
AP Biology Unit 7 Review: Natural Selection
Evolution vs. Natural Selection
Evolution is CHANGE = Change in allele frequency
Natural Selection = nature is choosing organisms that are more likely to survive & reproduce MORE
Variation is required
Sexual reproduction
Mutation
Horizontal gene transfer (bacteria)
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequency (by chance)
Needs a small population
Founder effect
BY CHANCE, a tiny subset of a large population gets cut out then finds a new population (natural disaster)
BIG change in allele frequency
Bottleneck effect
A tiny subset of a large populations survives while the rest die (natural disaster)
Change in allele frequency
Think about how a bottle slowly pours (lets say) tiny paper stars out, the massive amount of paper stars that stay in the bottle represent the organisms that died
Gene Flow
When a gene flows from one population to another
Change in allele frequency (no way!)
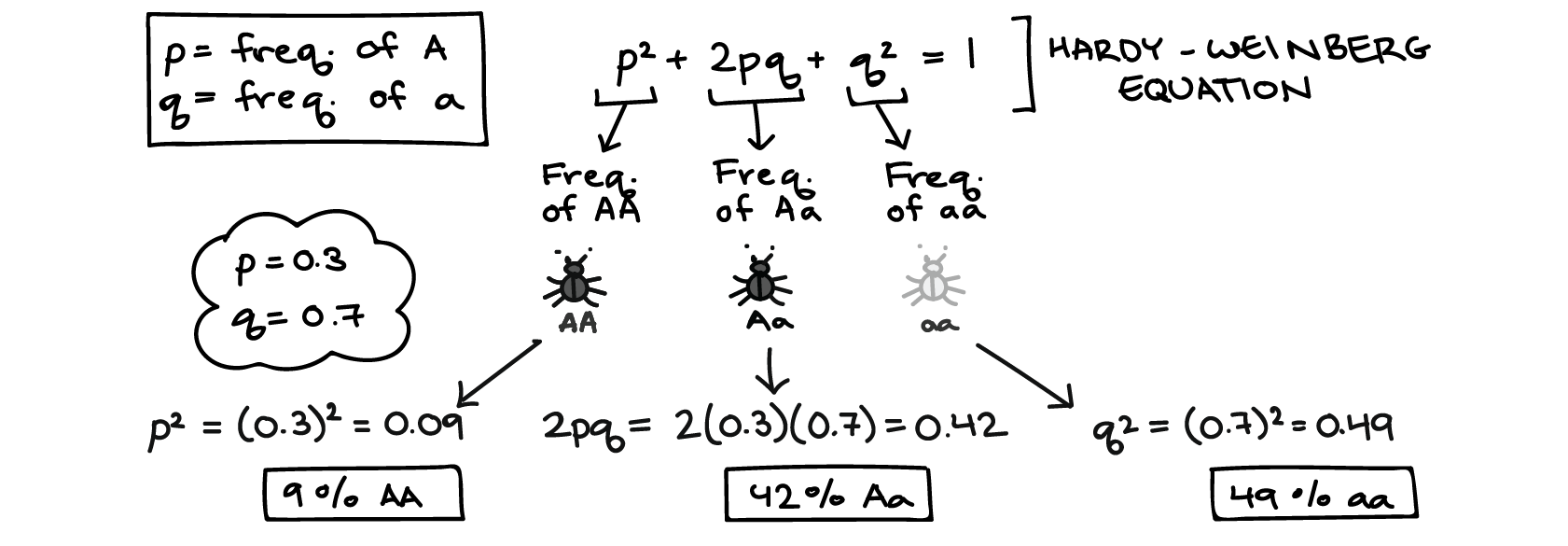
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Allele frequency (how frequent a trait is)
P = The number of a certain allele / total number of alleles in the entire population
P=200+100/600
Finding the dominant trait → HH has 100×2, Hh has 100, and 100 hh has 0
100 HH
100 Hh
100 hh
P² + 2pq + q² = 1
Big numbers
No mutation
No natural selection
No gene flow
No random mating
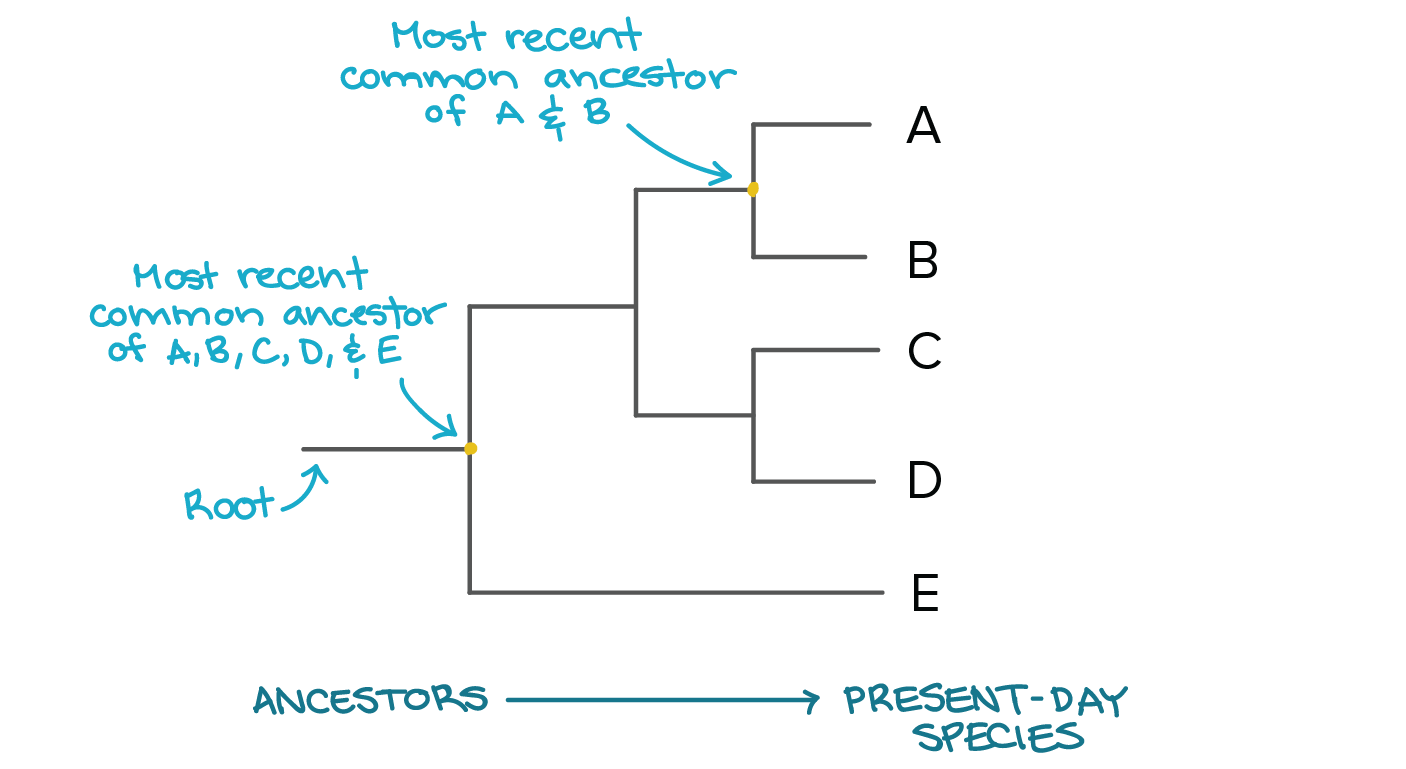
Phylogeny
Macroevolution - long periods of time
Common ancestors
Speciation
Species = Members can interbreed and have viable offspring
Horse + donkey = sterile mule
Allopatric
Geographically split apart and speciate
New food sources
Adaptations
Ex: Island vs. mainland
Sympatric
Still in the same location, but speciate
Different habitats, food source, etc.
Polyploid
Error in meiosis, extra chromosomes
Reproductive isolation
Stop reproducing
Non-viable offspring
Prezygotic
Habitat (different locations)
Temporal (mate at different times)
Mechanical (physically cannot)
Gametic (won’t fuse)
Behavior (courtship)
Postzygotic
Reduced hybrid viability (cannot live past a certain age, dies off)
Reduced hybrid fertility (sterile)
Hybrid breakdown (dies out eventually)
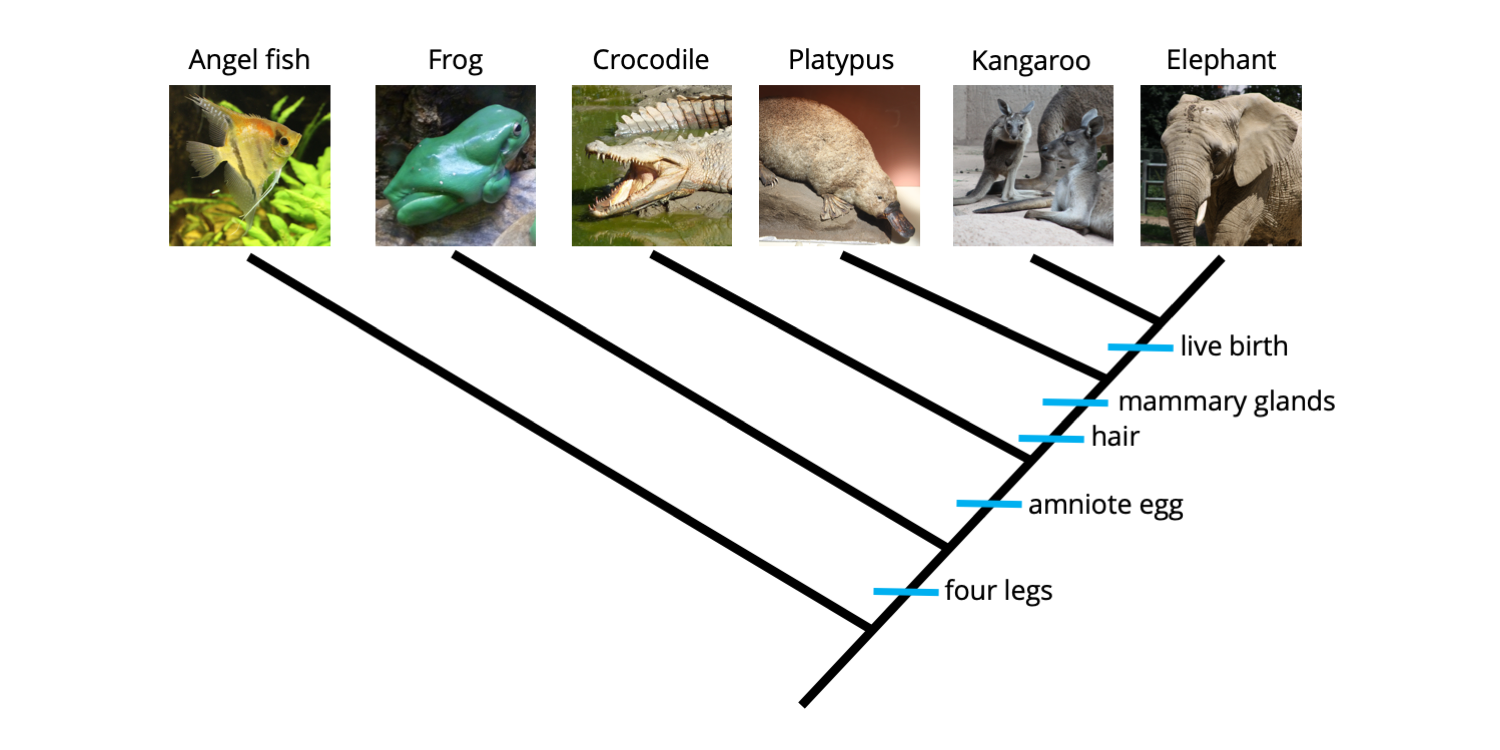
Common Ancestry
Structures:
Homologous features = same ancestry, different function
Vestigial structures = have due to common ancestry, but we don’t use it (tailbone)
Analogous structures = different ancestry, similar function
Evidence:
Molecular biology = less differences, closer relatedness (less time to diverge)
Biogeography
Fossils
Phylogenetic trees
Mass extinction
Permian Triassic (before dinosaurs)
Cretaceous Tertiary (dinosaurs died, debris, no sunlight by a meteoroid)
Right now
Origin of Earth
~4.5 billion years ago, Earth was found
~3.9 billion years, oceans form
~3.5 billion years ago, life formed (stromatolite fossils)
RNA world hypothesis (first life form)
Building blocks (monomers) created polymers, and so on…
Miller-Urey Experiment
Inorganic to organic
Organic could come from inorganic to produce life (not accurate to Earth’s initial atmosphere, but debatable and possible)

AP Biology Unit 7 Review: Natural Selection
Evolution vs. Natural Selection
Evolution is CHANGE = Change in allele frequency
Natural Selection = nature is choosing organisms that are more likely to survive & reproduce MORE
Variation is required
Sexual reproduction
Mutation
Horizontal gene transfer (bacteria)
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequency (by chance)
Needs a small population
Founder effect
BY CHANCE, a tiny subset of a large population gets cut out then finds a new population (natural disaster)
BIG change in allele frequency
Bottleneck effect
A tiny subset of a large populations survives while the rest die (natural disaster)
Change in allele frequency
Think about how a bottle slowly pours (lets say) tiny paper stars out, the massive amount of paper stars that stay in the bottle represent the organisms that died
Gene Flow
When a gene flows from one population to another
Change in allele frequency (no way!)
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Allele frequency (how frequent a trait is)
P = The number of a certain allele / total number of alleles in the entire population
P=200+100/600
Finding the dominant trait → HH has 100×2, Hh has 100, and 100 hh has 0
100 HH
100 Hh
100 hh
P² + 2pq + q² = 1
Big numbers
No mutation
No natural selection
No gene flow
No random mating

Phylogeny
Macroevolution - long periods of time
Common ancestors
Speciation
Species = Members can interbreed and have viable offspring
Horse + donkey = sterile mule
Allopatric
Geographically split apart and speciate
New food sources
Adaptations
Ex: Island vs. mainland
Sympatric
Still in the same location, but speciate
Different habitats, food source, etc.
Polyploid
Error in meiosis, extra chromosomes
Reproductive isolation
Stop reproducing
Non-viable offspring
Prezygotic
Habitat (different locations)
Temporal (mate at different times)
Mechanical (physically cannot)
Gametic (won’t fuse)
Behavior (courtship)
Postzygotic
Reduced hybrid viability (cannot live past a certain age, dies off)
Reduced hybrid fertility (sterile)
Hybrid breakdown (dies out eventually)
Common Ancestry
Structures:
Homologous features = same ancestry, different function
Vestigial structures = have due to common ancestry, but we don’t use it (tailbone)
Analogous structures = different ancestry, similar function
Evidence:
Molecular biology = less differences, closer relatedness (less time to diverge)
Biogeography
Fossils
Phylogenetic trees


Mass extinction
Permian Triassic (before dinosaurs)
Cretaceous Tertiary (dinosaurs died, debris, no sunlight by a meteoroid)
Right now
Origin of Earth
~4.5 billion years ago, Earth was found
~3.9 billion years, oceans form
~3.5 billion years ago, life formed (stromatolite fossils)
RNA world hypothesis (first life form)
Building blocks (monomers) created polymers, and so on…
Miller-Urey Experiment
Inorganic to organic
Organic could come from inorganic to produce life (not accurate to Earth’s initial atmosphere, but debatable and possible)

 Knowt
Knowt