Communicating At Work Chapt. 1
Nearly all communication is strategic:
Relational Communication:
“… messages that shape and reflect the way people regard one antother. …” (ex of both Instrumental and Relational, “How can I help you?” in the difference of tone is the relational communication.)
Instrumental Communication:
“… Messages aimed at accomplishing the task at hand.” (ex. “I need that Report by noon.” “How long does the report need to be?” )
Identity Management:
This involves the ways individuals present themselves in interactions, influencing perceptions and relationships.
Principles of Communication:
Communication is Irreversible
It is not possible to take back words and deeds, no matter how much you wish you could take them back.
Communication is a Process
Communication is not one single act. It has multiple moving parts.
Communication is Not a Panacea
Communication is not a cure-all. There is no such thing as an elixir of life for communication and even the most effective communicators cannot solve all problems.
Basics of the Communication Model:
Message:
Verbal or nonverbal elements of communication that are conveyed between senders and receivers.
Sender:
The person who transmits a message.
Receiver:
The person who receives the message and interprets its meaning.
Encoding:
The verbal or nonverbal method that the sender uses to transmit their message.
Decoding:
The way the receiver understands and interprets the message.
Channel:
The medium over which the message is delivered.
Feedback:
The receiver’s observable response to a sender’s message.
Noise:
Factors that interfere with the exchange of messages.
Environmental Noise:
Noise that is based on the communicators’ surroundings. (ex. Voices heard in the next room, a smelly cigar, someone’s phone going off in a meeting)
Physiological Noise:
Physical issues such as hearing disorders, illnesses, disabilities, and others that may make sending messages difficult.
Psychological Noise:
Factors withing the communicators that interfere with understanding, such as; egotism, defensiveness, assumptions, stereotypes, biases, hostility, preoccupation, and fear.
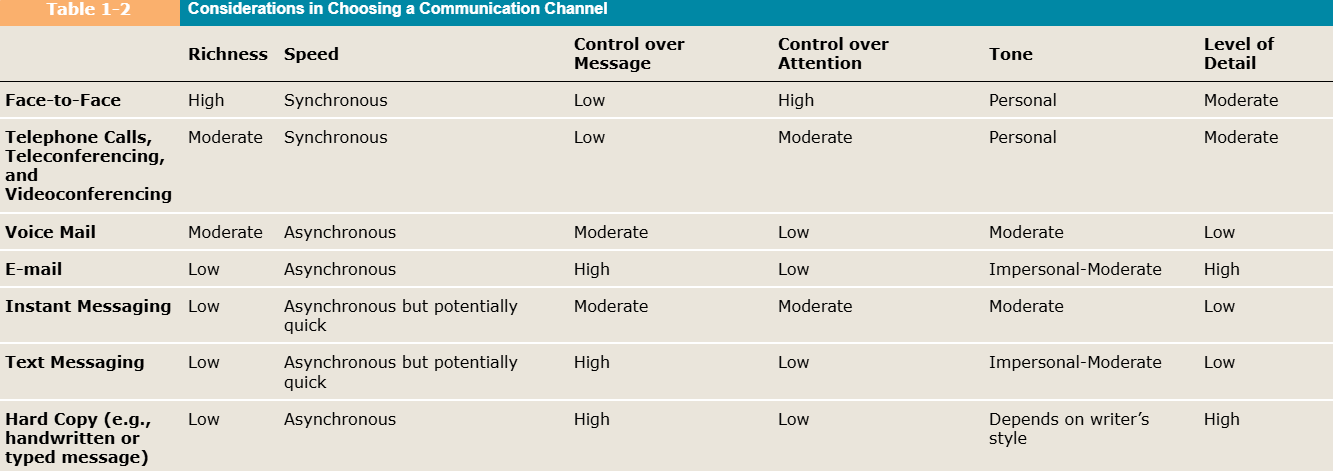
Communication Channels:
Channel Characteristics:
Richness:
The amount of information that can be transmitted using a given channel. There are a few things to consider in order to determine the richness of a channel.
1) Whether it can handle many types of cues at once.
2) Whether it allows for quick feedback from both senders and receivers.
3) Whether it allows for personal focus.
Speed:
How quickly the exchange of message occurs.
Synchronous Communication:
High speed or instantaneous. This will include face-to-face conversations, video chat, and telephone conversations.
No time lag separates the transmission and reception of messages, so immediate feedback is possible.
Asynchronous Communication:
Low speed. This includes e-mail, interoffice memos, and voice mail.
There is a lag between the transmission and reception of messages. Immediate feedback is not always possible.
Control:
The degree to which you can manage the communication process.
In written channels you may exert more control over how you encode a message. You write, proofread, and edit it until the message is exactly how you want it.
In a face-to-face channel, you have much more control over the receiver’s attention. You can reduce noise, interpret nonverbal signals, or explicitly ask the sender to pay attention.
Communication Networks:
Patterns of contact created by the flow of messages among communicators through time and space. There are two kinds of networks; formal and informal.
Formal Netwok:
Systems designed by management that dictate who communicates with each other.
Organizational Charts:
Visual representations of the hierarchy within an organization, depicting the roles and relationships between different positions.
Informal Network: