ESS 4.1-4.2
water cycle
most water on earth is: saltwater
water cycle storages:
- oceans
- soil mousture
- ice caps
- rivers/lakes
Transformation: change in state
transfer: chnage in location
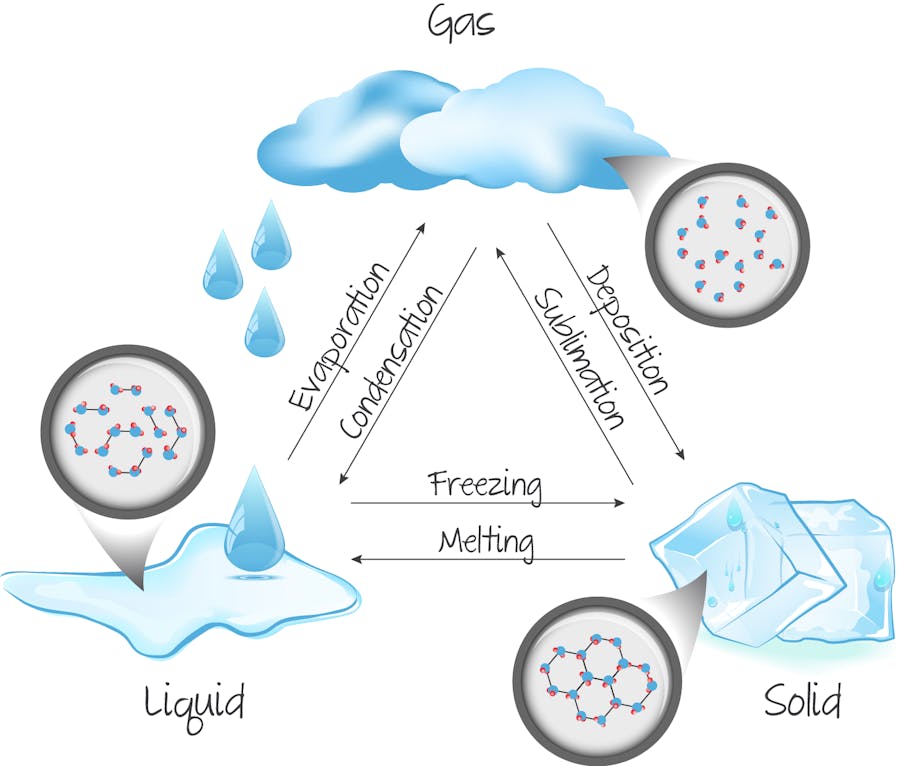
water cycle transformations:
- evaporation
- sublimination: solid → gas
- deposition: gas → solid
- condesation
- melting
- freezing
water cycle transfers:
- surface run off
- flooding
- precipitation
- absorption
water cycle:
vegetation (plants) : can slow movement of water
percolation: water flows into the ground, under influence of gravity
aquifer: underground zone
groundwater: largest freshwater source
ocean circulation systems
- Global conveyor belt: driven by differences in water density
- cold water is more dense
- saltier water is more dense
- water: high heat capactity → oceans warm & cool slowly
- atmosphere: low capacity
- how can global warming impact conveyor belt?
- if oceans become warmer they hold less carbon dioxide so with more co2 in the atmosphere, temperature rises even more
human act. on water cycle
- overall: changes in land use (human activity) impact water cycle
- deforestation:
- the trees absorb the water → forest acts as sponge
- with no forest → more runoff → floods
- urbanisation:
- water cannot pass through
- runoff catches pollutants from cities → lakes & streams
- high flood risk → no trees
- Agriculture:
- biggest water usage
- there is fertelizer and pesticide runoff
- excessive irrigation → poor soil
- how to avoid water pollution from this:
- limit fertelizers & pesticides
demand for water
- why?
- population growth
- more meat based diet → the production of meat uses more water
- Urbanization increase
- water stress: when demand exceeds availablity
managing water resources
- reservoirs: used to collect/store water → built by damming rivers & flooding valleys
- benefits:
- flood control
- water quality
- cons:
- chnage of habitat ecosystem
- relocation of people & species
- Desalination: makes freshwater from saltwater
- expensive
- greywater:
- using water from baths, washing machine
- can be used for toilet flushing, not ok to drink