Acropolis Parthenon - AP Art History notes (Golden Age)
About Acropolis Parthenon (Golden Age - Athens, Greece) 🏛
The Acropolis is destroyed by the Persians.
The Acropolis is dedicated to Athena.
Formula: ^^x = 2(y) + 1.^^
^^The Greeks believed this is the perfect equation for a building. (9:4 ratio).^^
^^Iktinos^^ and ^^Kallikrates^^ are responsible for the construction of the Pantheon.
Sculptures are designed by ^^Phidias. Sculptures are placed on the Metope of the Acropolis' Frieze.^^


Architecture 🏛
covered with a lot of relief sculptures.
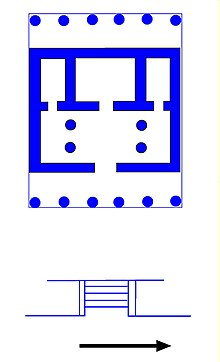
Types of Columns used:
- Doric (more plain/simple)
- Ionic (more curved capital design)
*The Acropolis (Parthenon) is rebuilt by war general **^^Pericles ^^*rather than spending the war money into defeating the Persians.
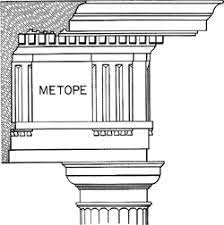
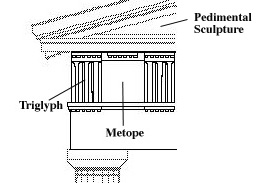
Sculpture are placed on the ^^Metope^^ of the Acropolis’ Frieze.
Metope: a square space between ^^triglyphs^^ in a Doric frieze. ^^(Contains statues).^^
- Metopes alternates between Triglyphs.
\
^^Frieze:^^ ^^Greek word for structure^^ ^^before the roof. Frieze always come before the roof.^^
Greeks would process to the Parthenon to honor the Gods.
Parthenon contains the Plaque of Egastines
(Ergastines are women weavers of peplos, changes peplos for Athena statue).
^^Triglyphs:^^ ^^A tablet in a Doric frieze with three vertical grooves^^. Triglyphs alternate with ^^metopes.^^ ^^Triglyphs are an aesthetic feature of Doric temples that do not serve any function besides design.^^
\
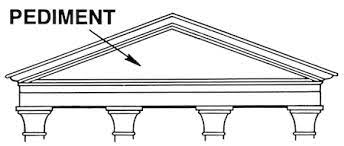
Pediment: ^^the triangular upper part of the front of a building^^ in classical style, typically surmounting a portico of columns.
- Images on the Frieze makes it;s way up to the ^^Pedement.^^
- Procession starts from the ^^Diplon cemetery^^ gates to the Acropolis and to the Parthenon.
Vocabulary:
- ^^metope^^
- frieze
- capital
- architrave
- ^^triglyphs^^
- Panatheanic Procession
- ^^Doric and Ionic^^ capitals
Plaque of Ergastines (Parthenon frieze) 🏛
Phideas depicted the people wearing ^^‘wet drapery’,^^ creates an illusion of creases and folds of clothing.
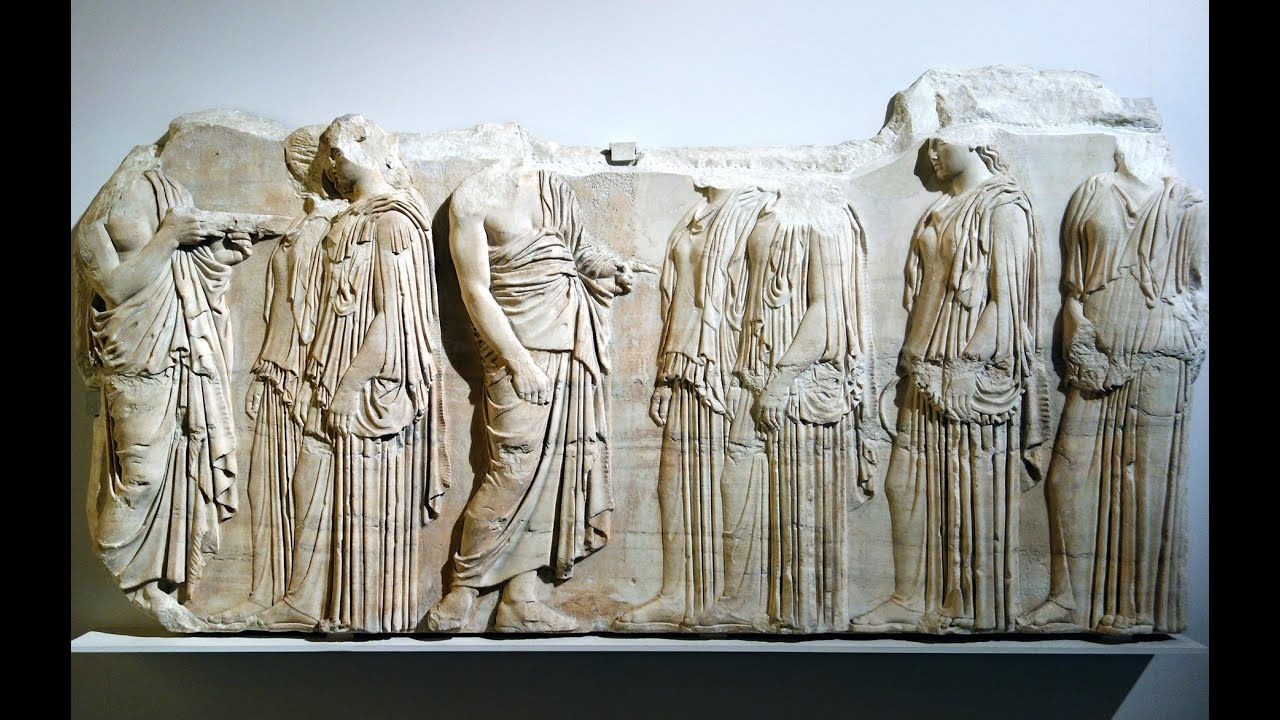

- Phidias has an idea of the ground in art.
- ^^isocephalism^^ ^^(idea of having multiple heads on the same level). (ISO)^^
- Mix of low and high relief. (Priest are mostly high relief) (women are depicted in low relief).
- Decorative, meant to be placed on the Frieze of the Parthenon.
- Depiction of the panatheanic procession of Athena.
East Pediment of the Parthenon (Birth of Athena)
Relief sculptures that fits on top of the East pediment of the Parthenon.
In relation with how and where the sun rises.
In the ^^west pediment,^^ Athena’s competition with ^^Poseidon (Neptune)^^ is placed there.
All demonstrations of Panatheanic processions.
\n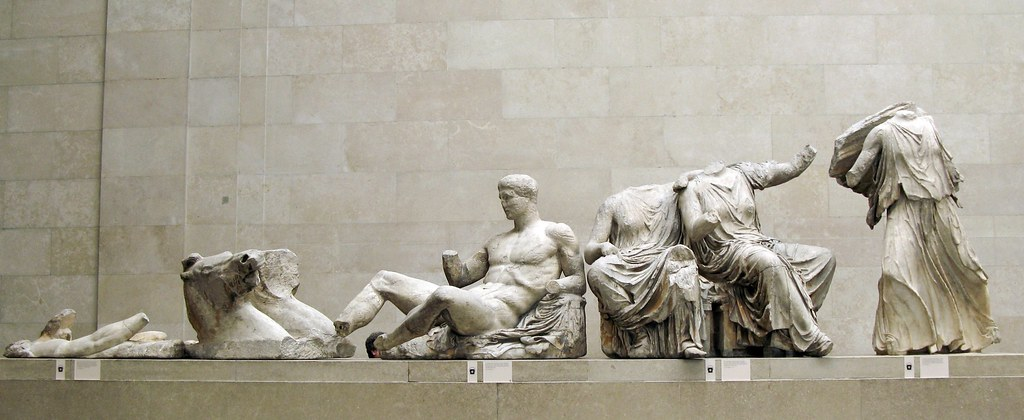 
The Temple of Athena Nike

Nike adjusting her Sandal:
Human glimpse of a goddess (^^genre scene^^ of Athena Nike adjusting her sandal).
- Demonstrations of physiognomy with wet drapery (exquisite).
- Greeks find the sculpture relatable and human.
- Flowing contours define anatomy.
- Athena Nike is depicted more humanly and delicate than the typical Greek God.
amphiprostyle: an ancient temple with a portico both at the front and the rear, where the columns on the narrow sides are not between antae.
The Erechtheion 🏛⚔🔱
A temple dedicated to Athena and ^^Poseidon.^^
^^Poseidon^^ ^^is also known as^^ ^^Neptune.^^
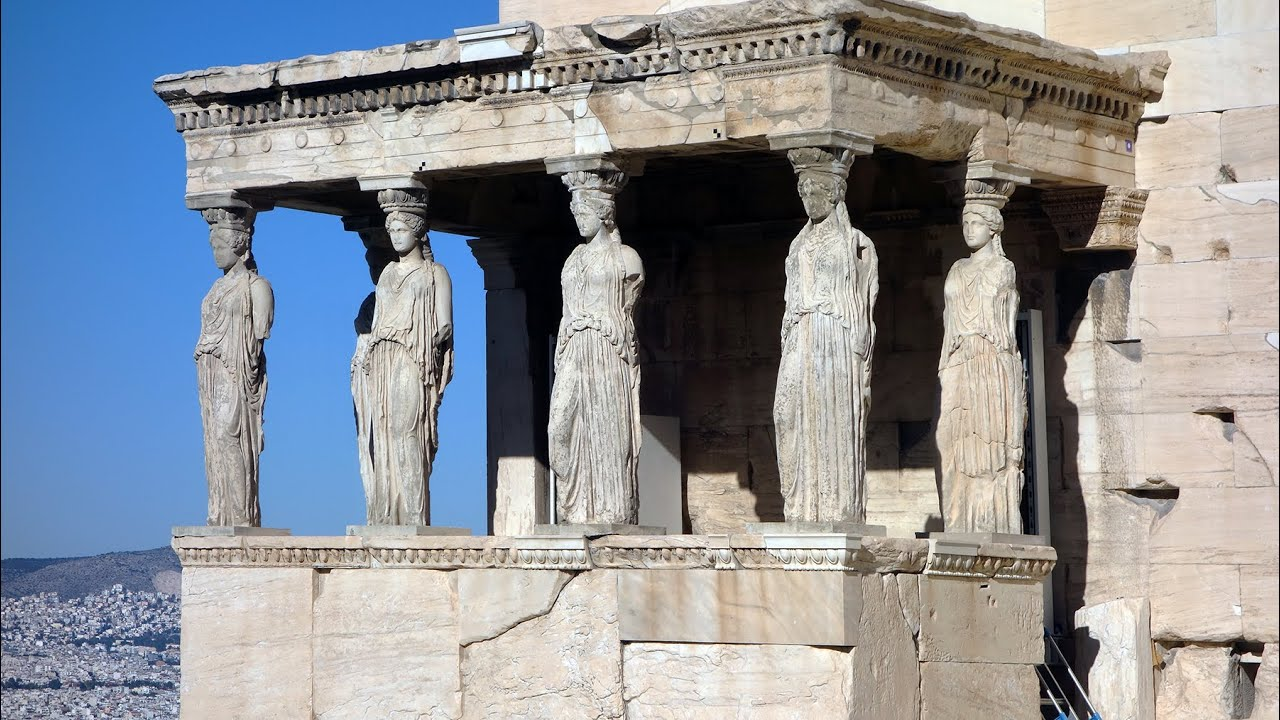

Grave Steve of Hegeso 🏛🪦
The slave girl is giving Hegeso a jewlelry box (pyxis) ; Hegeso is examining the jewelry. ^^Very common depiction of a Greek women.^^ Jewelry is symbolic of giving a dowry to a husband.
- Servant and Hegeso’s chair is beyond the frame.
- ^^Artist: Kallimachos^^

Key words:
Artistic:
Hierarchical scale
low relief
high relief
frame /out of frame
contrapposto (on servant)
^^improfile^^
wet drapery
capitals, pillars
marble
Places: ^^Dyplon cemetry^^
Function: grave marker, funerary.
Key characters:
- Hegeso (Deceased daughter - renamed)
- Servant girl
- Proxenos (father of Hegeso)
- ^^Kallimachos^^ (artist)
Narritive: ^^Proxenos^^ is the father of Hegeso. Hegeso did not live to outlive her father; therefore Proxenos commissioned a grave steve that depicts his deceased daughter sitting on a chair, examining a piece of jewelry that’s given along wiht a ^^pyxis^^ box, given by a servant girl.
Analysis: The jewelry and ^^pyxis^^ is symbolic of a dowry in marriage. Hegeso died young; and therefore did not get to marry. Hegeso is depicted as taller than the servant girl, to show status. This art piece functioned as a funerary grave marker.
Fun Facts 🏛
- Greek sculptures are more progressively high relief.
- The Plaque of Ergastines was the first artwork that first depicted humans in temples.
- Athena Nike adjusting her sandal is relatable to the Greeks; a genre scene of something any everyday person might do.
Key Vocabulary words 🏛
Architect vocabulary:
low relief
high relief
marble
pediment (roof structure)
metope
triglyphs
frieze
Acropolis
genre scene
^^amphiprostyle^^ (Temple of Athena Nike)
Plaque
parapet walls
Artistic vocabulary:
Idealized
decorative/artistic campaign
ground
isocephalism
contrappostal (contrast of forces)
panatheanic procession
Character vocabulary:
Egastines women (and peplos clothing)
Key people🏛
- ^^Iktinos^^ and ^^Kallikrates (artchitects)^^
- Phideas the Sculptor
- War general Pericles
- Athena and Athena NIKE
- ^^Poseidon/Neptune^^
- ^^Kallimachos^^ ^^(artist of the Grave Stele of Hegeso)^^