Introduction to Scripting
Objectives
UNIT 1 OBJECTIVE | COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES MET IN UNIT 1 |
Explain the differences between scripting and programming languages |
|
identify various types of scripting and programming languages |
|
Introduction to Scripting and Programming
origins of programming languages were created in the 1950s.
punch cards were used in the 1800s to create complex patterns in woven textiles.
first mechanical calculators were created in the nineteenth century using basic programming concepts like logic and looping.
the first computer was created in the 1950s and used programming languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL.
most programming languages take advantage of basic programming concepts such as variables, conditional statements, and looping.
IBM first introduced Job Control Language (JCL) in the 1960s, which allowed developers to use scripting as a means of creating a “sequence of direction” to control computer “punch card” programming jobs.
sequences were called batches which allowed to use simpler code.
Scripting — used in the field of digital media to create interactivity, animation, and dynamic content (e.g., Flash, ActionScript, JavaScript).
Programming — used in digital media to create applications (e.g. web programming).
both are important in the creation of:
Digital Design:
generating digital designs from a template.
automating repeated tasks
converting digital documents to multiple formats
creating new features.
Motion Graphics:
creating animation and movies
automating tasks
enhancing workflows
performing mathematical calculations
Web Technology:
presenting web pages
creating animations
using databases to create interactive, dynamic web pages
Differences Between Scripting and Programming
A. Interpreted Languages
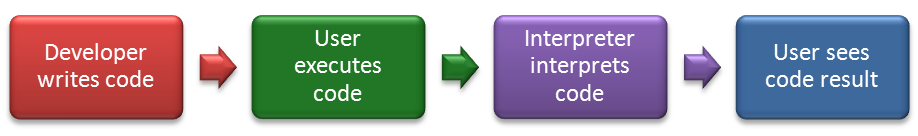
Interpreted languages execute code through an interpreter that turns code into a machine-readable format.
happens every time code is executed.
Ex. ActionScript, JavaScript, PHP, and Phyton.
How Interpreted Languages Work
B. Compiled Languages
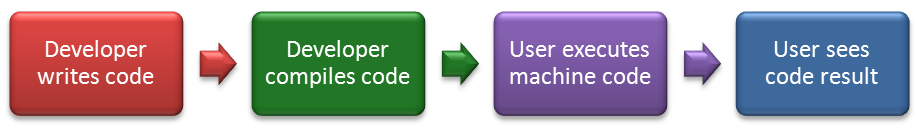
Compiled languages require code to undergo conversion into machine-readable code using a software program known as a compiler.
then executed directly by the CPU each time it executes rather than working through an interpreter.
ex. Visual Basic and C#
How Compiled Languages Work
Types of Scripting and Programming Languages
A. Markup (Presentation) Languages
Markup languages are used to mark up, or notate, text, either to create structured data or to specify how text should be presented.
‘../ ../ ’ commonly used on the web.
uses tags, or keywords, to determine how data should be structured or presented.
tags example:
<mytag>Inside My Tag</mytag>
examples of markup languages include: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), Extensible Markup Language (XML), Extensible Hypertext Markup Language (XHTML), and Cascading Stylesheets (CSS).
B. Web Client-Side Languages
Web client-side languages are used to create interaction that is executed on a client, such as a web browser, instead of a server.
‘../ ../ ’ commonly used on the web to generate interaction between a user and a webpage.
example: JavaScript.
C. Web Server-Side Languages
Web server-side languages are used to create interaction that is requested by a client, processed on a server, and then returned to a client, such as a web browser or mobile device.
commonly used on the web to create interaction between a website and a database
examples: Python, ColdFusion Markup Language ( CFML ), PHP: HyperText Processor ( PHP ), and Visual Basic.NET (VB.NET)
D. Application-Specific Languages
Application-specific languages are used to create interactivity within a specific software application.
ActionScript — built-in scripting language inside Adobe Flash, and ExtendedScript in Adobe After Effects (form of JavaScript).
Linden Script in Second Life.
Software Application | Scripting Language |
Adobe After Effects | Omino Python |
Blender | Python |
Adobe InDesign | XML and JavaScript |
Unity | C# |