State of Matter
Matter can take different shape based on its intermolecular force or the container it’s in. Solid, liquid, gas and plasma are interconnected with each other through phase changes.
Solid | Liquid | Gas | Plasma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Kinetic Molecular Model | Vibrates in its position | Moves past one another (Flow) | Molecules move quickly | Molecules move quickly |
Shape | Definite | Takes the shape of the container | Takes the shape of the container | Takes the shape and the container |
Volume | Definite | Definite | Assume the shape of the container | Assume the shape of the container |
Rigidity | Very strong | Less rigid | Non rigid | Non rigid |
Intermolecular force | Very strong | Strong | Weak | Non |
Intermolecular space | Very closed and foxed | Close but random | Far apart and random | Not applicable |
Compressibility | Virtually incompressible | Slightly compressible | Very compressible | Slightly compressible |
Examples | Rocks, metals, wood | Water, oil, alcohol | Air, ozone, carbon dioxide | Stars, lightning, neon lights |
Solid
Solid matter has definite volume and definite shape
Because of intermolecular forces, atoms are tightly packed together with a narrow space in between
Has rigidity because of tightly packed atoms (resistance to external force; hard to compress)
Liquid
Liquid are often classified as fluid for its ability to flow and take shape of its container
Liquid has no definite shape but has definite volume
Intermolecular force on liquids is weaker than the solids allowing them to slide past each other when compressed
Gas
Gases are also a fluid, it can flow from one place to another
Gas does not have a definite shape and volume because they continuously move apart from each other.
Gas takes the shape of the container
Intermolecular force are very weak so they create a huge space between each particles. This makes them highly compressible and non rigid.
Plasma
Plasma do not have definite shape and volume like gas.
They move apart from each other but unlike gas, plasma can sometimes pass through the container
Phase Change
Phase change is the transition of matter from one state to another. The addition or removal of heat/energy to a matter that rearrange the atoms.
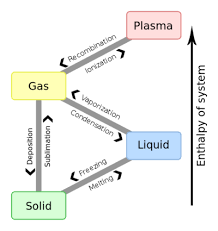 Heat addition
Heat addition
Melting - solid to liquid
Vaporization - liquid to gas
Ionization - gas to plasma
Sublimation - solid to gas
Heat removal
Freezing - liquid to solid
Condensation - gas to liquid
Recombination - plasma to gas
Deposition - gas to solid
Endothermic Process
As the energy/heat increases, the particles gain more kinetic allowing them to move freely and rapidly. The energy is absorbed from its surrounding.
Melting (Solid-to-Liquid)
As the particles gain heat, they overcome the intermolecular force holding them together
Sublimation (Solid-to-Gas)
Same to melting, it just absorb heat and becomes gas directly without the liquid phase. Ex. Dry ice
Vaporization (Liquid-to-Gas)
Particles gain heat and builds kinetic energy allowing them to escape liquid state and become gasses
Ionization (Gas-to-Plasma)
When molecules gain enough energy they can ionize, meaning they lose electrons forming cation and anion.
Exothermic Process
The heat leaves the matter, decreasing the kinetic energy and the movement of it. The energy is released to its surrounding.
Recombination (Plasma-to-Gas)
When positive ions and negative ions combine forming stable molecules. This often releases energy
Condensation (Gas-to-Liquid)
Molecules lose kinetic energy gradually and starts attracting each other
Deposition (Gas-to-Solid)
Molecules forms a strong attraction without going through liquid phase
Freezing (Liquid-to-Solid)
As the intermolecular force between molecules gets stronger and stronger, the molecules gets more rigid and tight.