Injuries and Disorders of the Skin- Chapter 3.3
The skin is routinely subject to minor injuries and is exposed to a variety of common infections.
Decubitus Ulcers:
Decubitus ulcers (bedsores)- skin injuries %%caused by an area of localized pressure%% that restricts blood flow
- %%Without normal blood supply%% to provide nutrients and oxygen, skin cells die
- Can occur anywhere on the body, but %%most form over bony areas%% such as the lower back, coccyx (tailbone), hips, elbows, and ankles
Bedsore treatment- prescription of oral antibiotics to address or prevent infection or removal of damaged tissues
Methods of tissue removal:
Debridement- the %%removal of dead tissue%% using a surgical or chemical procedure
Vacuum-assisted closure- vacuum tube is attached to the wound, it %%draws moisture%% from the ulcer
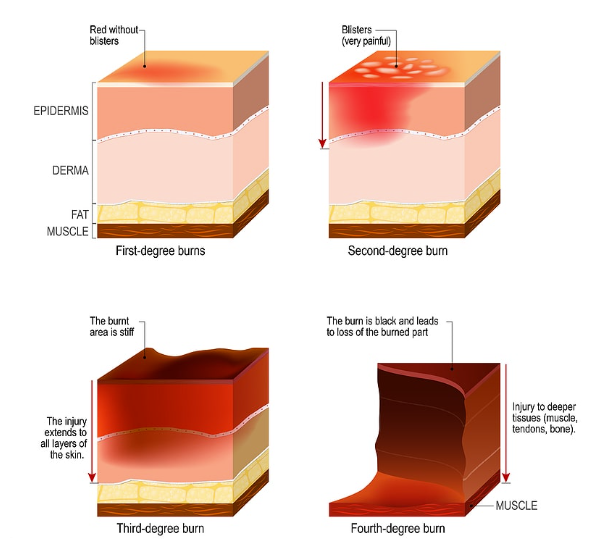
Burns:
First Degree- affects %%only the epidermal layer%% of skin, symptoms are reddening of the skin and mild pain
Second Degree- damage to both the %%epidermis and the upper portion of the underlying dermis%%, symptoms are very %%painful blisters%%
- These are both referred to as “partial-thickness burns”
Third Degree (full thickness burn)- destroys %%entire thickness%% of the skin, appear grayish-white or blackened, not painful due to %%nerve endings being destroyed%%
- Treatment includes skin grafting due to lack of ability to regenerate
 Viral Infections:
Viral Infections:
Herpes- viral infection that produces small, painful, blister-like sores
Herpes varicella (chickenpox)- a common childhood disease, highly contagious, spreads quickly and widely- symptoms are %%itchy, fluid filled blisters%%
Herpes zoster (shingles)- chickenpox can %%resurface%% as shingles in %%adult age%%, can be xtremely painful, symptoms are blistering rash with headache, fever, and feeling ill
- Can lead to more serious symptoms such as chronic nerve pain
- %%Vaccine%% for shingles is recommended for adults older than 60 years
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)- %%generates “cold sores”%% or “fever blisters” around the mouth
Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2)- %%genital form%% of herpes
- Person may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and swollen glands.
Common warts- typically appear on the hands or fingers and tend to disappear without treatment
Plantar warts- develop on the soles of the foot, %%grow inward,%% can become painful
- can be removed by surgery, cryotherapy (freezing), and topical medications such as salicylic acids
Fungal Infections:
%%tinea%%- tend to occur in areas of the body that are moist, fungal infections
tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)- the most common fungal infection, characterized by cracked, flaky skin between the toes or on the side of the foot, highly contagious
- tinea pedis treatment- keeping the feet clean and dry, especially between the toes, and using antifungal powder or cream
tinea cruris (jock itch)- primarily affects males around the groin and scrotum
- caused by the combination of prolonged sweating and friction from clothes
- spread through direct contact with infected skin or unwashed clothing
- tinea cruris treatment- typically is treated by keeping the skin clean and dry, wearing loose clothing, and applying a topical antifungal or drying powder
tinea corporis (ringworm)- %%red, ring-shaped rash%% with a pale center somewhat resembles the shape of a worm
- tinea corporis causes- prolonged sweating and %%poor hygiene%%, is especially common in children
- highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with the infection on someone’s body or through contaminated areas
tinea unguium- a fungal infection %%under the nails of the fingers or toes%%, it causes discoloration and thickening of the infected nail.
- treatment for tinea unguium- over-the-counter antifungal creams do not help this condition, a prescription antifungal medication must be taken orally for several weeks
Bacterial Infections:
Impetigo- a highly contagious %%staphylococcus%% infection
- impetigo symptoms- are %%pink, blister-like bumps%%, usually on the face around the mouth and nose, that develop a yellowish crust before they rupture
- common in elementary school children
Cellulitis- a %%staphylococcus%% infection, characterized by an %%inflamed area of skin%% that is red, swollen, and painful
- origin of cellulitis often is an %%open wound or ulceration%%
- a serious condition that can become life threatening if not treated with antibiotics
Inflammatory Conditions of the Skin and Membranes-
Pleurisy- is an %%inflammation of the pleura%%, the membrane that lines the thoracic (chest) cavity and lungs
- pleurisy causes- an infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, can also be caused by cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, injury to the chest, a blockage in the blood supply to the lungs, or the harmful presence of inhaled asbestos
Peritonitis- an %%inflammation of the peritoneum%%, the membrane that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers the abdominal organs
- Peritonitis causes- by the %%accumulation%% of blood, bodily fluids, or pus %%in the abdomen%%
- Peritonitis symptoms- abdominal pain and tenderness that may worsen with movement or touch, abdomen may also be swollen, can include fever and chills, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and decreased urine and stool output
Psoriasis- is a common skin disorder that involves %%redness and irritation%%
- Psoriasis symptoms- regions of thick, red skin with flaky, silver-white patches called scales that itch, burn, crack, and sometimes bleed
- Psoriasis is not contagious and may be hereditary, and typically develops between 15 and 35 years of age
Skin Cancer:
Basal cell carcinoma- most common form of skin cancer, also the %%least malignant%%
- caused by overproduction of cells in the stratum basale that push upward, forming dome-shaped bumps
- usually noticed and surgically removed before they can spread and become dangerous
Squamous cell carcinoma- caused by %%overproduction of cells in the stratum spinosum%% layer of the epidermis
- appear as a scaly, reddened patch that progresses to an ulcer-like mass with a raised border, grow rapidly and can easily spread to nearby lymph nodes
- With early removal by surgery or radiation treatment, these cancers can be completely cured
malignant melanoma- %%cancer of the melanocytes%%
- typically dark colored and irregular in shape, a malignant melanoma can appear pink, red, or “fleshy”
- change in the size, shape, color, or elevation of a mole are typical warning signs of a malignant melanoma.