Bernoulli's Principle
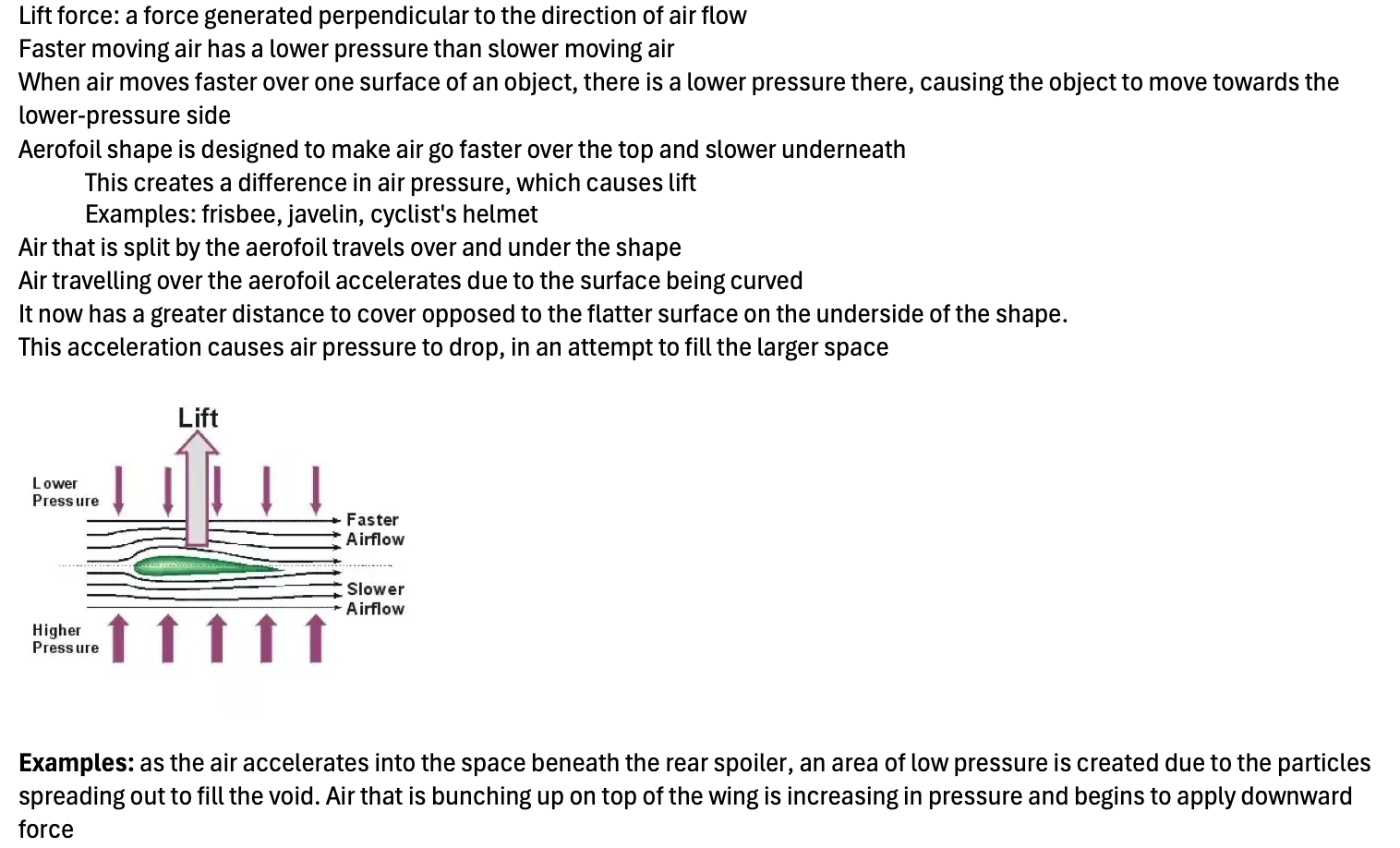
Lift force: a force generated perpendicular to the direction of air flow
Faster moving air has a lower pressure than slower moving air
When air moves faster over one surface of an object, there is a lower pressure there, causing the object to move towards the lower-pressure side
Aerofoil shape is designed to make air go faster over the top and slower underneath
This creates a difference in air pressure, which causes lift
Examples: frisbee, javelin, cyclist's helmet
Air that is split by the aerofoil travels over and under the shape
Air travelling over the aerofoil accelerates due to the surface being curved
It now has a greater distance to cover opposed to the flatter surface on the underside of the shape.
This acceleration causes air pressure to drop, in an attempt to fill the larger space
Examples: as the air accelerates into the space beneath the rear spoiler, an area of low pressure is created due to the particles spreading out to fill the void. Air that is bunching up on top of the wing is increasing in pressure and begins to apply downward force