Unit 5, Chapter 16 AP BIO
Ch. 17 - Protein Synthesis Overview
Part 1
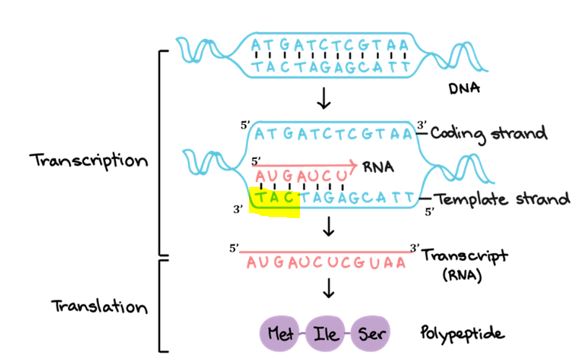
Central Dogma - DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is translated into polypeptides(proteins)
 Annoying terminology!
|
Transcription & RNA Processing
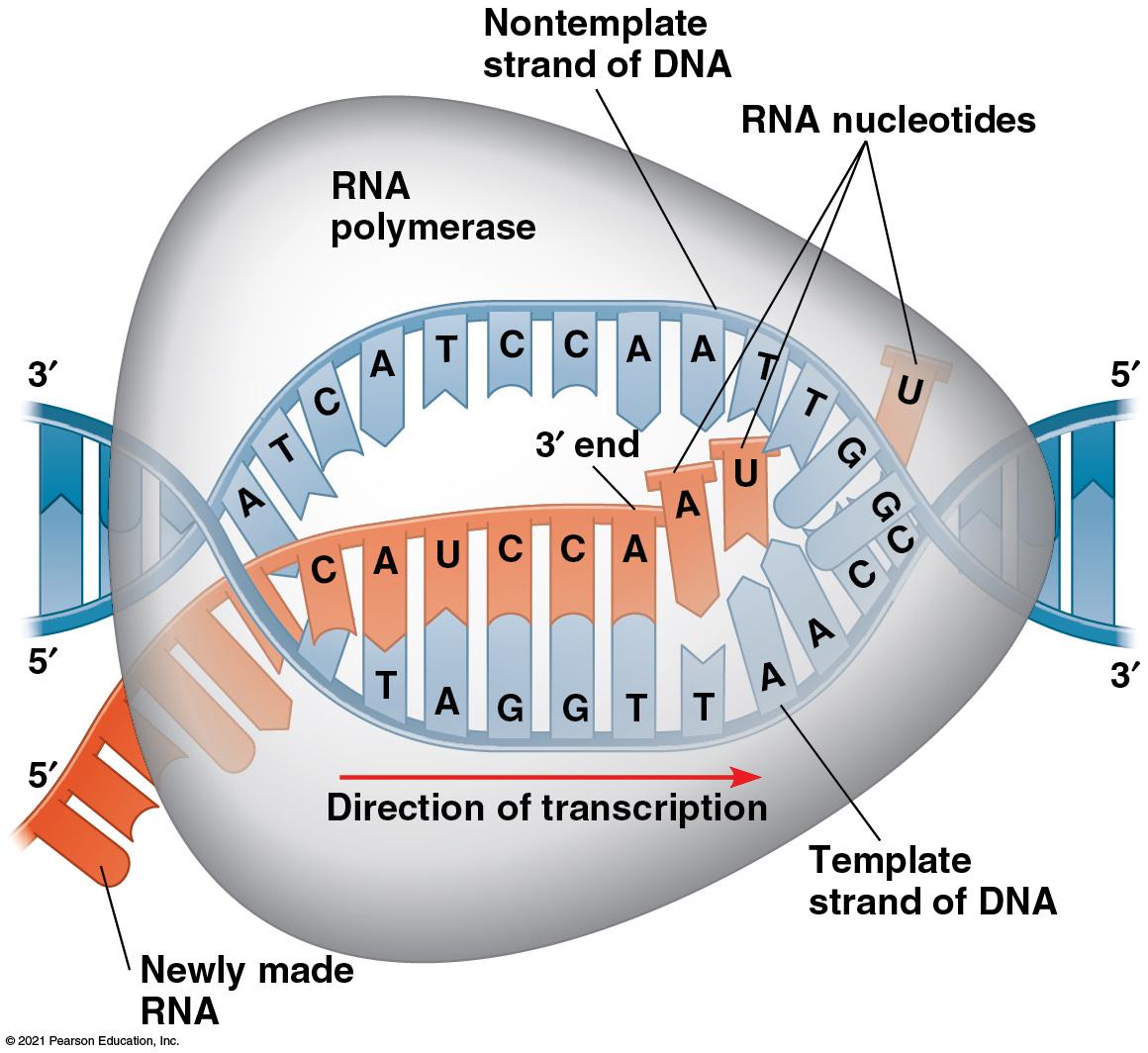 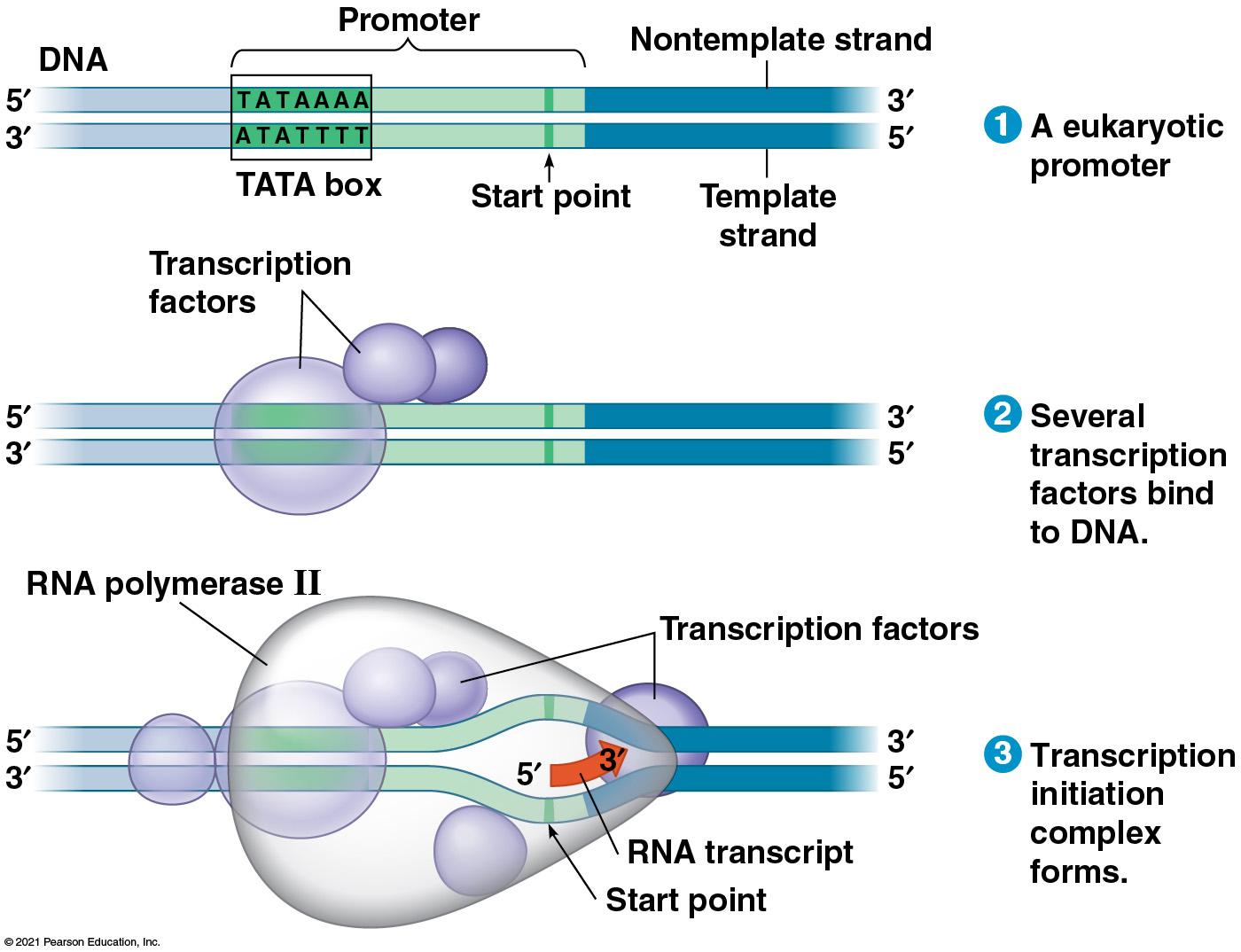 |
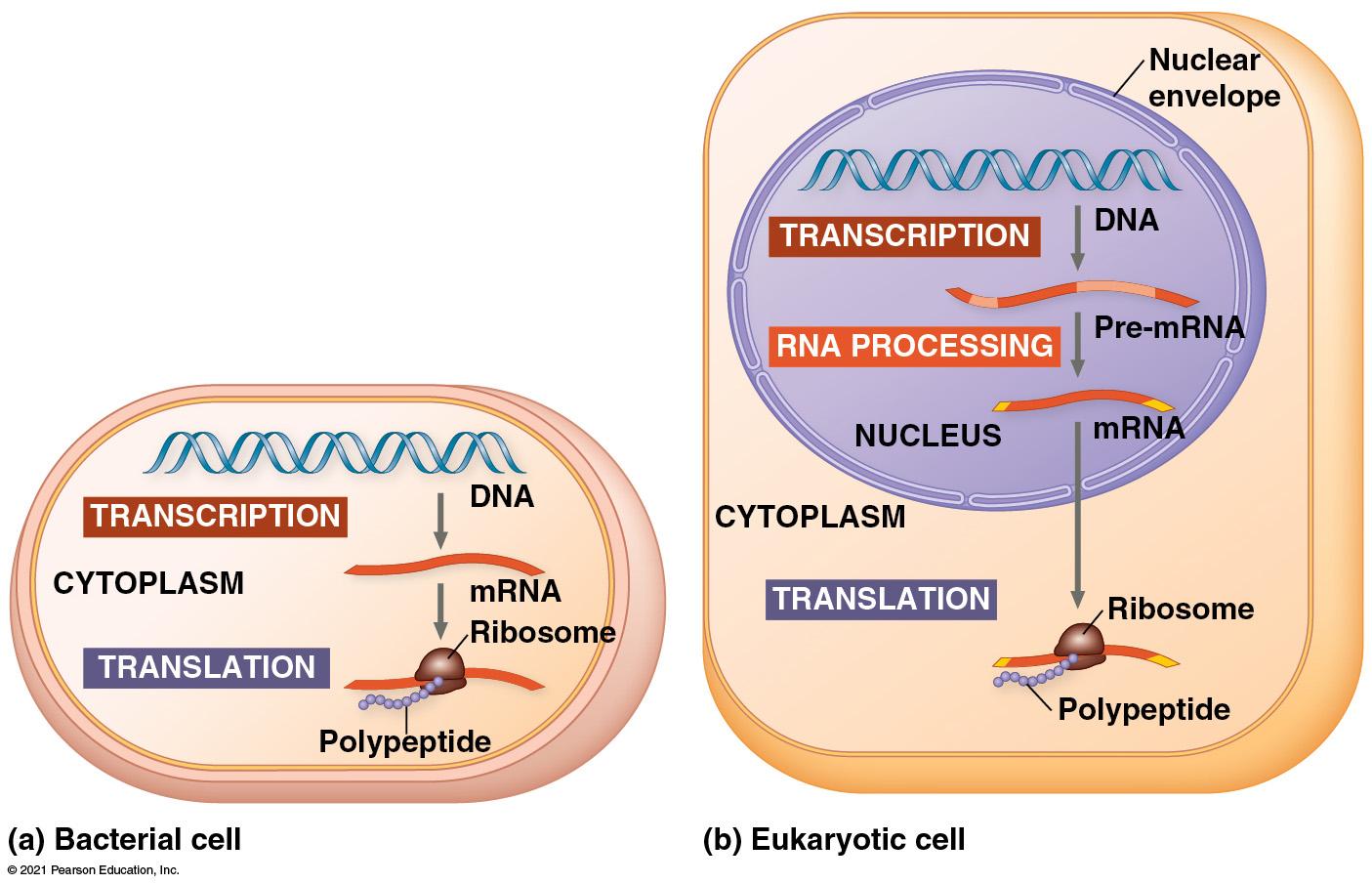 Difference between proks & euks: Prokaryotic cells - mRNA can bind to ribosome right away Eukaryotic cells - mRNA has to be Processed (spliced and Capcised) |
RNA Processing - “Cut & Cap” the pre-mRNA 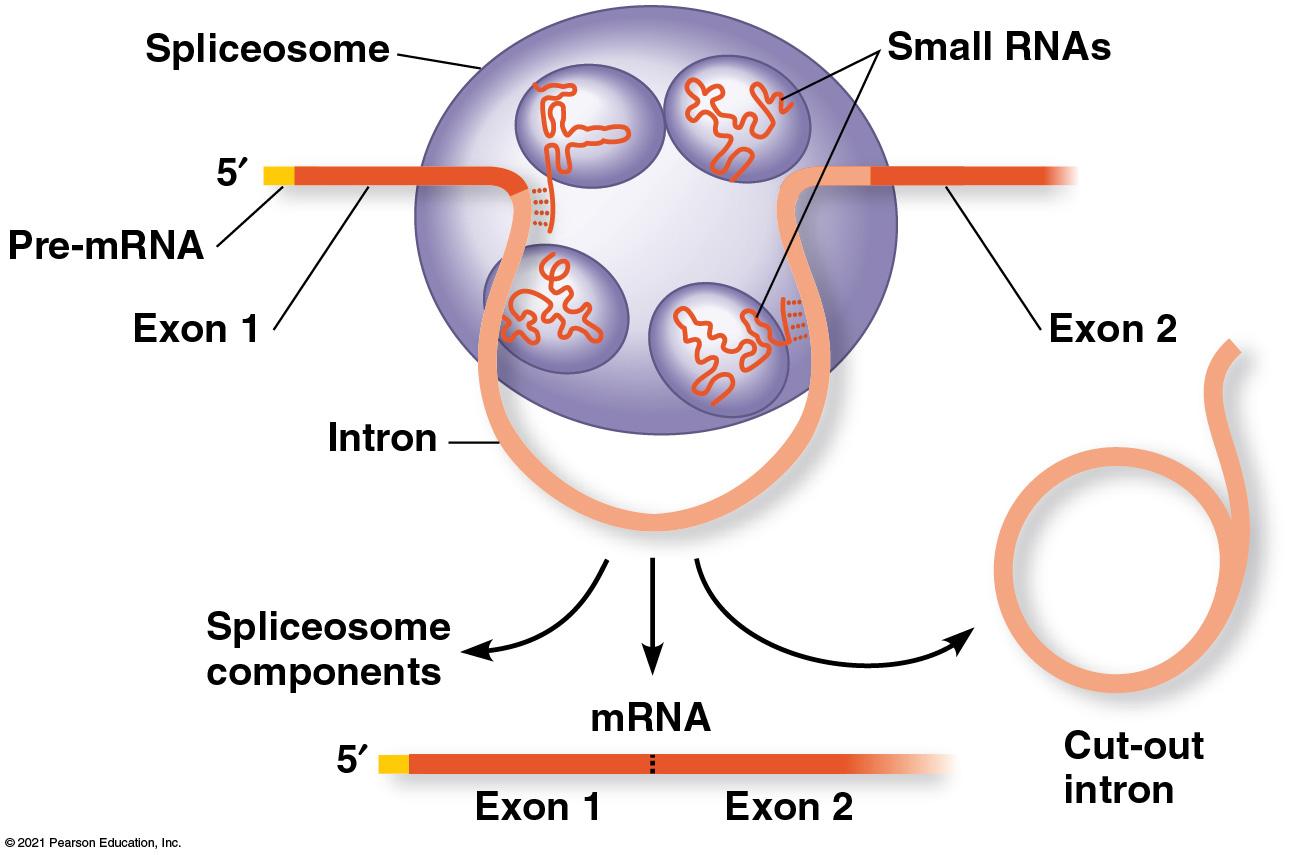
5’ end gets a G nucleotide cap 3’ end gets a poly-A tail (multiple A nucleotides) WHY add cap & tail? - Allows mRNA to leave the nucleus - Protects mRNA from hydrolytic enzyme - Allows mRNA to bind to the ribosome
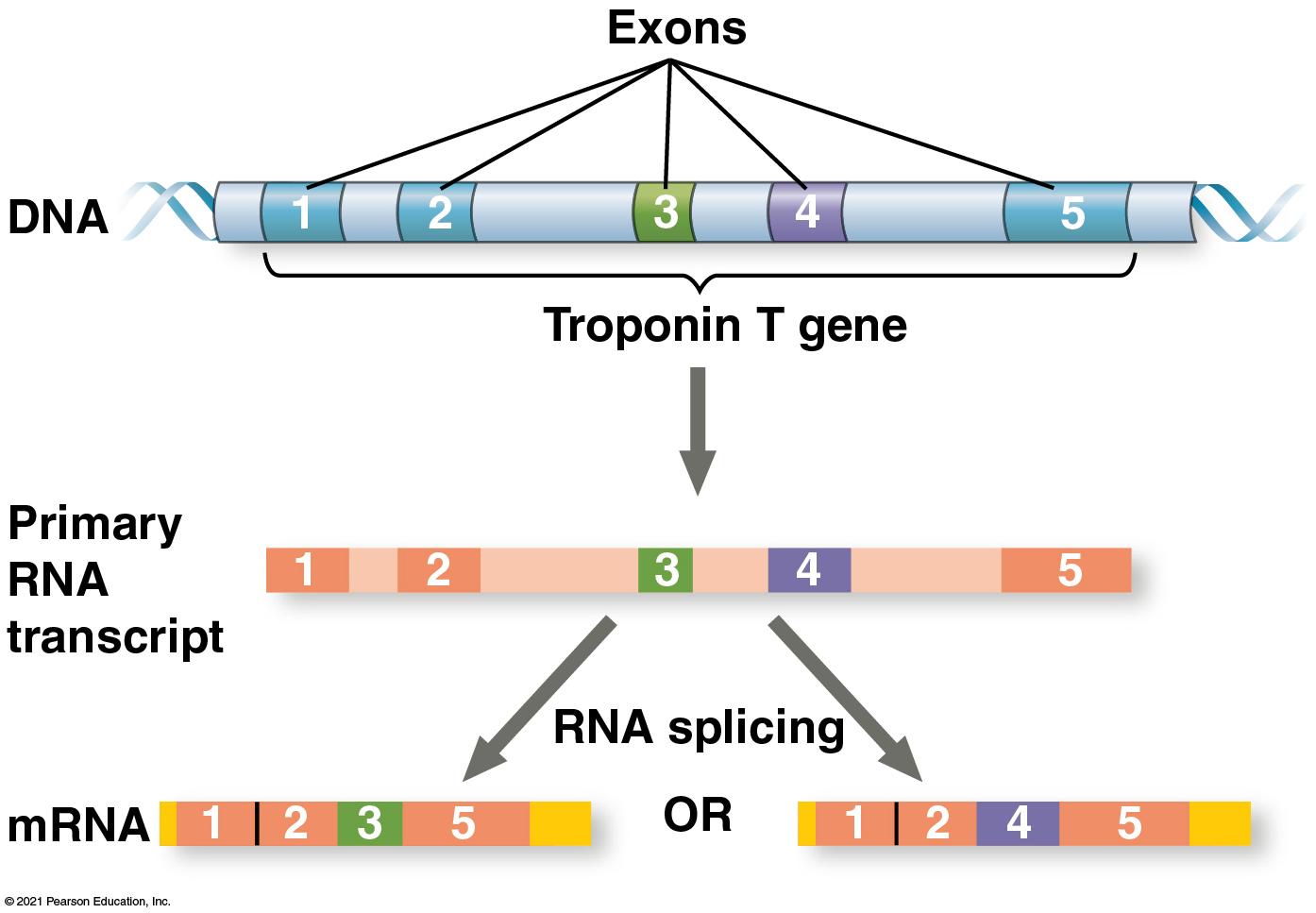
_Alternate splicing_- can put exons together in different order
|
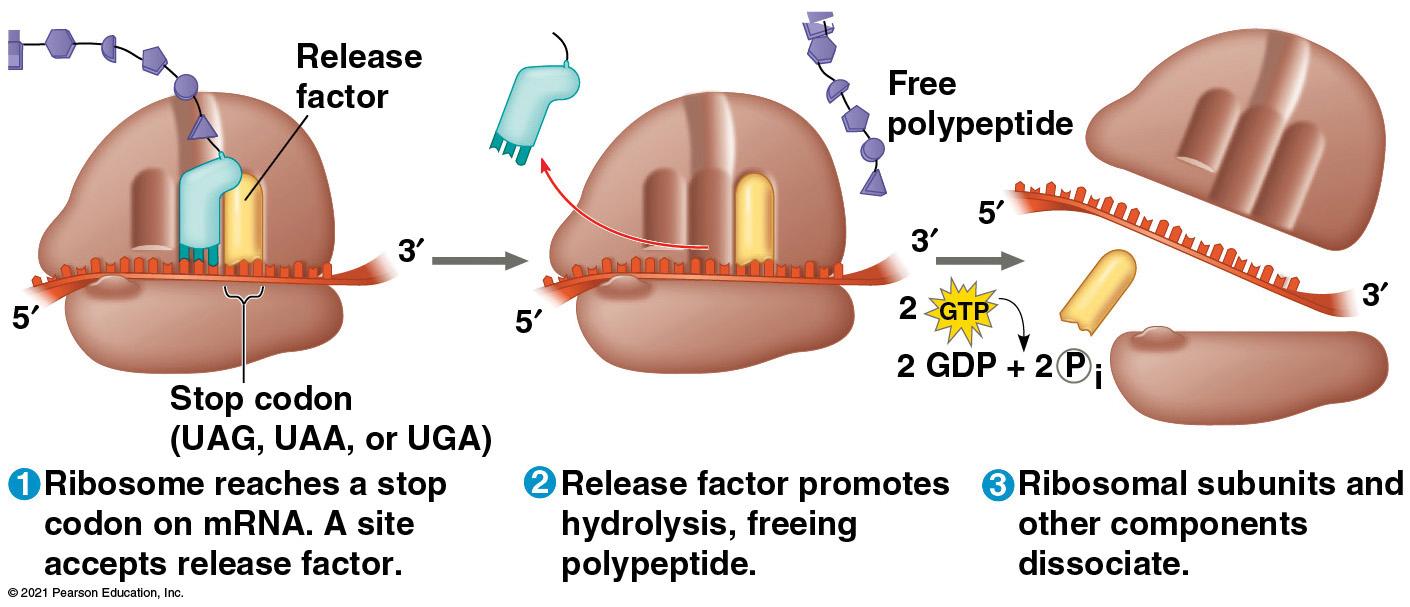
Translation
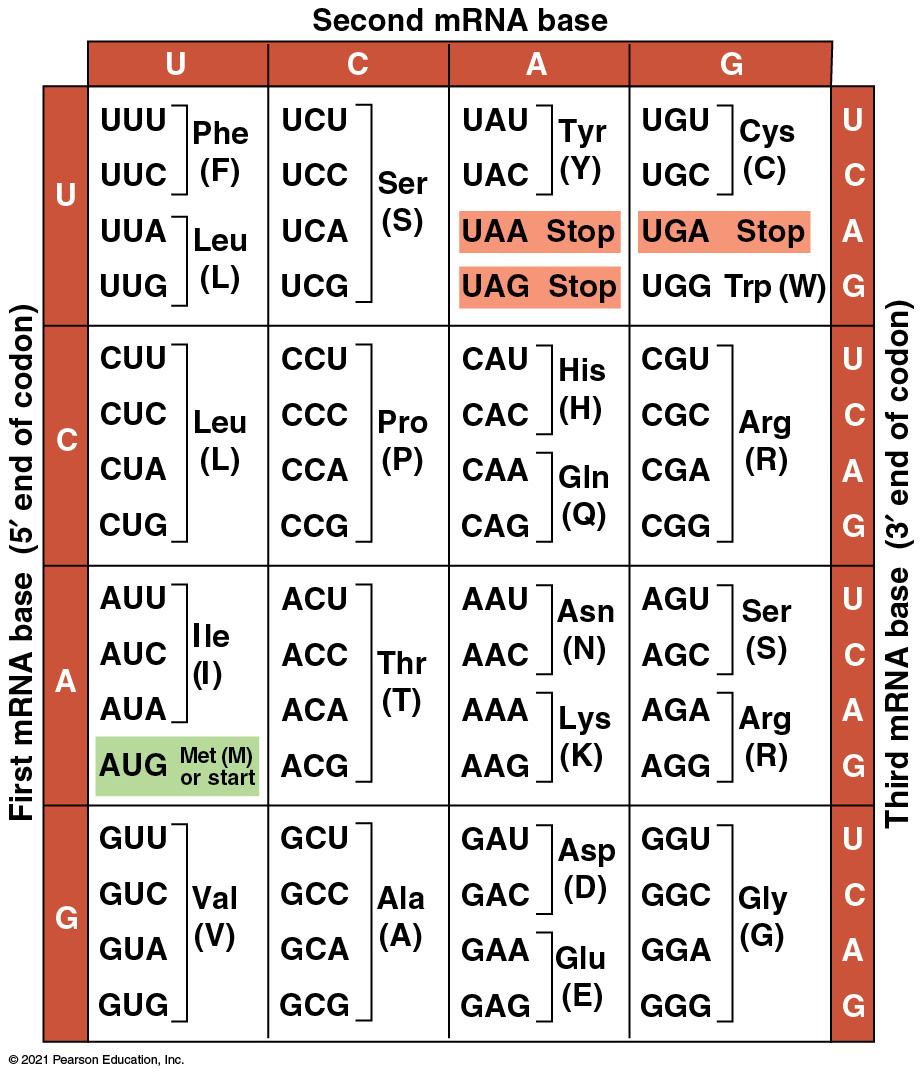
Triplet code - RNA is read in 3-letter sequences (codon) 1 amino acid = 1 codon = 3 nucleotides
|
Practice!
DNA 5’ATGCCCATTACTCGGTAA 3’ 3’TACGGGTAATGAGCCATT 5’ Met, Ala, His, Tyr, Pro
|