Unit 7
Overview:
Energy flows in a linear function; compounds are going to cycle between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
An ecosystem is made out of living things as well as nonliving things, with the main light source being the sun.
Photosynthesis needs sunlight as a fuel and then releases organic molecules and O2 as waste. The waste then acts as fuel for cellular respiration with the release of ATP for cellular work. Which has a waste product of CO2 and H2O which gets used up by photosynthesis, creating a cycle.
Heat energy cannot be recycled.
Entropy is being generated in two ways, waste energy, and cellular respiration waste products.
Simplified chemical formula for cellular respiration
6O2 (g) + C6H12O6(aq) → 6CO2(g) + 6H20(l)
Coupling reactions:
ADP + Pi → ATP
Gets energy from Glucose, creating potential and chemical energy
Redox Reactions:
Split into 2 parts, oxidation & reduction
OIL: oxidation is lost; losing an electron
RIG: reduction is gained; gain of electron
Performed by dehydrogenase, a coenzyme that helps the reaction occur
In the case of the formula, oxidation is happening from oxygen to carbondioxide and reduction is happening from glucose to water
Phosphorylation
When a chemical gains a phosphate group
Two types:
Substrate level phosphorylation
When a phosphate group form an organic molecule is picked up by another organic molecule
Oxidative phosphorylation
When a chemical gains a phosphate group using the energy from the oxidation of another chemical
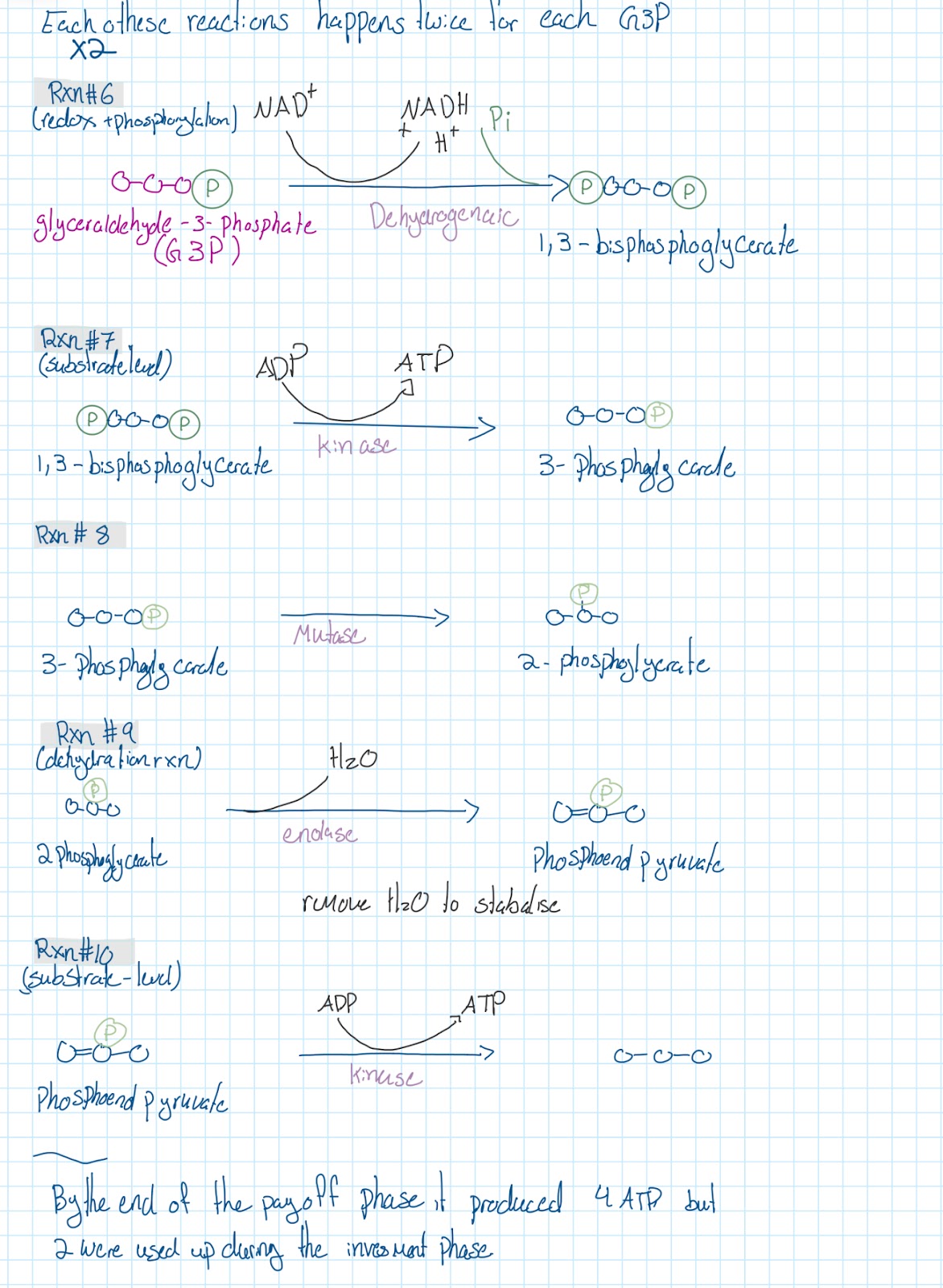
Glycolysis
Overall reaction
Takes place in the cytoplasm
Glucose →→→→→→ 2 pyruvates
Creates:
2 ATP by using 2 ADP & Pi
2 NADH & H* by using 2 NAD*
Ten RXNS of glycolysis
 Linkage Reaction
Linkage Reaction 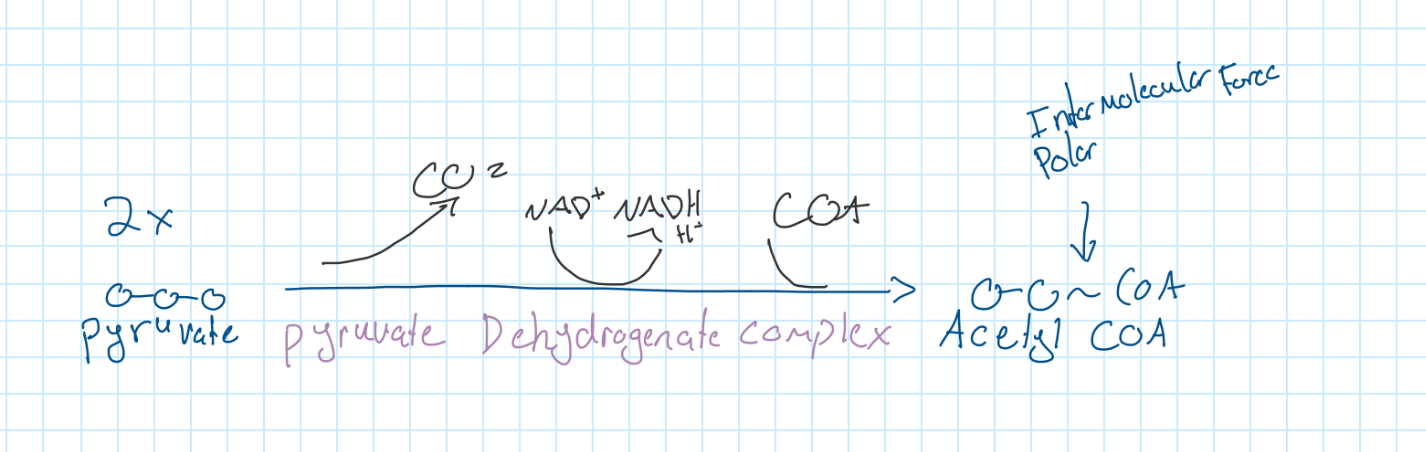
Krebs Cycle
The goal of the krebs cycle is to trap as much energy as possible form Acetyl CoA in NADH. FADH2 & ATP
Two e- carrieres
NAD* + 2e- + 2H* → NADH + H*
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
FAD + 2e- + 2H* → FADH2
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
For one glucose molecule
Stage | ATP | NADH | FADH2 | CO2 |
Glycolysis | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Link | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
Krebs | 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
Total | 4 | 10 | 2 | 6 |
Electron Transport Chain
Poisons
Rotenone:
Attaches to complex 1, stopping the flow of electrons, kills you
Cyanide:
Attaches to complex 4, preventing the flow of electrons, stops the reduction of O2. it is irreversible and can kill anyone with small amounts
Carbon monoxide:
Attaches to complex 4, preventing the flow of electrons, stops the reduction of O2. Reversible if caught early enough
DNP:
Creates holes in the phospholipid bilayer, disrupting the H+ gradient. In large amounts can kill the person, overall stop the flow of ATP
Oligomycin:
Stops ATP synthase, stopping the flow of H+, which stops the creation of ATP
Producing Energy in the absence of O2
ADP & Pi → ATP
Glucose →→→→→→ 2 pyruvates
NAD* → NADH + H*
If there is sufficient oxygen, it goes through cellular/Aerobic respiration in the mitochondria
If not, it goes through fermentation, anaerobic respiration
Fermentation
Lactic Acid
Done by humans/animals/bacteria/fungi
Lactic acid is a warning mechanism informing you that you are out of oxygen
Alcohol
Done by plants/bacteria/fungi (yeast)
 Knowt
Knowt
