Chapter 4: Control Volume Analysis Using Energy
Key Terms and Concepts
conservation of mass - mass rate balance for control volumes, where m is the instantaneous mass flow rate at the inlet (i) and exit (e)
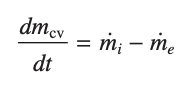
one-dimensional flow - when a flowing stream of matter entering or exiting a control volume is normal to the boundary at locations where mass enters or exits the control volume, or when all intensive properties (including velocity and density) are uniform with position over inlet or exit area through which matter flows
steady state - the ideal state where all properties are unchanging in time (the total amount present at any given instant remains constant)
energy rate balance (of cv) - used when several locations through which mass enters the system
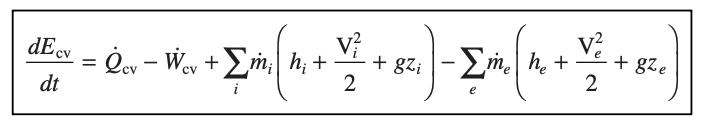
nozzle - a flow of passage of varying cross-sectional area in which the velocity of a fluid increases in the direction of flow
diffuser - the velocity of the fluid decreases in the direction of flow
turnbine - a device in which power is developed as a result of a gas or liquid passing through a set of blades attached to a shaft free to rotate
compressors/pumps - devices in which work is done on the substance flowing through them in order to change the state of the substance, typically to increase the pressure and/or elevation
transient operation - when the state changes with time