Waves Motion
Wave motion is the transfer of energy without matter (no matter movement, but just energy transformation)
Two types of waves:
Transverse wave
Longitudinal wave
Waves that require a medium(material the wave is traveling through) to travel through are called mechanical waves (eg, sound).
Waves that do not require a medium are called non-mechanical waves(e.g., light)
Why can't we hear the sun? We can’t hear it because the sound doesn't travel through empty space.
Transverse waves:
Particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of the motion
Example: light
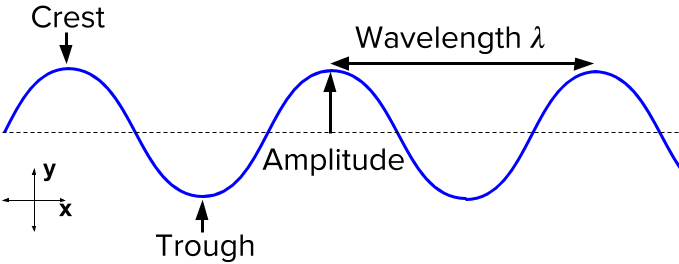
Frequency (f) is how many waves are produced each second, measured in Hertz (Hz)
Wavelength (入)is the distance between 2 successive waves, measured in meters(m).
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum distance it extends from the middle (equilibrium position)
Crest is the maximum amplitude above the middle position
Trough is the maximum amplitude below the middle position
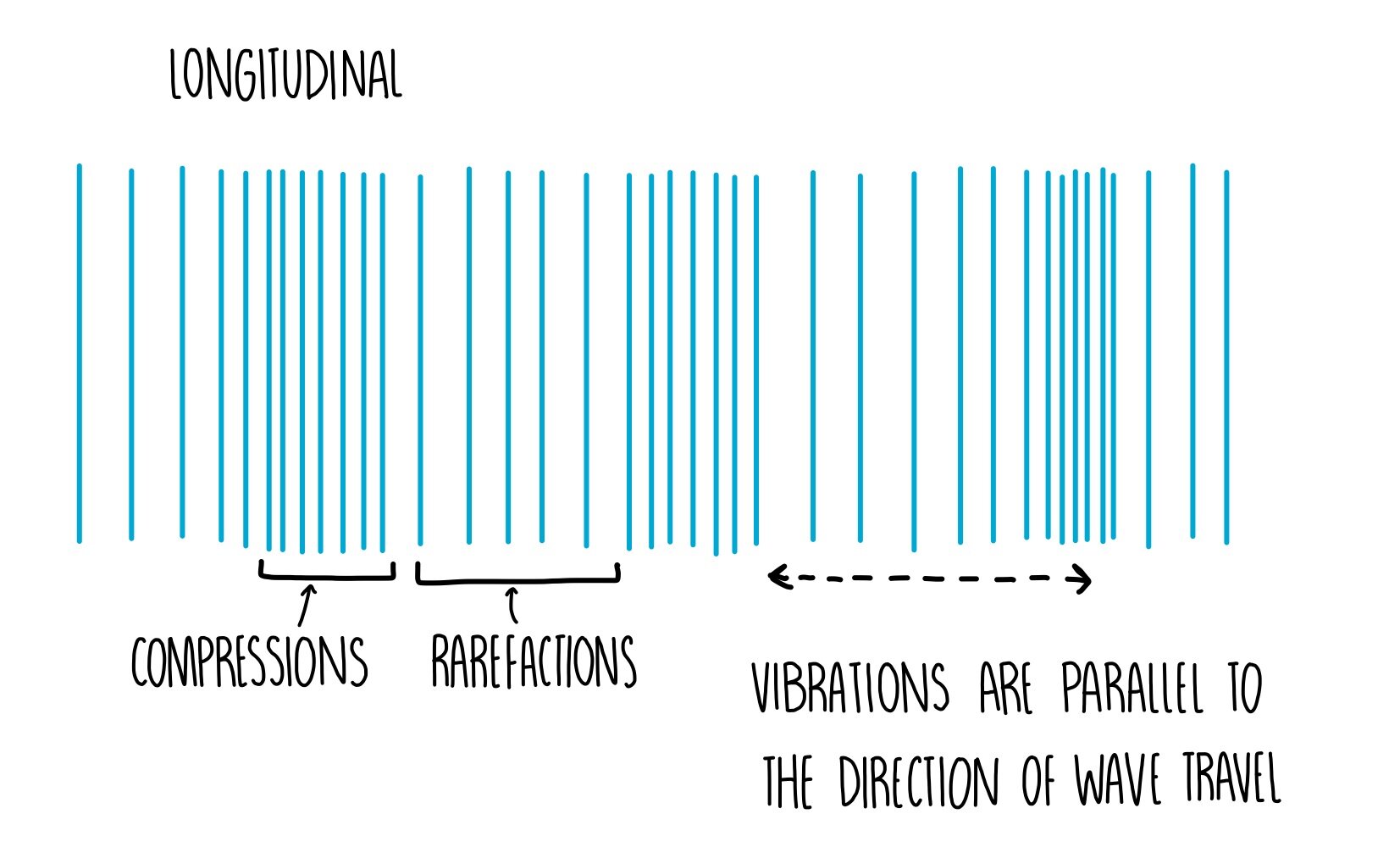
Longitudinal waves:
Particles vibrate in the same direction as the wave. Example Sound
Speed of waves (V) is how fast the wave moves, and changes with the Medium
Mechanical waves travel faster through denser materials (solids) and at higher temperatures. For gases, they travel faster through fewer gases.
Non-mechanical waves travel faster through the less dense medium (less particle interference)
Sound is faster in water than in air is denser
Why does it affect it
Sound needs particles to vibrate
In water, there is no interference, and more particles will be active
More energy = faster, and so higher temperature sound travels faster
Why is it slower in gas
Since there is more space, the particles are more spread out, so they need to be moving faster to travel
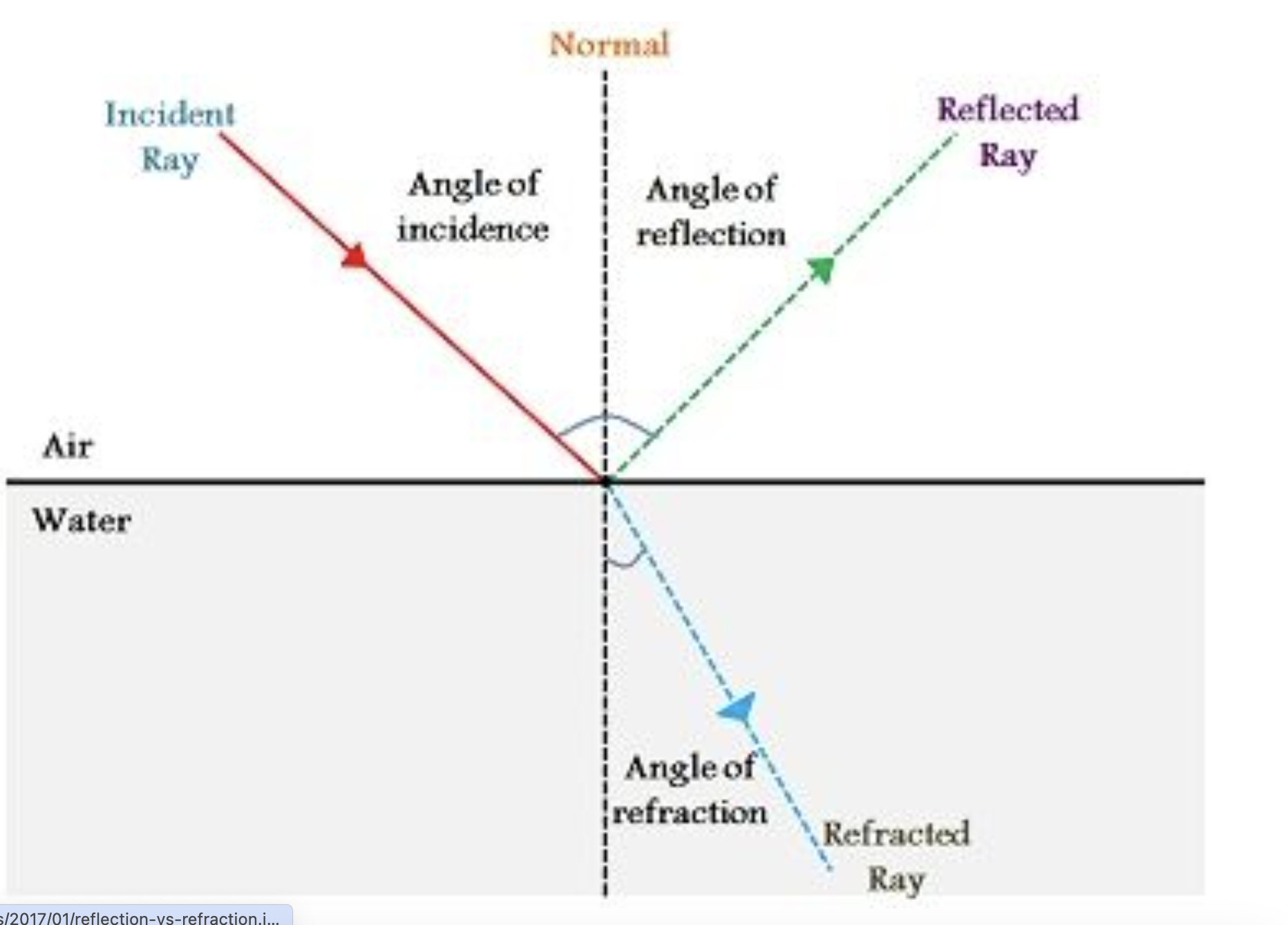
The law of refraction
States that when light hits an object like a mirror, the reflected ray bounces off of the object at the same angle as it strikes the object.
Meanign that if light hits a mirror on an ange, the angle of reflection would also be 30.
The equation for this is 0i = 0r
The angle of incidence is rqual to angle of reflection.
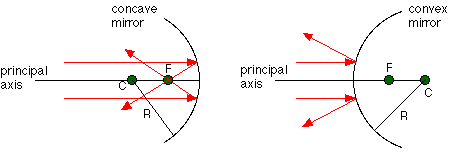
Curved mirrors