Amino Acids - 20
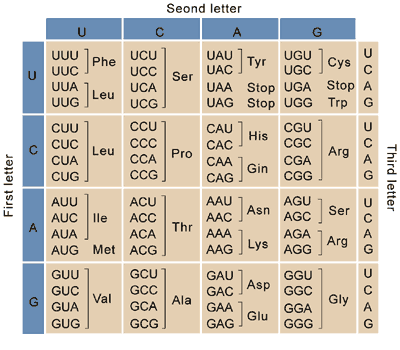
Reading a Codon Chart
A codon chart shows us how to convert 3 nucleotides (UCAG) into an amino acid
Codon- A three-base sequence of RNA
“Encodes” for an amino acid
mRNA is read in terms of codons
UUU => phe (phenylalanine) STOP
AUG => Met (methionine) START
Ribosomes “translate” mRNA to assemble amino acids
Anticodon: the matching 3 base sequences on the tRNA
start - end
CGAUG|ACC|UGG|AAC|UAAUCG
Genetic Mutations can affect the shape of proteins
Sickle cell disease is caused by a change to nucleotide sequence
Hemoglobin - the protein that binds oxygen in red blood cells
Normal hemoglobin DNA sequence:
DNA ⇒ ...TGA GGA CTC CTC...
mRNA ⇒ ...ACU CCU GAG GAG...
Amino acids ⇒ ...Thr - Pro - Glu - Glu...
Mutated hemoglobin DNA sequence:
DNA ⇒ ...TGA GGA CAC CTC...
mRNA ⇒ ...ACU CCU GUG GAG...
Amino acids ⇒ ...Thr - Pro - Val - Glu..
Super charged → no charge
Clinical applications of the central dogma
Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
Transport across the Cell Membrane
 Note
Note Studied by 4017 people
Studied by 4017 people Note
Note Studied by 5 people
Studied by 5 people Note
Note Studied by 51 people
Studied by 51 people Note
Note Studied by 21 people
Studied by 21 people Note
Note Studied by 22 people
Studied by 22 people Note
Note Studied by 4 people
Studied by 4 people Knowt
Knowt