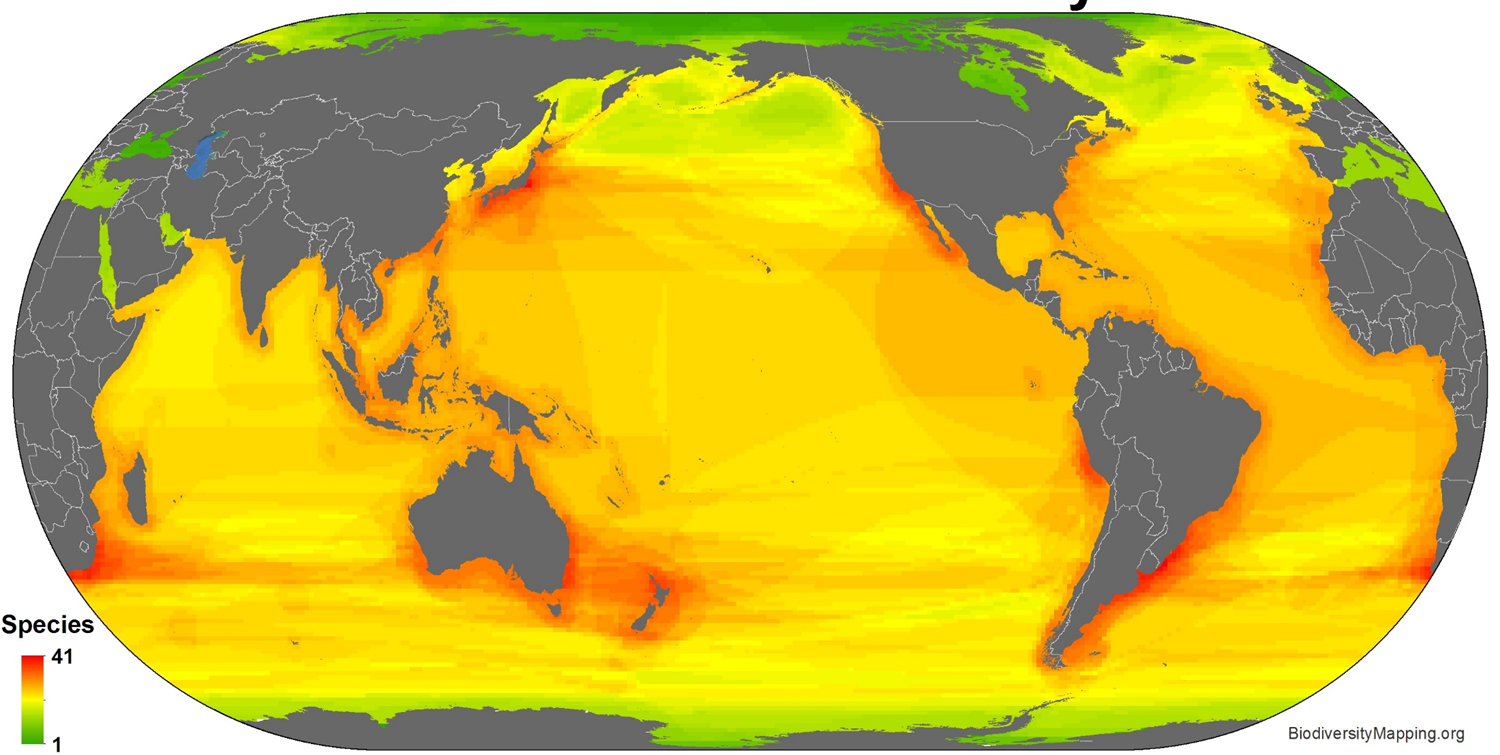
Marine mammal diversity
Diversity of Louisiana Mammals
10 orders, 69 species excluding domestic species
Didelphimorphia (opossums) - 1
Cingulata (armadillos) - 1
Sirenia (manatees, dugongs) - 1
Cetacea (whales, dolphins) - 1 (+8 possible offshore)
Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) - 1 (+1 introduced)
Chiroptera (bats) - 12
Eulipotyphla (shrews, moles, hedgehogs) - 5
Carnivora (carnivores)
Canidae (dogs) - 3 (+extirpated Red Wolf)
Felidae (cats) - 2
Mephitidae (skunks) - 2
Mustelidae (weasels, otters) - 3
Procyonidae (raccoons, coatis) - 2
Ursidae (bears) - 1
Rodentia (rodents)
Castoridae (beaver) - 1
Geomyidae (pocket gophers) - 1
Heteromyidae (pocket mice) - 1
Cricetidae (New World rats and mice) - 10
Muridae (Old World rodents) - 3 (introduced)
Echimyidae (nutria and spiny rats) - 1 (introduced)
Sciuridae (squirrels, chipmunks) - 4
Lagomorpha (rabbits) - 2
Primates - 1
Who is absent from LA - why?
orders absent from LA (of ~26 total)
Monotremata (monotremes - platypus and echidnas)
5-6 orders of marsupials
5 ‘afrotherian’ orders (hyrax, elephants, aardvarks, etc. plus manatees)
Pilosa - anteaters and sloths
Primates (+ 2 related orders - treeshrews and flying lemurs)
Philodota - Pangolins
Compare to -
birds - 30-40 orders total, 1/3 absent from LA
Amphibians - only 1 orders (of 3 total), caecilians is absent
Reptiles - 1 order (of 4 total) tuataras, is absent
terrestrial mammals couldn’t move from their land for a long time
Ecology of selected LA mammals
Virginia Opossum
common, habitat generalist
omnivorous
only representative of S. American marsupial radiation in N. America
short life span (1-4 years)
mating in Jan, 2 week gestation, young extremely dependent at birth
White-tailed Deer
Cervidae - deer
most common cervid in N. America
highly adaptable, habitat generalist
browser
considerable maternal investment, complicated social system
mate sept-march, gestation ~200 days
Red Bat
order Chiroptera - bats
Solitary
insectivorous
common in LA, particularly along riparian area
LA bats probably include migrants
our LA bats are part of an Old World radiation
delayed fertilization
parturition in May-June
Coyote
Family Canidae
generalist
distribution expanding
Keystone species in some systems - top carnivore in most of US
complicated and flexible social system with extended parental care
River Otter
Mustelidae - weasels
riparian areas throughout NA- mostly aquatic
primarily carnivorous
high social
delay implantation + long gestation = 11-13 months
Northern Raccoon
Procyonidae
omnivorous
dexterous
habitat generalist but often near water
family originated in northern New World
distributed from tropics to boreal forest
complex social structure
part of mesocarnivore release
Louisiana Black Bear
Ursidae
omnivorous, habitat generalists
geographically isolated to 3 pops in LA
listen under ESA in 1992
Historically most abundant in MAV
Considerable maternal investment
Beaver
Castoridae
manipulate aquatic systems - ecosystem engineers
generalist herbivores
established social/family groups
broad historical distribution in NA and Eurasia
Hispid Cotton Rat
Cricetidae - most New World Rats
Herbivorous, granivorous
early successional habitats
good swimmers
litters may range to 15 and have 2 pulses per year, multiple litters in each pulse
pops fluctuate within years, greatest density during fall
Nutria
Myiocastoridae
Nonnative wetland nuisance
severe effects on aquatic systems
generalist herbivores
nonseasonal breeders, first estrus can be at 6 months age (8 young/female/year)
Eastern Cottontail
Leporidae - rabbits
herbivore/granivore
widest distribution of any rabbit, occupies nearly every habitat
sympatric with other rabbits
may produce 3-6 litters annually, over entire year
may reach very high densities (lowery reprots >6 mil killed in Missouri in 1958)
Current marsupial distribution - Oldest fossils are 125 mybp from China, but Australian marsupials are descended from a S. American ancestor. maybe across Antarctica?
Ungulate diversity worldwide - East Africa
Wallace’s Line
New Guinea and Australia are distinct from neighboring Java, Sumatra, etc. because of a deep channel separating them. Java, Sumatra and Borneo are connected to Asia at times of low sea level