microorganisms in relation to human health: chapter 3
The Bacterial Infection
%%Build%%
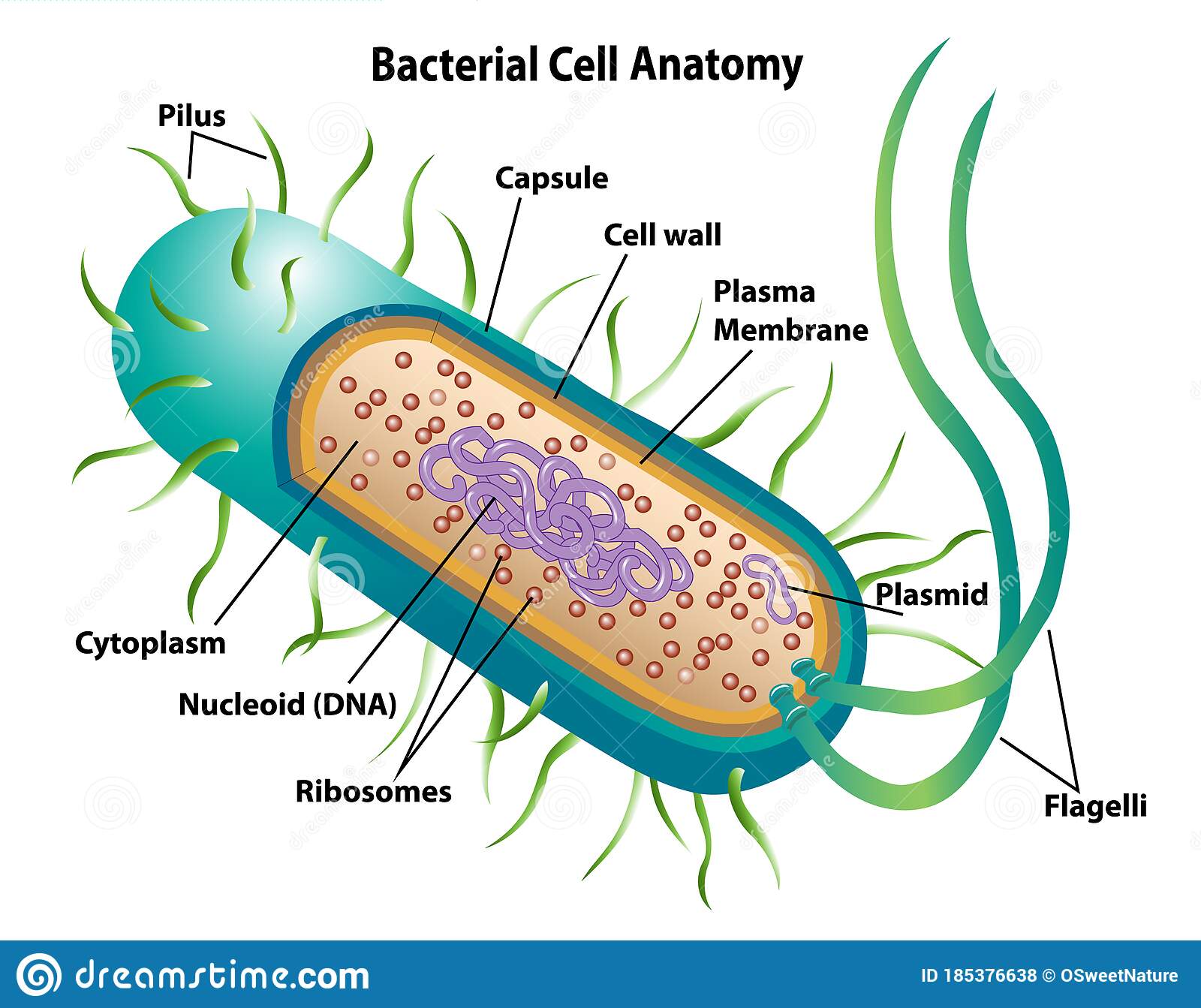
- bacteria = single-celled + prokaryote ( circular DNA)
- consists of a cell envelope and cell contents
- They have no cell organelles with separate functions. They only have ribosomes
%%How do they make us sick?%%
- Bacterial degradation enzymes can affect the host’s tissue
- When bacteria are massively present in the host’s body. They can cause an exaggerated reaction
- Toxins can disrupt the host’s metabolism
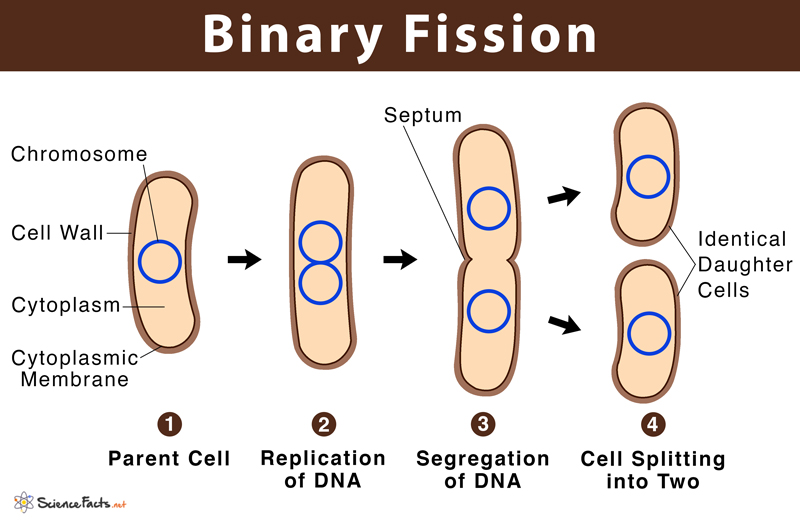
%%How do they multiply?%%
Binary fission = duplicating the genetic substance and then splitting to make two daughter cells that are identical to that of the parent. = asexual reproduction
%%How to combat a bacterial infection?%%
- Antibiotics → disturb the metabolism by for example preventing the protein production of the bacteria
- The body has an immune system
-side note-
It is recommended to eat yoghurt when you are taking antibiotics.
antibiotics → also affect intestine bacteria
yoghurt = fermented food → helps improve gut health
The Fungal Infection
%%Build%%
- fungi = wire-shaped + eukaryote (linear DNA) + aerobic organisms
- plants, fungi, animals → fungi and animals have no chloroplasts → they both are heterotrophs → fungi have a cell wall
- Most fungi consist of hyphens that branch out in or over a substrate and that’s the place where the fungi grow.
%%How do they make us sick?%%
fungi = heterotrophs → will use parts of the human body as food
- They secrete digestive enzymes
- These break down tissue cells and the host gets sick
- The fungus absorbs the released nutrients
%%How do they multiply?%%
Fungi’s multiplication is very complex. 1/3 can reproduce in different ways (sexual or asexual). So we will limit it to the factors that can influence the process.
- A warm and humid environment (think of foot fungi in pools)
- A reduced functioning/resistance of the immune system
- The disappearance of the biological equilibrium → disrupts the relationship between the body’s own bacteria and fungi
- %%How to combat a fungal infection?%%
- Antimycotics → affect the cell wall → causes a leakage → the other cell parts to leak away → fungus dies
The Viral Infection
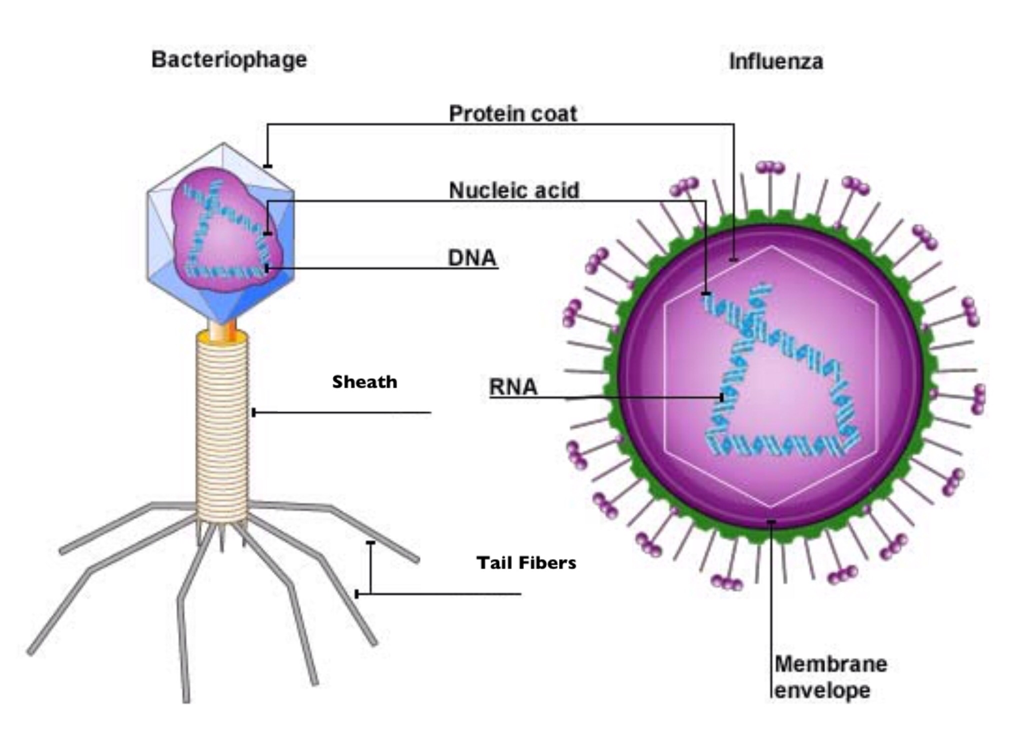
%%Build%%
- A virus consists of the inside 2/3 parts
- nucleic acid (DNA)
- protein coat (capsid)
- envelope (only by animal viruses)
- They can come in a variety of forms → most common = helix form and regular polyhedron
%%How do they make us sick?%%
- They bind to the protein coat of the host cell
- The host cell starts to multiply the virus
- This is at the expense of the hereditary material and proteins of the host cell, which itself dies
%%How do they multiply%%
- The virus binds with specific protein molecules from the protein coat to specific receptor molecules of the host cell
- Certain proteins from the protein coat pierce a hole in the cell membrane of the host cell through which the viral genetic material is introduced.
- The viral hereditary material will now insert itself into the DNA of the host cell and thus force the cell to make viral hereditary material and viral coat proteins
- New viruses are created after combining viral genetic material and coat proteins
- New viruses are released massively from the ruptured host cell
%%How to combat a viral infection?%%
- Antiviral medication can inhibit or stop the virus from multiplying
- The body can build up a resistance
- Vaccines can prevent an infection