
Evolution by Natural Selection
The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
Independently proposed by multiple scientists in the 1850’s, however Darwin is the most prevalent due to his evidence and processes provided within his book The Origin of Species. Darwin’s theory of natural selection was “Not incorecct, just simply not complete”.
Form the basis for more advanced classes later in which Darwin’s ideas are combined with population genetics – what we call neo-Darwinism or the new synthesis. Darwin's mechanism is now known to have been correct but the processes of evolution and new species formation are both now know to be much more complex than Darwin suspected.

Videos
Evolution Primer: How does Natural Selection really work?
Conditions Necessary for Natural Selection to Occur
They must reproduce
Genetic Inheritence
Genetic Variation
Competition for Resources
Different variants must have different fitness
The successful competitors will, because they have more resources, be more likely to reproduce and to give rise to individuals that reach breeding age than will those individuals that got less or none of the resources. It’s not a clear cut case of one group of individuals breeding and another group or individuals not breeding, but instead there is a higher likelihood or probability that those individuals that have more resources will produce relatively more offspring compared to those individuals that get less resources.
Reproduction
Reproduction at the population level
Mendelian Inheritence
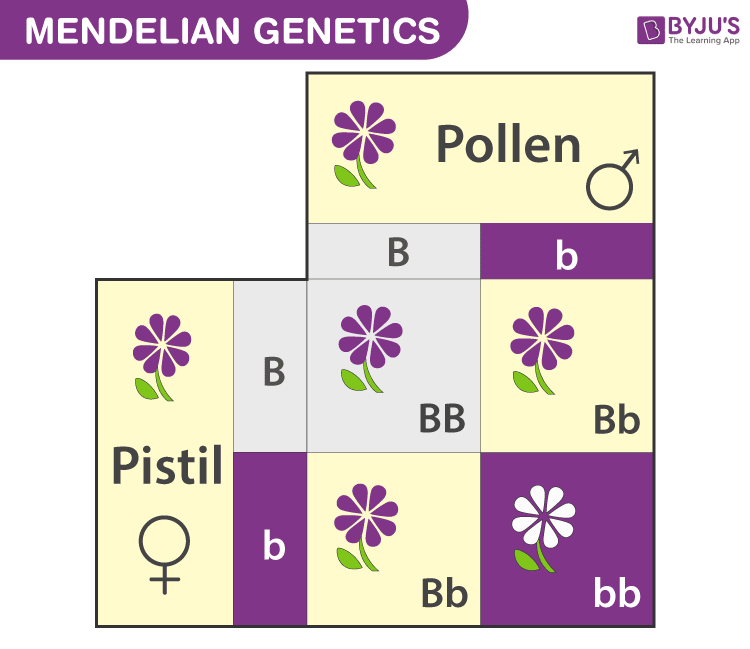
Characteristics of parents are passed to offspring
Darwin was unsure of how this happened but saw the occurance
Mendel’s work filled in the gap, “discrete things” passed from one generation to another unaltered
“Descrete things” were Genes
Genes do not blend, but a copy is passed down
If a blend was seen, natural selection would not be as efficient.
Phenotypical Variation
Variation is due to mutations within the genes
The main important mutations occur within Gametes, which cause changes in the phenotype
Competition
Competition holds selective pressure upon an organism due to finite resources
If there is no competition within a species, there will be no natural selection
The competitors need to fulfill the ecological niche or a similar one.

Different Fitness
In 1924, Haldone came up with a quantifiable defition to fitness propsed by Darwin and Mendel.
Simply put “survival of the fittest”
Quantifiable by numbering indivduals of a species that reach reproductive age, which allows for a mean of offspring to be created.
If the organism has a higher offspring count than the mean it has a higher fitness
Adaptation

NS leads to different adaptations in different ecological niches and this is a large part of why different organisms look different to one another. The idea of adaptation is central to the theory of evolution. An adaptation can be any kind of feature that favors the production of more offspring, than would otherwise be present in a particular environment.
Important to realize that fitness is relative to a particular habitat
Only natural selection produces adaptations but evolution can occur via genetic drift.
Natural selection works on adaptations simultainesouly
How much pressure is place upon a specific adaptation depends on the organism’s environment.
This is known as “Mosaic Evolution”
Evolution by Natural Selection
The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
Independently proposed by multiple scientists in the 1850’s, however Darwin is the most prevalent due to his evidence and processes provided within his book The Origin of Species. Darwin’s theory of natural selection was “Not incorecct, just simply not complete”.
Form the basis for more advanced classes later in which Darwin’s ideas are combined with population genetics – what we call neo-Darwinism or the new synthesis. Darwin's mechanism is now known to have been correct but the processes of evolution and new species formation are both now know to be much more complex than Darwin suspected.

Videos
Evolution Primer: How does Natural Selection really work?
Conditions Necessary for Natural Selection to Occur
They must reproduce
Genetic Inheritence
Genetic Variation
Competition for Resources
Different variants must have different fitness
The successful competitors will, because they have more resources, be more likely to reproduce and to give rise to individuals that reach breeding age than will those individuals that got less or none of the resources. It’s not a clear cut case of one group of individuals breeding and another group or individuals not breeding, but instead there is a higher likelihood or probability that those individuals that have more resources will produce relatively more offspring compared to those individuals that get less resources.
Reproduction
Reproduction at the population level
Mendelian Inheritence

Characteristics of parents are passed to offspring
Darwin was unsure of how this happened but saw the occurance
Mendel’s work filled in the gap, “discrete things” passed from one generation to another unaltered
“Descrete things” were Genes
Genes do not blend, but a copy is passed down
If a blend was seen, natural selection would not be as efficient.
Phenotypical Variation
Variation is due to mutations within the genes
The main important mutations occur within Gametes, which cause changes in the phenotype
Competition
Competition holds selective pressure upon an organism due to finite resources
If there is no competition within a species, there will be no natural selection
The competitors need to fulfill the ecological niche or a similar one.

Different Fitness
In 1924, Haldone came up with a quantifiable defition to fitness propsed by Darwin and Mendel.
Simply put “survival of the fittest”
Quantifiable by numbering indivduals of a species that reach reproductive age, which allows for a mean of offspring to be created.
If the organism has a higher offspring count than the mean it has a higher fitness
Adaptation

NS leads to different adaptations in different ecological niches and this is a large part of why different organisms look different to one another. The idea of adaptation is central to the theory of evolution. An adaptation can be any kind of feature that favors the production of more offspring, than would otherwise be present in a particular environment.
Important to realize that fitness is relative to a particular habitat
Only natural selection produces adaptations but evolution can occur via genetic drift.
Natural selection works on adaptations simultainesouly
How much pressure is place upon a specific adaptation depends on the organism’s environment.
This is known as “Mosaic Evolution”
 Knowt
Knowt