Serology
Serology
Presumptive testing: a screening test done when you think a fluid is blood or semen. VIaible color change to the sample when a potential component of fluid is present
- Kastle- Meyer (KM)
- Acid Phosphatase (AP)
Confirmatory testing – performed after a presumptive test gives a positive result. Confirmatory tests will verify the presence of a specific fluid.
- Takayama crystal test for blood, RSID Blood Test
- Microscopic Sperm searches, RSID Semen Strip Test
Blood
- Cellular material (solid materials; 45%)
- red blood “cells” (erythrocytes)
- no nucleus
- contains antigens—responsible for blood types
- white blood cells (leucocytes)
- platelets (thrombocytes)
- Plasma (fluid portion of blood; 55%)
- 95% water
- Antibodies
- vitamins/minerals
- 500+ proteins
Blood Typing
- An individual whose blood is type A has A antigens on his/her red blood cells.
- Type B has B antigens.
- Type AB has both A and B antigens.
- Type O has neither A nor B antigens.
- Type A blood has only anti-B antibodies and no anti-A.
- Type B blood has only anti-A and no anti-B.
- Type AB blood has neither anti-A nor anti-B.
- Type O blood has both anti-A and anti-B.
Presumptive Testing
Kastle-Meyer Test (KM)
- KM reagent added to stain
- color change at this point: false positive
- 3% H2O2 subsequently added
- Pink color change – KM positive sample
- Highly indicative of blood
Luminol test or Bluestar test
- used to search out trace amounts of blood located at crime scenes.
- These tests produce light (chemiluminescence) in a darkened area.
- Luminol is extremely sensitive and is capable of detecting blood that has been diluted up to 100,000 times.
Confirmatory Testing
- Takayama crystal test for blood
- a crystalline test that is viewed using a microscope.
- RSID Blood Test
Semen
- Avg. ejaculate is 3.5mL
- Medical Conditions:
- Oligospermia – low sperm count
- Aspermia – no sperm
- Vasectomy –surgical procedure that leaves the male incapable of producing sperm
Components of Semen
- spermatozoa
- Sugars
- Sucrose
- Fructose
- sorbitol
- • proteins
- • inorganic ions
- Na, K, Ca, Mg
- • buffering agents
- Bicarbonate
- guards against pH change in semen
Presumptive Testing
Acid Phosphatase Test
- An enzyme secreted into seminal fluid
- A purple color indicates the presence of acid phosphatase enzyme.
- Found in high concentrations in semen
- Not unique to semen
- vaginal secretions
- blood of males with prostate cancer
- Enzymatic activity
- Drops significantly after 4-6 months
- Visual examination with naked eye
- Crusty white or yellowish staining
- Alternate Light Source (ALS) examination
- Possible semen stains will fluoresce due to bacterial growth.
- Fresh semen stains will not fluoresce
* Semen can be specifically identified by the presence of spermatozoa
Confirmatory Testing
Christmas Tree Staining
- Red
- aluminum sulfate + Nuclear Fast Red
- stains DNA (nuclei)
- Green
- picric acid + indigo carmine (PIC)
- stains cytoplasm
RSID (Rapid Stain Identification)
- Test for presence of semenogelin
Sexual Assault Evidence
- Pubic combings
- Pubic hair controls (25)
- External genital swabs
- Vaginal swabs
- Cervix swabs
- Rectal swabs
- Swabs of body areas such as breasts
- Oral swabs
- Head hairs (25)
- Blood sample
- Buccal swab
- Fingernail scrapings
- Urine specimen
- All clothing
Saliva
Components
- Human salivary glands produce 1-1.5L/day
- 99.5% water plus electrolytes
- Mucus
- White blood cells
- Epithelial cells
- Enzymes
- Amylase (enzyme that digests starch; α & β)
- α amylase found in saliva and pancreas
Presumptive Testing
- Starch-iodine assays
- Amylase overlay assay and amylase radial diffusion
- Tests for presence of starch
- If starch is present - will change to dark blue-black in the presence of iodine
- False positive reactions- any substance with amylase activity (e.g. bacteria, plants, vomit)
- Not species-specific
- Seratec® α-Amylase Test (monoclonal antibody test)
- Positive (two lines): A line appears in the Control region, and a positive line appears within the test region.
- Phadebas Amylase Test
- Add saliva stain to water
- Add tablet that consists of insoluble starch bound to a blue dye
- If amylase is present, it will break down the starch and release the blue dye
Confirmatory Testing
- RSID for saliva
Urine
- All animals must get rid of excess nitrogen from the breakdown of proteins and amino acids
- Aquatic animals get rid of nitrogen as ammonia; Birds and terrestrial animals use uric acid; Mammals use urea and expel it in urine
Presumptive testing
- Urease Test
- Uses Whatman Filter Paper: If urea is present, then urease will catalyze the reaction of urea to ammonia and the paper will turn blue
- RSID-Urine
- tests for a glycoprotein abundant in urine
- NOT HUMAN SPECIFIC
- No confirmatory tests for urine!
Targeted testing: Direct to DNA
- Modern DNA quantitation kits more sensitive than serology
- Which samples have male DNA?
- Maximizes the chance of getting a DNA profile
- For searching in CODIS
- More efficient than serology testing
- Allows the lab to analyze evidence and obtain info necessary to search CODIS in a more timely manner
Benefits
- detect best sample(s) from kit to send for amplification
- detect presence of male DNA on samples where serology would not be an effective screening tool
- digital penetration cases
- sexual assaults without ejaculation
- reduce false positives (serology positive, no male profile)
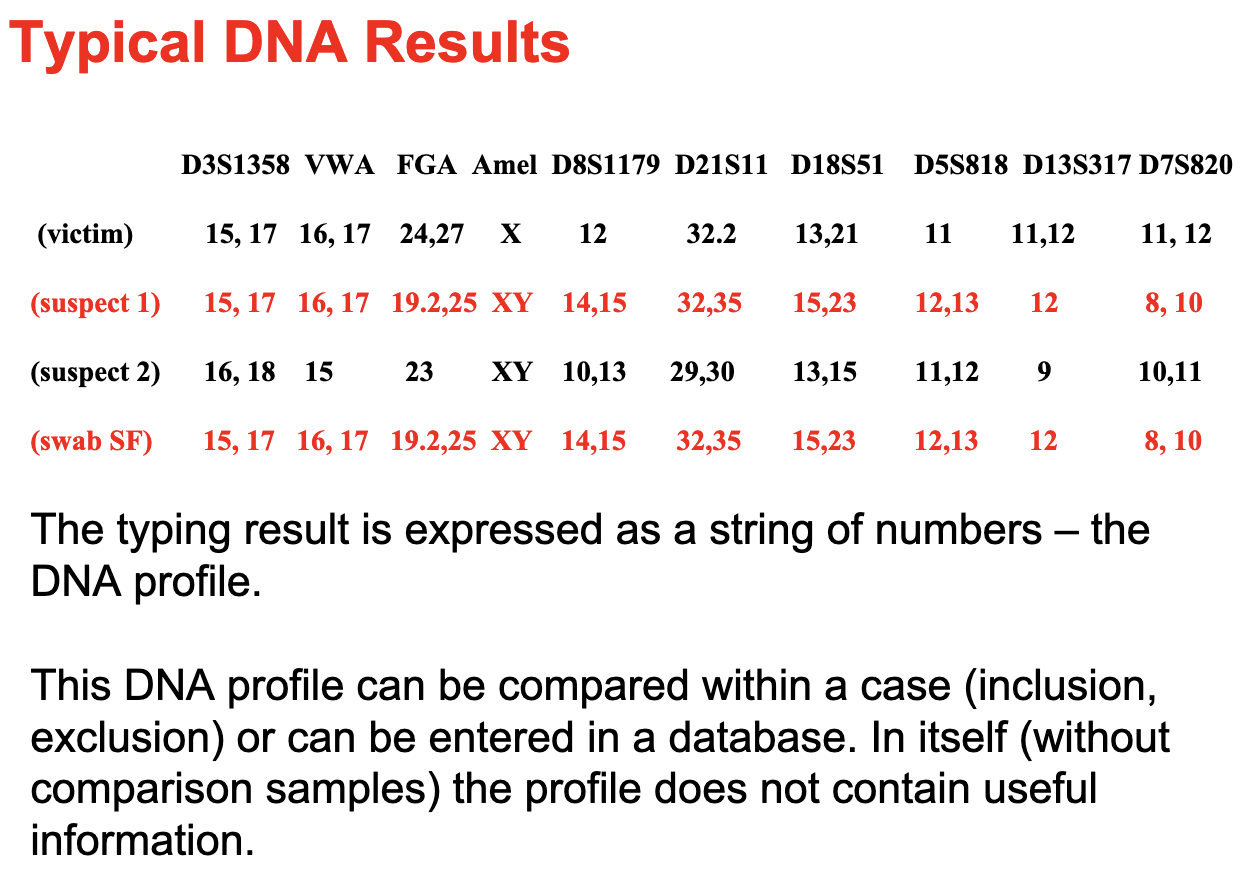
DNA
Characteristics
- Genetic material that makes us who we are
- Present in almost all of your cells
- The same in all of your cells, which allows us to compare blood to saliva to skin cells
- Unique to every individual; no one else on the planet has the same DNA as you unless you have an identical twin
What part is analyzed?
- 24 different DNA locations are typically analyzed as part of a DNA profile:
- These 24 DNA locations are know as Short Tandem Repeats (STR’s) and have no known function
- Profiles Do Not include DNA for any visible traits such as race, eye color, hair color or diseases
Short Tandem Repeats
- Small regions along the DNA chain where a sequence (T, C, A, T) is repeated consecutively
- The number of repeats in a region can vary from person to person.
- The number of repeats are counted like “train cars.”
Samples for DNA testing
- Evidence from scene
- Crime Scene Unit
- From victim’s body
- Rape kits
- Autopsy
- Exemplars (blood or mouth swab)
- Victim
- Suspect
- Witnesses
- Elimination samples
Touch DNA
- (skin cell) DNA evidence can be defined as evidence with no visible staining
- Would likely contain DNA resulting from the transfer of epithelial cells to an object.
- Can simply touching an object leave skin cells?
- Does not guarantee a meaningful DNA profile.
Types of DNA
- STR
- Biological stains, hair roots, tissue
- Y STR
- Sexual assault mixtures, body ID
- mt DNA
- Hair shafts, body ID
What DNA does NOT do
- Forensic DNA testing does NOT provide the race of the biological fluid donor
- Forensic DNA testing does NOT provide the height, weight, hair color, birthdate, hobbies, or address of the donor
- Forensic DNA testing does NOT indicate when the stain was deposited or when the person died
Contamination
- the introduction of anything to the scene or to a piece of evidence that was not
- previously there”
- Can happen at any step after the crime has been committed
- First responders to the scene
- At evidence collection
- During item sampling at the laboratory
- At any of the DNA processing steps
- Active or “Direct” transfer: direct contact/touching of an item or surface
- Passive or “Indirect” transfer: your DNA detected on an item after not having touched it
Cross contamination
- Transfer of material from one item of evidence to another
- (i.e. items packaged together in a bag)
- Transfer of material from an item or tool to a piece of evidence
- (i.e. not cleaning scissors used to cut blood stains from one case to the next)
- Transfer of material on gloves from one item/case to another
- (i.e. not changing gloves between items/cases)
Cases of Contamination
- “Phantom of Heilbronn”
- DNA evidence from forty crimes
- Six murders over sixteen years, dozens of high-profile thefts, and a deadly arson case
- $400,000 bounty was placed
- German police declared the perpetrator the “country’s most dangerous woman”
- Cleverly evaded her sloppy criminal work and evidence left behind
- An extensive manhunt for over 15 years despite
- The cotton swabs used by many state police departments were found to have been contaminated before shipping by a factory worker
Mechanisms of transfer
- Direct transfer
- Transferring cells and DNA to an object or surface after touching it
- Aerosol transfer
- Transfer of DNA through saliva
- Talking, shouting, coughing, sneezing, etc., over the evidence
- Indirect transfer
- DNA on an item without having touched it
- Secondary transfer
- Shaking hands
- Touching doorknob
- Tertiary transfer
- 1st person touches doorknob. 2nd person touches doorknob then pen
- Secondary transfer
- DNA on an item without having touched it
Role of Forensic Biologist
- Examine physical evidence for the presence of biological fluids or skin cells.
- Identify the fluid.
- Individualize the source of the fluid or skin cells through the generation of DNA profiles.
- Associate or link the evidence with another case or a known individual through these DNA profiles.
Sample Flow
- Evidence Examinartion
- Gloves, lab coats, eye protection, masks, hair covering
- Cover table with paper
- Examine by eyes, touch, smells
- Pens, scissors, tissues, swabs, rulers, digital camera, microscope, Sharpies
- Bleach & alcohol
- Paperwork & notes
- Extraction
- Chelex®
- blood, semen, saliva, hair
- Organic
- tissue, hairs
- M48 (QIAgen)
- exemplars, blood, “other” evidence
- SDS/Proteinase K
- nails
- nails
- Chelex®
- Quantification
- real-time PCR (Quantifiler Trio)
- Need as little as 37.5 pg (3.75-11g) of DNA to generate a DNA profile
- Amplification
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- DNA target Loci
- STRs/DNA typing
- Separation & Analysis
- ABI 3500xl capillary electrophoresis
- GeneMapper/GeneMarker software
- Separation & Analysis
Statistics
Statistics: the power of STRs
- Comes from combinations of loci
- Independent frequencies can be multiplied
- The 24 forensic loci yield overall frequencies which are virtually unique
CODIS
- Combined DNA Index System
- LDIS- local DNA index system—> SDIS- state DNA index system —> NDIS- national “ “
- Laws permit collection of convicted offenders
- Allows for country wide comparison of DNA evidence
- Case to case hits – combine investigation
- Case to offender matches – case potentially solved
- Missing Persons Index
Indexes of different types of samples
- Forensic (evidence) samples
- Convicted offenders/Arrestees (Depends on State rules)
- Missing persons reference samples
- Unidentified human remains