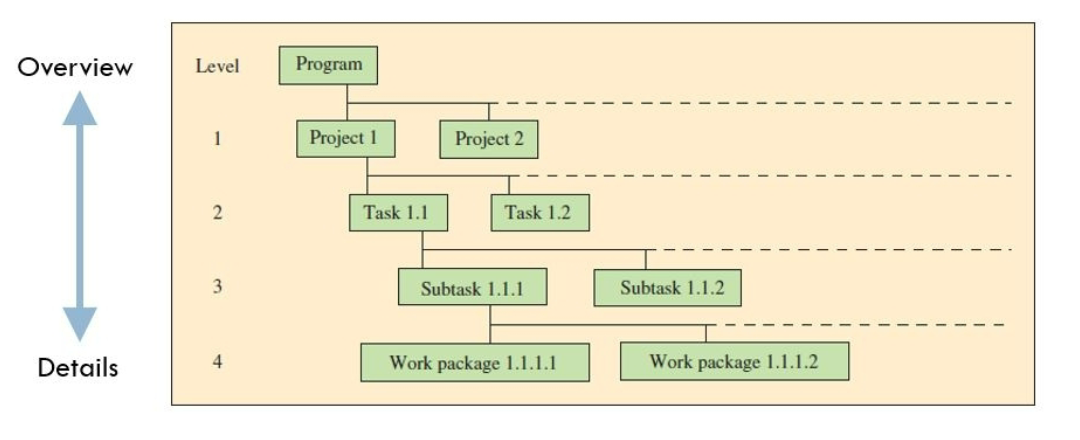
Project Management
Temporary and customized initiative that consists of many smaller tasks and activities that must be coordinated and completed
◦ Goal: To finish the entire initiative on time and within budget
What is project management?
Planning, directing, and controlling resources (people, equipment, material, etc.) to meet the technical, cost, and time constraints of the project.
Project definition
Defining goals, scope, risks, budget, timeline, and resources.
Identifying the activities that must be completed and the sequence
to perform them
Project planning
Determining resource and financing needs for each activity
Project scheduling
Specifying a time schedule for the completion of each activity
Project control
Establishing controls for determining progress and responding to problems
What makes a project successful?
Time, Cost, Quality, Client Satisfaction
Activities: Discrete tasks that consume resources and time
Immediate predecessors: Activities that must be completed immediately before an activity may start
◦ Precedence relationships ensure that activities are performed in the proper sequence when they are scheduled
Project network: Consists of nodes and arcs, which define the precedence relationships between activities
◦ Nodes: Set of circles or boxes, which represent activities
◦ Arcs: Set of arrows
◦ This is called an activity-on-node (AON) network representation
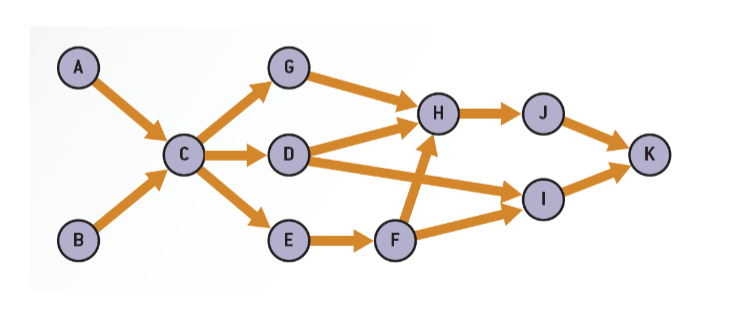
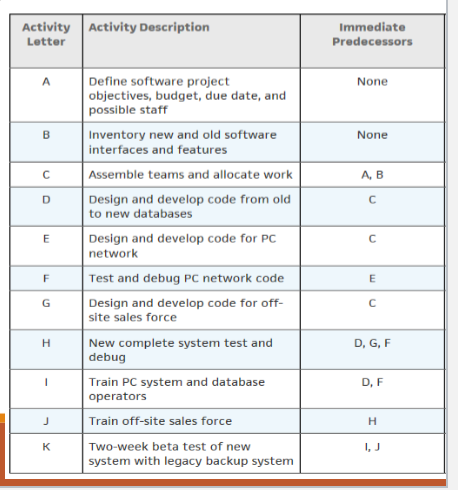
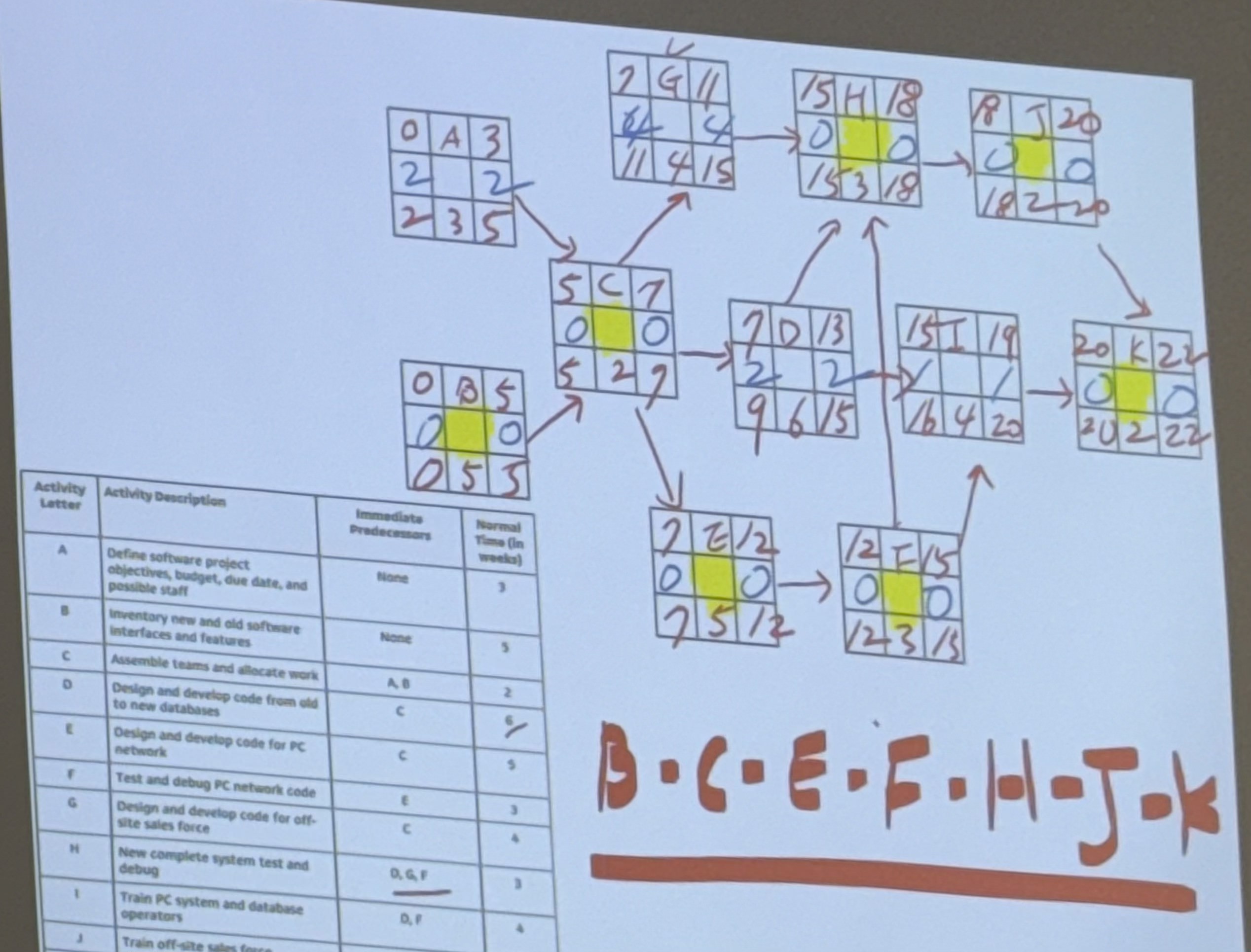
Critical path: Sequence of activities that takes the longest time and defines the total project completion time
We need to find two starting time and two ending times for each activity to conduct CPM
Earliest start (ES)- earliest possible date on which an activity can start
Earliest Finish (EF) – earliest possible date on which an activity can be completed
EF = ES + T, where T is activity duration
Latest start (LS) – latest possible date that an activity may begin without
delaying the project completion ; LS = LF - T
Latest Finish (LF) – latest possible date an activity can be completed without delaying the project completion; LF= LS + T
Slack time: is the length of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the entire project
Slack = LS –ES or LF –EF
Critical Path: Activities with Zero slack are critical activities
Project Crashing: is a technique used to shorten the project schedule by reducing the duration of critical path activities, often through additional resources or overtime.
Crash time: the amount of time that an activity can be shortened without affecting the overall project timeline.
Crash cost: the additional cost incurred when resources are added to expedite the completion of a critical path activity.
Crash cost per unit of time equation:
Crash Cost per Unit of Time = (Crash cost - normal Cost) / (Normal time - Crash Time)
Crashing an activity: the process of reducing the duration of a project by allocating extra resources to critical path activities, often resulting in increased costs but enabling faster project completion.
Uncertainty in Project Management
Project evaluation and review technique (PERT) is another approach to project management.
PERT was developed to handle uncertainties in activity completion times.
In contrast, CPM assumes that activity times are constant.
PERT planning usually involves the following steps:
1. Identifying Tasks and Milestones
2. Placing the Tasks in a Proper Sequence
3. Network Diagramming
Optimistic time - Activity time under ideal conditions
Most probable time - Most likely activity time under normal conditions
Pessimistic time - Activity time if breakdowns or serious delays occur
Expected Time = (a + 4m + b)/6
Variance = (b – a)2/36
◦ Where, a is the optimistic time estimate
◦ m is most likely or probable
◦ b is the pessimistic time estimate
PERT assumes a beta probability distribution